Neohesperidin
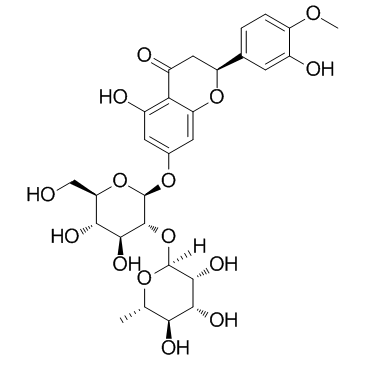
Neohesperidin structure
|
Common Name | Neohesperidin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 13241-33-3 | Molecular Weight | 610.561 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 933.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C28H34O15 | Melting Point | 239-243ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 306.7±27.8 °C | |
Use of NeohesperidinNeohesperidin is a flavonoid compound found in high amounts in Poncirus trifoliata with anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. |
| Name | neohesperidin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Neohesperidin is a flavonoid compound found in high amounts in Poncirus trifoliata with anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Neohesperidin induces cell apoptosis in human breast adenocarcinoma MDA-MB-231 cells. The IC50 values of neohesperidin at 24 and 48 h are 47.4±2.6 μM and 32.5±1.8 μM, respectively. The expressions of P53 and Bax in the neohesperidin-treated cells are significantly up-regulated, while that of Bcl-2 is down-regulated[1]. Neohesperidin exhibits antioxidant activity (IC50=22.31 μg/mL) in the DPPH radical-scavenging assay[2]. |
| In Vivo | Neohesperidin (50 mg/kg) significantly inhibits 55.0% of HCl/ethanol-induced gastric lesions. In pylorus ligated rats, neohesperidin (50 mg/kg) significantly decreases the volume of gastric secretion and gastric acid output, and increases the pH[1]. Treatment of neohesperidin significantly decreases fasting glucose, serum glucose, and glycosylated serum protein (GSP) in mice. It significantly elevates oral glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity and decreases insulin resistance in the diabetic mice. Neohesperidin significantly decreases serum triglycerides, total cholesterol, leptin level, and liver index in the mice[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice: All the mice are fasted 6 h before the test and then fed with water or neohesperidin by gavage. The mice are intraperitoneally injected with either 2 g/kg BW glucose or 1 IU/kg BW insulin for OGTT and ITT, respectively. Blood samples are collected from the tail vein for the measurement of basal blood glucose levels (0 min) before the injection of glucose or insulin. Additional blood glucose levels are measured at 30, 60, 90 and 120 min[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 933.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 239-243ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C28H34O15 |
| Molecular Weight | 610.561 |
| Flash Point | 306.7±27.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 610.189758 |
| PSA | 234.29000 |
| LogP | 2.44 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.695 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DJ2981400 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
|
Comparative metabolic and transcriptional analysis of a doubled diploid and its diploid citrus rootstock (C. junos cv. Ziyang xiangcheng) suggests its potential value for stress resistance improvement.
BMC Plant Biol. 15 , 89, (2015) Polyploidy has often been considered to confer plants a better adaptation to environmental stresses. Tetraploid citrus rootstocks are expected to have stronger stress tolerance than diploid. Plenty of... |
|
|
Ougan (Citrus reticulata cv. Suavissima) flavedo extract suppresses cancer motility by interfering with epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in SKOV3 cells.
Chin. Med. 10 , 14, (2015) Ougan (Citrus reticulata cv. Suavissima) flavedo extract (OFE) exhibited potential anti-tumor effects with unclear underlying mechanisms. This study aims to evaluate the potential anti-metastatic acti... |
|
|
Hesperidin, nobiletin, and tangeretin are collectively responsible for the anti-neuroinflammatory capacity of tangerine peel (Citri reticulatae pericarpium).
Food Chem. Toxicol. 71 , 176-82, (2014) Inhibiting microglial activation-mediated neuroinflammation has become a convincing target for the development of functional foods to treat neurodegenerative diseases. Tangerine peel (Citri reticulata... |
| HESPERETIN-7-NEOHESPERIDOSIDE |
| Hesperetin7-neohesperidoside |
| 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 7-[[2-O-(6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranosyl]oxy]-2,3-dihydro-5-hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-, (2S)- |
| (2S)-5-Hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-7-yl 2-O-(6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside |
| hesperetin 7-O-neohesperoside |
| Neohesperidin |
| Neohesperdin |
| MFCD00017357 |
| Hesperetin-7-O-neohesperidoside |
| EINECS 236-216-9 |
| (S)-4'-Methoxy-3',5,7-trihydroxyflavanone-7-[2-O-(α-L-rhamnopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside] |
| 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 2,3-dihydro-7-((2-O-(6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy)-5-hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-, (S)- |
| Hesperetin 7-O-neohesperidoside |
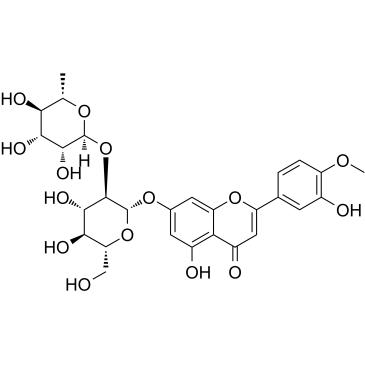 CAS#:38665-01-9
CAS#:38665-01-9
