Cysteamine Hydrochloride
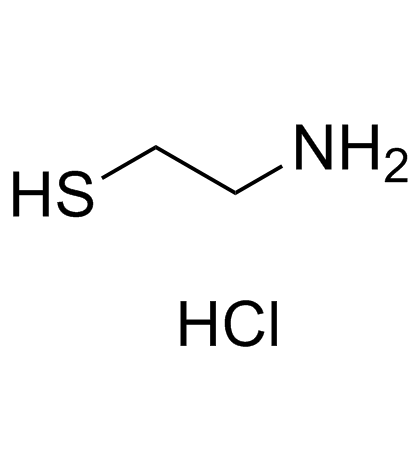
Cysteamine Hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Cysteamine Hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 156-57-0 | Molecular Weight | 113.610 | |
| Density | 0.75 | Boiling Point | 116.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H8ClNS | Melting Point | 67-71 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 24.2ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Cysteamine HydrochlorideCysteamine Hydrochloride is an agent for the treatment of nephropathic cystinosis and an antioxidant.Target: OthersCysteamine has been shown to increase intracellular glutathione levels in cystinotic cells, thus restoring the altered redox state of the cells. Also increased rates of apoptosis in cystinotic cells, which are thought to be the result of increased caspase 3 and protein kinase Cε activity, is counteracted by Cysteamine administration. Cysteamine has antioxidant properties as a result of increasing glutathione production. Cysteamine is an excellent scavenger of OH and HOCl; it also reacts with H2O2. Cysteamine increases the production of several heat shock proteins (HSP), including the murine Hsp40. Cysteamine exerts a dose-dependent effect on the doxorubicin-induced death of cancer cells, measured in both HeLa cells and B16 cells, whereas Cysteamine treatment alone had no influence on cell survival. In addition, in a doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer cell line, the addition of Cysteamine to doxorubicin results in a dramatic increase in cell death [1]. Cysteamine (100 μM) significantly is able to increase the intracellular GSH levels and the percentage of embryos that developed to the blastocyst stage of culture matured oocytes [2]. |
| Name | Cysteamine hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Cysteamine Hydrochloride is an agent for the treatment of nephropathic cystinosis and an antioxidant.Target: OthersCysteamine has been shown to increase intracellular glutathione levels in cystinotic cells, thus restoring the altered redox state of the cells. Also increased rates of apoptosis in cystinotic cells, which are thought to be the result of increased caspase 3 and protein kinase Cε activity, is counteracted by Cysteamine administration. Cysteamine has antioxidant properties as a result of increasing glutathione production. Cysteamine is an excellent scavenger of OH and HOCl; it also reacts with H2O2. Cysteamine increases the production of several heat shock proteins (HSP), including the murine Hsp40. Cysteamine exerts a dose-dependent effect on the doxorubicin-induced death of cancer cells, measured in both HeLa cells and B16 cells, whereas Cysteamine treatment alone had no influence on cell survival. In addition, in a doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer cell line, the addition of Cysteamine to doxorubicin results in a dramatic increase in cell death [1]. Cysteamine (100 μM) significantly is able to increase the intracellular GSH levels and the percentage of embryos that developed to the blastocyst stage of culture matured oocytes [2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 0.75 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 116.4ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 67-71 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C2H8ClNS |
| Molecular Weight | 113.610 |
| Flash Point | 24.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 113.006599 |
| PSA | 64.82000 |
| LogP | 1.37720 |
| Vapour Pressure | 16.7mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable, but hygroscopic. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | VERY SOLUBLE |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S36/37/39-S26 |
| RIDADR | UN 3335 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | KJ0200000 |
| HS Code | 2921199090 |
|
~98% 
Cysteamine Hydr... CAS#:156-57-0 |
| Literature: Cui, Ying; Tan, Shiyu; Luo, Ziping; Dong, Lichun Asian Journal of Chemistry, 2010 , vol. 22, # 4 p. 3221 - 3227 |
|
~% 
Cysteamine Hydr... CAS#:156-57-0 |
| Literature: US5017725 A1, ; |
|
~% 
Cysteamine Hydr... CAS#:156-57-0 |
| Literature: US5017725 A1, ; |
|
~61% 
Cysteamine Hydr... CAS#:156-57-0 |
| Literature: Dutta, Anand S.; Giles, Michael, B.; Gormley, James J.; Williams, Joseph C.; Kusner, Edward J. Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 1: Organic and Bio-Organic Chemistry (1972-1999), 1987 , p. 111 - 120 |
|
~% 
Cysteamine Hydr... CAS#:156-57-0 |
| Literature: US4507500 A1, ; |
|
~% 
Cysteamine Hydr... CAS#:156-57-0 |
| Literature: Asian Journal of Chemistry, , vol. 24, # 7 p. 3247 - 3248 |
|
~% 
Cysteamine Hydr... CAS#:156-57-0 |
| Literature: Chemische Berichte, , vol. 22, p. 1138 Chemische Berichte, , vol. 24, p. 1110 |
|
~% 
Cysteamine Hydr... CAS#:156-57-0 |
| Literature: Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, , vol. 52, # 11 p. 2911 - 2918 |
|
~% 
Cysteamine Hydr... CAS#:156-57-0 |
| Literature: Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds (New York, NY, United States), , vol. 22, # 2 p. 161 - 166 Khimiya Geterotsiklicheskikh Soedinenii, , vol. 22, # 2 p. 206 - 211 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2930909090. other organo-sulphur compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Real-time monitoring of H2O2 release from single cells using nanoporous gold microelectrodes decorated with platinum nanoparticles.
