Catechin
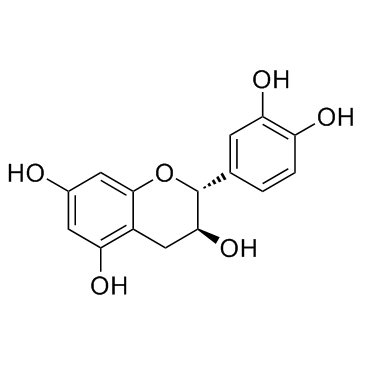
Catechin structure
|
Common Name | Catechin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 154-23-4 | Molecular Weight | 290.268 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 630.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H14O6 | Melting Point | 175-177ºC (anhydrous)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 335.0±31.5 °C | |
Use of CatechinCatechin inhibits cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) with an IC50 of 1.4 μM. |
| Name | (+)-catechin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Catechin inhibits cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) with an IC50 of 1.4 μM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
COX-1:1.4 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Catechin exhibits >95% inhibitory activity at 70 μg/mL against cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) with an IC50 of 1.4 μM[1]. A dose-dependent reduction in color is observed after 24 hours of treatment with Catechin, and 54.76% of the cells are dead at the highest concentration of Catechin tested (160 μg/mL) whereas the IC50 of Catechin is achieved at 127.62 μg/mL Catechin. A dose- and time-dependent increase in the induction of apoptosis is observed when MCF-7 cells are treated with Catechin. When compare to the control cells at 24 hours, 40.7 and 41.16% of the cells treated with 150 μg/mL and 300 μg/mL Catechin, respectively, undergo apoptosis. The expression levels of Caspase-3, -8, and -9 and p53 in MCF-7 cells treated with 150 μg/mL Catechin for 24 h increase by 5.81, 1.42, 3.29, and 2.68 fold, respectively, as compare to the levels in untreated control cells[2]. |
| In Vivo | Animals treated with Catechin at the lowest tested dose, i.e., 50 mg/kg, p.o. have spent comparatively more time in exploring the novel object in the choice trial, however, the difference is not statistically significant. Catechin prevents the time-induced episodic memory deficits in a dose-dependent manner, the most effective being 200 mg/kg, p.o.. Treatment with Catechin prevents the rise in MPO level compare to DOX alone treatment group (21.98±9.44 and 36.76±4.39% in the hippocampus and the frontal cortex respectively)[3]. |
| Cell Assay | The Cell viability assay is performed to assess the toxicity of different concentrations of Catechin on MCF-7 cells. Briefly, MCF-7 cells (2×104 cells/well) are plated in 96-well plates and treated with 0 μg/mL Catechin and 160 μg/mL Catechin for 24 hours. Then, 40 μL of the Cell Titer Blue solution is directly added to the wells and incubated at 37°C for 6 hours. The fluorescence is recorded with a 560 nm/590 nm (excitation/emission) filter set using a microplate fluorescence reader, and the IC50 is calculated. Quadruplet samples are run for each concentration of Catechin in three independent experiments[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats[3] Twelve weeks old, healthy male rats weighing 200 to 230 g are used in this study. Rats are divided into four experimental groups (n=9 each) for one vehicle and three groups of Catechin (three doses). The doses of Catechin are prepared at 50, 100, 200 mg/kg in 0.25% w/v sodium carboxy methylcellulose (CMC) and administered orally for 7 days prior to and during the experimental trials. Episodic memory, the conscious memory of the past experiences is evaluated in this study[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 630.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 175-177ºC (anhydrous)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C15H14O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 290.268 |
| Flash Point | 335.0±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 290.079041 |
| PSA | 110.38000 |
| LogP | 0.49 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.742 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2932999099. other heterocyclic compounds with oxygen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Effect of different aging techniques on the polysaccharide and phenolic composition and sensory characteristics of Syrah red wines fermented using different yeast strains.
Food Chem. 179 , 116-26, (2015) The effect of high levels of the polysaccharide Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast strain (HPS) and another conventional yeast strain (FERM) on the polysaccharide and phenolic composition of Syrah red win... |
|
|
Green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate triggered hepatotoxicity in mice: responses of major antioxidant enzymes and the Nrf2 rescue pathway.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 283(1) , 65-74, (2015) (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), a constituent of green tea, has been suggested to have numerous health-promoting effects. On the other hand, high-dose EGCG is able to evoke hepatotoxicity. In t... |
|
|
Bi-layer composite dressing of gelatin nanofibrous mat and poly vinyl alcohol hydrogel for drug delivery and wound healing application: in-vitro and in-vivo studies.
