Pyrazolanthrone (SP600125)
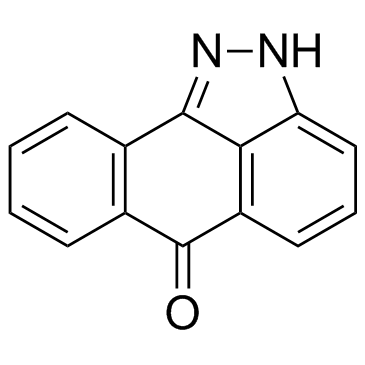
Pyrazolanthrone (SP600125) structure
|
Common Name | Pyrazolanthrone (SP600125) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 129-56-6 | Molecular Weight | 220.226 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 489.3±14.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H8N2O | Melting Point | 281~282℃ | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 246.8±26.5 °C | |
Use of Pyrazolanthrone (SP600125)SP600125 is a reversible and ATP-competitive JNK inhibitor with IC50s of 40, 40 and 90 nM for JNK1, JNK2 and JNK3, respectively. |
| Name | Dibenzo[cd,g]indazol-6(2H)-one |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | SP600125 is a reversible and ATP-competitive JNK inhibitor with IC50s of 40, 40 and 90 nM for JNK1, JNK2 and JNK3, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
JNK1:40 nM (IC50) JNK2:40 nM (IC50) JNK3:90 nM (IC50) Autophagy |
| In Vitro | SP600125 is an ATP-competitive inhibitor of JNK2 with a Ki value of 0.19±0.06 μM. SP600125 inhibits the phosphorylation of c-Jun with IC50 of 5 μM to 10 μM in Jurkat T cells. In CD4+ cells, such as Th0 cells isolated from either human cord or peripheral blood, SP600125 blocks cell activation and differentiation and inhibits the expression of inflammatory genes COX-2, IL-2, IL-10, IFN-γ, and TNF-α, with IC50 of 5 μM to 12 μM[1]. In a mouse beta cells MIN6, SP600125 (20 μM) induces the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and its downstream CREB-dependent promoter activation[2]. In HCT116 cells, SP600125 (20 μM) blocks the G2 phase to mitosis transition and induces endoreplication. This ability of SP600125 is independent of JNK inhibition, but due to its inhibition of CDK1-cyclin B activation upstream of Aurora A and Polo-like kinase 1[3]. |
| In Vivo | Administration of SP600125 at 15 or 30 mg/kg i.v. significantly inhibits TNF-α serum levels, whereas oral administration dose-dependently blocks TNF-α expression with significant inhibition observed at 30 mg/kg per os[1]. SP600125 attenuates LPS-induced ALI in rats in vivo. The expression levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in the BALF in rats in the SP600125 group are significantly decreased[4]. |
| Cell Assay | Determination of mRNA half-life is performed essentially, except that CD14+ cells are stimulated with (bacterial) lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 50 ng/mL) for 2 h before addition of actinomycin D (5 μg/mL). SP600125 (25 μM) or vehicle (0.5% DMSO vol/vol) is added immediately following the actinomycin D. Analysis is performed by using real-time reverse transcription (RT)-PCR. Total RNA is extracted with an RNeasy Mini kit. TNF mRNA is measured by real time RT-PCR, using a TNF Taqman probe. All data are normalized by using glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) expression. The TNF-α forward primer is 5′-CTGGCCCAGGCAGTCAGAT-3′ and the reverse primer is 5′-TATCTCTCAGCTCCACGCCATT-3′. The Taqman probe sequence is 5′-FAM-CCTGTAGCCCATGTTGTAGCAAACCCTCA-TAMRA-3′[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] Female CD-1 mice (8-10 weeks of age) are dosed i.v. or per oswith SP600125 in PPCES vehicle (30% PEG-400/20% polypropylene glycol/15% Cremophor EL/5% ethanol/30% saline), final volume of 5 mL/kg, 15 min before i.v. injection with LPS in saline (0.5 mg/kg). At 90 min, a terminal bleed is obtained from the abdominal vena cava, and the serum is recovered. Samples are analyzed for mouse TNF-α by using an ELISA. Rats[4] A total of 40 male Wistar rats are randomly divided into four groups (n=10): the control group, LPS group, normal saline group (NS) and the SP600125 group. Acute lung injury (ALI) is induced via intratracheal injection of LPS. Briefly, the rats are anesthetized with pentobarbital sodium followed by intratracheal injection of 5 mg/kg LPS. The rats are then placed in a vertical position and rotated for 1 min to distribute the LPS in the lungs. Normal saline or SP600125 is administered via intraperitoneal injection (15 mg/kg) 10 min after the LPS injection. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 489.3±14.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 281~282℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C14H8N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 220.226 |
| Flash Point | 246.8±26.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 220.063660 |
| PSA | 45.75000 |
| LogP | 3.18 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.799 |
| Water Solubility | H2O: insoluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | CB4585000 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|
~% 
Pyrazolanthrone... CAS#:129-56-6 |
| Literature: US2004/72888 A1, ; Page 14 ; US 20040072888 A1 |
|
~96% 
Pyrazolanthrone... CAS#:129-56-6 |
| Literature: Kim, MeeKyoung; Wiemer, David F. Tetrahedron Letters, 2004 , vol. 45, # 25 p. 4977 - 4980 |
|
~87% 
Pyrazolanthrone... CAS#:129-56-6 |
| Literature: Slouka, Jan; Bekarek, Vojtech; Lycka, Antonin Collection of Czechoslovak Chemical Communications, 1982 , vol. 47, # 6 p. 1746 - 1756 |
|
~% 
Pyrazolanthrone... CAS#:129-56-6 |
| Literature: Collection of Czechoslovak Chemical Communications, , vol. 47, # 6 p. 1746 - 1756 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
| anthra[1,9-cd]pyrazol-6(2H)-one |
| 1,9-PYRAZOLOANTHRONE |
| Dibenz[cd,g]indazol-6(2H)-one |
| 1,6-dihydrodibenzo[cd,g]indazol-6-one |
| Dibenzo[cd,g]indazol-6(2H)-one |
| 2H-Dibenzo[CD,G]Indazol-6-One |
| MFCD00022289 |
| EINECS 204-955-6 |
| SP600125 |
![2-acetyl-2H-dibenzo[cd,g]indazol-6-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/248/54345-84-5.png)