Lidocaine

Lidocaine structure
|
Common Name | Lidocaine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 137-58-6 | Molecular Weight | 234.337 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 372.7±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H22N2O | Melting Point | 66-69°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 179.2±30.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of LidocaineLidocaine, an amide local anesthetic, has anti-inflammatory properties in vitro and in vivo, possibly due to an attenuation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, intracellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), and reduction of neutrophils influx.Target: Lidocaine is a common local anesthetic and antiarrhythmic drug. Lidocaine is used topically to relieve itching, burning and pain from skin inflammations, injected as a dental anesthetic or as a local anesthetic for minor surgery. Lidocaine, the first amino amide–type local anesthetic, was first synthesized under the name xylocaine by Swedish chemist Nils Lofgren in 1943. His colleague Bengt Lundqvist performed the first injection anesthesia experiments on himself.Lidocaine is approximately 95% metabolized (dealkylated) in the liver by CYP3A4 to the pharmacologically-active metabolites monoethylglycinexylidide (MEGX) and then subsequently to the inactive glycine xylidide. MEGX has a longer half life than lidocaine but also is a less potent sodium channel blocker. The elimination half-life of lidocaine is approximately 90–120 minutes in most patients. This may be prolonged in patients with hepatic impairment (average 343 minutes) or congestive heart failure (average 136 minutes). |
| Name | lidocaine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Lidocaine, an amide local anesthetic, has anti-inflammatory properties in vitro and in vivo, possibly due to an attenuation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, intracellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), and reduction of neutrophils influx.Target: Lidocaine is a common local anesthetic and antiarrhythmic drug. Lidocaine is used topically to relieve itching, burning and pain from skin inflammations, injected as a dental anesthetic or as a local anesthetic for minor surgery. Lidocaine, the first amino amide–type local anesthetic, was first synthesized under the name xylocaine by Swedish chemist Nils Lofgren in 1943. His colleague Bengt Lundqvist performed the first injection anesthesia experiments on himself.Lidocaine is approximately 95% metabolized (dealkylated) in the liver by CYP3A4 to the pharmacologically-active metabolites monoethylglycinexylidide (MEGX) and then subsequently to the inactive glycine xylidide. MEGX has a longer half life than lidocaine but also is a less potent sodium channel blocker. The elimination half-life of lidocaine is approximately 90–120 minutes in most patients. This may be prolonged in patients with hepatic impairment (average 343 minutes) or congestive heart failure (average 136 minutes). |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 372.7±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 66-69°C |
| Molecular Formula | C14H22N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 234.337 |
| Flash Point | 179.2±30.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 234.173218 |
| PSA | 32.34000 |
| LogP | 3.63 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.512 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | practically insoluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P312 + P330 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | 3249 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | AN7525000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
|
~% 
Lidocaine CAS#:137-58-6 |
| Literature: Arkiv foer Kemi, , vol. 22A, # 18 p. 11 |
|
~% 
Lidocaine CAS#:137-58-6 |
| Literature: Arkiv foer Kemi, , vol. 22A, # 18 p. 11 |
|
~% 
Lidocaine CAS#:137-58-6 |
| Literature: Langmuir, , vol. 26, # 13 p. 10561 - 10571 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924299090. other cyclic amides (including cyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Osmoregulatory bicarbonate secretion exploits H(+)-sensitive haemoglobins to autoregulate intestinal O2 delivery in euryhaline teleosts.
J. Comp. Physiol. B, Biochem. Syst. Environ. Physiol. 184(7) , 865-76, (2014) Marine teleost fish secrete bicarbonate (HCO3 (-)) into the intestine to aid osmoregulation and limit Ca(2+) uptake by carbonate precipitation. Intestinal HCO3 (-) secretion is associated with an equi... |
|
|
Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Inhibition Improves Corneal Epithelial Innervation and Wound Healing in Diabetic Rats.
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 56(3) , 1948-55, (2015) We evaluated the effect of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibition by using 1,5-isoquinolinediol (ISO) on corneal epithelial innervation in diabetic rats.ISO (3 mg/kg, intraperitoneal) or vehicl... |
|
|
Effect of N-acetylcysteine infusion on exercise-induced modulation of insulin sensitivity and signaling pathways in human skeletal muscle.
Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 309 , E388-97, (2015) -Reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced in skeletal muscle may play a role in potentiating the beneficial responses to exercise; however, the effects of exercise-induced ROS on insulin action and prot... |
| 2-Diethylamino-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide |
| Lignocaine |
| 4,4'-DIMETHOXY DIPHENYL SULFOXIDE LIDOCAINE-D6 |
| 2-Diethylamino-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide,Lignocaine,Xylocaine |
| Maricaine |
| MFCD08443609 |
| Gravocain |
| 2-(Diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-acetamide |
| Lidoderm |
| N1-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-(diethylamino)acetamide |
| 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide |
| XYLOCAINE |
| N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-N,N-diethylglycinamide |
| 2-Diethylamino-2',6'-acetoxylidide |
| N-(2,6-Diméthylphényl)-N,N-diéthylglycinamide |
| Anestacon |
| L-Caine |
| Leostesin |
| Esracaine |
| Acetamide, 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)- |
| Lidothesin |
| 2-Diethylamino-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide Lignocaine Xylocaine |
| N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N2,N2-diethylglycinamide |
| lignocainum hydrochloricum |
| Lidocaine |
| w-Diethylamino-2,6-dimethylacetanilide |
| EINECS 205-302-8 |

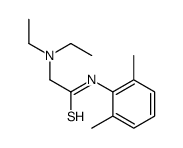 CAS#:109366-65-6
CAS#:109366-65-6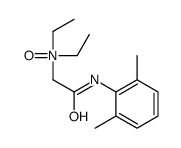 CAS#:2903-45-9
CAS#:2903-45-9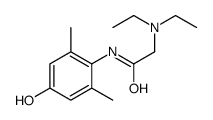 CAS#:39942-41-1
CAS#:39942-41-1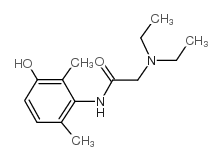 CAS#:34604-55-2
CAS#:34604-55-2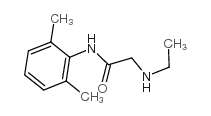 CAS#:7728-40-7
CAS#:7728-40-7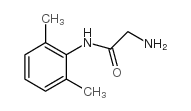 CAS#:18865-38-8
CAS#:18865-38-8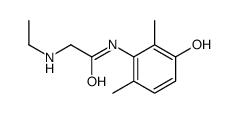 CAS#:34604-56-3
CAS#:34604-56-3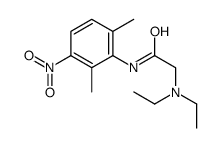 CAS#:39942-49-9
CAS#:39942-49-9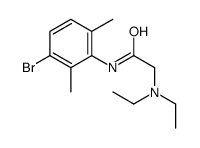 CAS#:1044658-01-6
CAS#:1044658-01-6