J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 9(9) , 1495-508, (2013) Present investigation involves the development of a bi-layer dressing of gelatin nanofibrous mat loaded with epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)/poly vinyl alcohol (PVA) hydrogel and its in-vivo evaluatio... |
| (2R,3S)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromene-3,5,7-triol |
| (2R,3S)-2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)chroman-3,5,7-triol |
| Sunkatol No. 1 |
| (+)-Cianidanol |
| Dexcyanidanol |
| 2H-1-Benzopyran-3,5,7-triol, 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-, (2R,3S)- |
| Catechuic acid |
| 3-Cyanidanol, (+)- |
| (+)-(2R:3S)-5,7,3',4'-Tetrahydroxyflavan-3-ol |
| (+)-3,3',4',5,7-Flavanpentol Hydrate |
| Catechin |
| (2R,3S)-2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphényl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromène-3,5,7-triol |
| (+)-3,3,4,5,7-Flavanpentol |
| trans-(+)-3,3',4',5,7-Flavanpentol |
| (+)-Cyanidanol-3 |
| (2R,3S)-2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-chromanetriol |
| (+)-Catechin Hydrate |
| (2R,3S)-2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzopyran-3,5,7-triol |
| (+)-catechin |
| (2R,3S)-2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-3,5,7-triol |
| Catechinic acid |
| 2H-1-Benzopyran-3,5,7-triol, 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-, (2R-trans)- |
| EINECS 205-825-1 |
| (2R,3S)-2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)chromane-3,5,7-triol |
| Cyanidol |
| D-Catechol |
![(2R-trans)-2-[3,4-bis(phenylmethoxy)phenyl]-3,4-dihydro-5,7-bis(phenylmethoxy)-2H-1-benzopyran-3-ol Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/113/20728-73-8.png) CAS#:20728-73-8
CAS#:20728-73-8 CAS#:23567-23-9
CAS#:23567-23-9 CAS#:69127-11-3
CAS#:69127-11-3![(2R,3S)-2,3-trans-6-[(2R,3S,4S)-2,3-trans-3,4-trans-3,3',4',7-tetrahydroxyflavan-4-yl]-3,3',4',5,7-pentahydroxyflavan Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/129/69176-55-2.png) CAS#:69176-55-2
CAS#:69176-55-2 CAS#:20315-25-7
CAS#:20315-25-7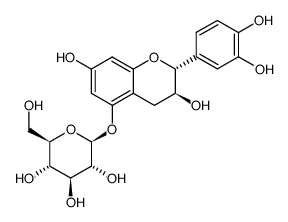 CAS#:88126-53-8
CAS#:88126-53-8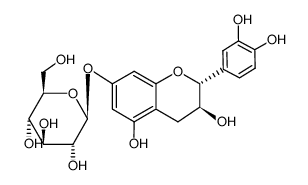 CAS#:88197-03-9
CAS#:88197-03-9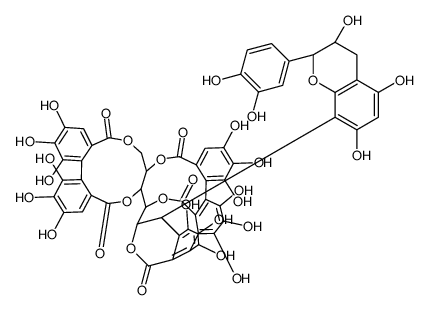 CAS#:108906-66-7
CAS#:108906-66-7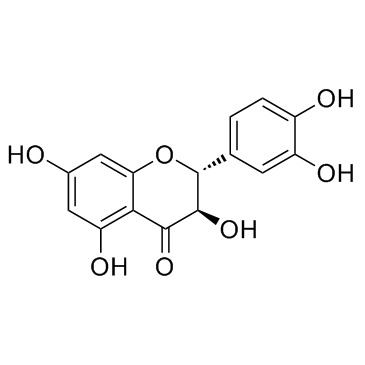 CAS#:480-18-2
CAS#:480-18-2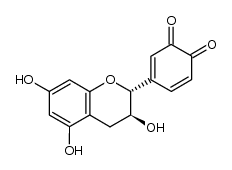 CAS#:122440-41-9
CAS#:122440-41-9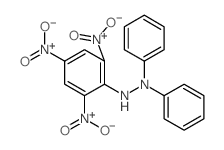 CAS#:1707-75-1
CAS#:1707-75-1 CAS#:108-73-6
CAS#:108-73-6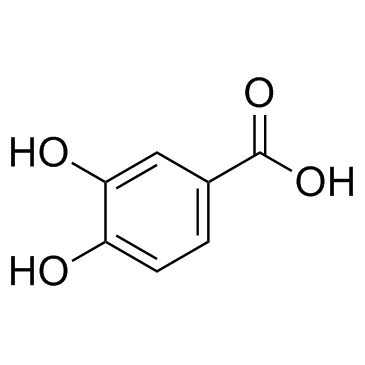 CAS#:99-50-3
CAS#:99-50-3 CAS#:1083-30-3
CAS#:1083-30-3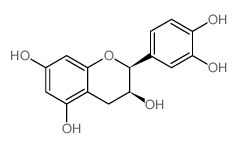 CAS#:35323-91-2
CAS#:35323-91-2 CAS#:490-46-0
CAS#:490-46-0