Analyst 140 , 3753-8, (2015) Here, we report a self-supported nanoporous gold microelectrode decorated with well-dispersed and tiny platinum nanoparticles as an electrochemical nonenzymatic hydrogen peroxide biosensor. Nanoporous... |
|
|
Development of surface plasmon resonance imaging biosensors for detection of ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase L1.
Anal. Biochem. 469 , 4-11, (2014) We have developed a new method for highly selective determination of the ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1) concentration using a surface plasmon resonance imaging (SPRI) technique and ... |
|
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain canc... |
| 2-AMino&CYSTEAMINE HCL |
| 1-Amino-2-mercaptoethane hydrochloride |
| 2-aminoethylmercaptan hydrochloride |
| 2-Mercapto ethyl amine hydrochloride |
| EINECS 205-858-1 |
| β-Mercapto ethylamine hydrochloride |
| CYSTEAMINE HCL SOLID |
| Cysteinamine Hydrochloride |
| thiol hydrochloride |
| 2-Mercaptoethylamine hydrochloride |
| Cysteamine Hydrochloride |
| 2-Aminoethanethiol hydrochloride (1:1) |
| Cysteamine (Hydrochloride) |
| 2-Aminoethanethiol Hydrochloride |
| Thioethanolamine hydrochloride |
| 2-Mercaptoethanamine Hydrochloride |
| CYSTEAMINIUM CHLORIDE |
| 2-Mercaptoethylamin |
| 2-amino-ethanethiol hydrochloride |
| 1-Aminoethane-2-thiol hydrochloride |
| Cysteamine HCl |
| mea hydrochloride |
| b-Mercaptoethylamine Hydrochloride |
| 2-Amino-ethanethiol.HCl |
| Ethanethiol, 2-amino-, hydrochloride (1:1) |
| β-Mercaptoethylamine hydrochloride |
| MFCD00012904 |
| Decarboxycysteine hydrochloride |
| 2-Amino-ethanethiol;hydrochloride |
| 2-Mercaptoethylammonium chloride |
| Aminoethanethiol hydrochloride |




![2-[(3-chlorobenzyl)thio]ethanamine(SALTDATA: FREE) structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/253/106670-33-1.png) CAS#:106670-33-1
CAS#:106670-33-1![2-[(4-METHYLBENZYL)THIO]ETHANAMINE structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/215/106670-34-2.png) CAS#:106670-34-2
CAS#:106670-34-2 CAS#:110487-07-5
CAS#:110487-07-5![[2-(Pyridin-2-ylthio)ethyl]amine dihydrochloride structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/237/42416-20-6.png) CAS#:42416-20-6
CAS#:42416-20-6 CAS#:4569-82-8
CAS#:4569-82-8![2-[[(5-methyl-1H-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]thio]ethylamine dihydrochloride structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/467/38603-72-4.png) CAS#:38603-72-4
CAS#:38603-72-4 CAS#:31404-08-7
CAS#:31404-08-7 CAS#:1420-88-8
CAS#:1420-88-8![2-[(4-Fluorobenzyl)sulfanyl]ethanamine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/330/143627-49-0.png) CAS#:143627-49-0
CAS#:143627-49-0![2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)methylsulfanyl]ethanamine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/168/48133-71-7.png) CAS#:48133-71-7
CAS#:48133-71-7
