Paricalcitol
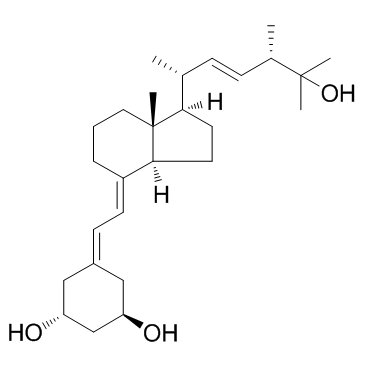
Paricalcitol structure
|
Common Name | Paricalcitol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 131918-61-1 | Molecular Weight | 416.637 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 564.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C27H44O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 238.3±24.7 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of ParicalcitolParicalcitol is a vitamin D receptor agonist, used for the prevention and treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism (excessive secretion of parathyroid hormone) associated with chronic renal failure. |
| Name | paricalcitol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Paricalcitol is a vitamin D receptor agonist, used for the prevention and treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism (excessive secretion of parathyroid hormone) associated with chronic renal failure. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Paricalcitol (3×10-8 M; HP + PC) produces a significant reduction in calcification relative to the observed in cells in HP medium. Paricalcitol causes a reduction in the levels of nuclear β-catenin to a level similar to that observed in control cells[1]. |
| In Vivo | Paricalcitol (300 ng/kg/day) significantly decreases Tau, and prevents LV dysfunction in mice. Paricalcitol reduces mRNA expression of ANP, fibronectin and collagen III in the TAC-pari mice[2]. |
| Animal Admin | After TAC or sham surgery, a subset of the mice is treated with paricalcitol, a selective vitamin D receptor activator, which activates the VDR, at a final dose of 300 ng/kg/day. Paricalcitol is dissolved in a 95% propylene glycol and 5% ethyl alcohol solution. Mice are intraperitoneally injected with paricalcitol (or vehicle only) three times per week on Monday, Wednesday and Friday for five consecutive weeks. An established anti-hypertrophic and anti-fibrotic treatment, namely the angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) losartan is also included. Previous experiments have shown it is feasible and efficacious to dissolve losartan in the drinking water at a concentration of 30 mg/kg/day; mice are treated for five consecutive weeks. So, in total eight groups are studied. Sham (n=10), TAC (n=10), Sham + losartan (Sham-los, n=10), TAC + losartan (TAC-los, n=10), Sham + paricalcitol (Sham-pari, n=10), TAC + paricalcitol (TAC-pari, n=10), Sham + paricalcitol + losartan (Sham-combi, n=10) and TAC + paricalcitol + losartan (TAC-combi, n=10). |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 564.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C27H44O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 416.637 |
| Flash Point | 238.3±24.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 416.329041 |
| PSA | 60.69000 |
| LogP | 5.83 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.609 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 + H311-H330-H372 |
| Precautionary Statements | Missing Phrase - N15.00950417-P260-P280-P302 + P352 + P312-P304 + P340 + P310-P403 + P233 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1 / PGI |
|
Paricalcitol, a vitamin d receptor activator, inhibits tumor formation in a murine model of uterine fibroids.
Reprod. Sci. 21(9) , 1108-19, (2014) We examined the antitumor and therapeutic potentials of paricalcitol, an analog of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 with lower calcemic activity, against uterine fibroids using in vitro and in vivo evaluation... |
|
|
Mesenchymal stem cells and a vitamin D receptor agonist additively suppress T helper 17 cells and the related inflammatory response in the kidney.
Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 307(12) , F1412-26, (2014) Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) suppress T helper (Th)17 cell differentiation and are being clinically pursued for conditions associated with aberrant Th17 responses. Whether such immunomodulatory effec... |
|
|
Spotlight on paricalcitol in secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Treat. Endocrinol. 4(3) , 185-6, (2005) Paricalcitol (Zemplar) is a synthetic vitamin D2 analog that inhibits the secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH) through binding to the vitamin D receptor. It is approved in the US and in most Europea... |
| 9,10-secoestra-5,7-diene-1,3-diol, 17-[(1R,2E,4S)-5-hydroxy-1,4,5-trimethyl-2-hexenyl]-, (1R,3R,7E,17β)- |
| (1R,3R)-5-[(2E)-2-{(1R,3aS,7aR)-1-[(1R,2E,4S)-5-hydroxy-1,4,5-triméthylhex-2-én-1-yl]-7a-méthyloctahydro-4H-indén-4-ylidène}éthylidène]cyclohexane-1,3-diol |
| (1a,3b,7E,22E)-19-Nor-9,10-secoergosta-5,7,22-triene-1,3,25-triol |
| (1R,3R,7E,17β)-17-[(2R,3E,5S)-6-Hydroxy-5,6-dimethylhept-3-en-2-yl]-9,10-secoestra-5,7-diene-1,3-diol |
| (7E,22E)-19-Nor-9,10-secoergosta-5,7,22-triene-1a,3b,25-triol |
| 1,3-Cyclohexanediol, 5-[(2E)-2-[(1R,3aS,7aR)-octahydro-1-[(1R,2E,4S)-5-hydroxy-1,4,5-trimethyl-2-hexen-1-yl]-7a-methyl-4H-inden-4-ylidene]ethylidene]-, (1R,3R,5Z)- |
| Paracalcin |
| 19-Nor-1a,25-dihydroxyvitamin D2 |
| (1R,3R,7E,17β)-17-[(2R,3E,5S)-6-Hydroxy-5,6-dimethyl-3-hepten-2-yl]-9,10-secoestra-5,7-diene-1,3-diol |
| (1α,3β,7E,22E)-19-Nor-9,10-secoergosta-5,7,22-triene-1,3,25-triol |
| (1R,3R)-5-[(2E)-2-[(1R,3aS,7aR)-1-[(E,2R,5S)-6-hydroxy-5,6-dimethylhept-3-en-2-yl]-7a-methyl-2,3,3a,5,6,7-hexahydro-1H-inden-4-ylidene]ethylidene]cyclohexane-1,3-diol |
| Zemplar |
| (1R,3R)-5-[(2E)-2-{(1R,3aS,7aR)-1-[(1R,2E,4S)-5-Hydroxy-1,4,5-trimethylhex-2-en-1-yl]-7a-methyloctahydro-4H-inden-4-yliden}ethyliden]cyclohexan-1,3-diol |
| (1R,3R,7E,17β)-17-[(1R,2E,4S)-5-hydroxy-1,4,5-trimethylhex-2-en-1-yl]-9,10-secoestra-5,7-diene-1,3-diol |
| (1R,3R)-5-[(2E)-2-{(1R,3aS,7aR)-1-[(1R,2E,4S)-5-hydroxy-1,4,5-trimethylhex-2-en-1-yl]-7a-methyloctahydro-4H-inden-4-ylidene}ethylidene]cyclohexane-1,3-diol |
| Paricalcitol |
| 19-Nor-1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D2 |
| (1R,3R,7E,17β)-17-[(2R,3E,5S)-6-Hydroxy-5,6-dimethylhept-3-en-2-yl]-9,10-secoestra-5,7-dien-1,3-diol |
| 1,3-Cyclohexanediol, 5-[(2E)-2-[(1R,3aS,7aR)-octahydro-1-[(1R,2E,4S)-5-hydroxy-1,4,5-trimethyl-2-hexen-1-yl]-7a-methyl-4H-inden-4-ylidene]ethylidene]-, (1R,3R)- |