H-D-Arg-OH
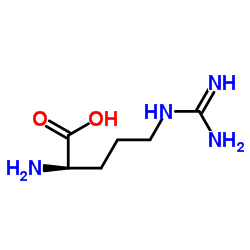
H-D-Arg-OH structure
|
Common Name | H-D-Arg-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 157-06-2 | Molecular Weight | 174.201 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 367.6±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H14N4O2 | Melting Point | 221-224ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 176.1±30.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of H-D-Arg-OHD-arginine (H-D-Arg-OH) is the D-isomer of arginine. Arginine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. D-Arginine is an inactive form of L-arginine[1]. |
| Name | D-arginine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | D-arginine (H-D-Arg-OH) is the D-isomer of arginine. Arginine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. D-Arginine is an inactive form of L-arginine[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 367.6±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 221-224ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C6H14N4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 174.201 |
| Flash Point | 176.1±30.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 174.111679 |
| PSA | 125.22000 |
| LogP | -1.79 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.601 |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36 |
| Safety Phrases | S26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | CF1934220 |
| HS Code | 2925290090 |
|
~% 
H-D-Arg-OH CAS#:157-06-2 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 102, # 15 p. 5115 - 5117 |
|
~% 
H-D-Arg-OH CAS#:157-06-2 |
| Literature: Archives of Biochemistry, , vol. 60, p. 496 Journal of Biochemistry (Tokyo, Japan), , vol. 45, p. 687,691 |
| HS Code | 2925290090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2925290090 other imines and their derivatives; salts thereof。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Cloning a neutral protease of Clostridium histolyticum, determining its substrate specificity, and designing a specific substrate.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 99 , 10489-99, (2015) Islet transplantation is a prospective treatment for restoring normoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes. Islet isolation from pancreases by decomposition with proteolytic enzymes is necessary fo... |
|
|
Arginase promotes skeletal muscle arteriolar endothelial dysfunction in diabetic rats.
Front. Immunol. 4 , 119, (2013) Endothelial dysfunction is a characteristic feature in diabetes that contributes to the development of vascular disease. Recently, arginase has been implicated in triggering endothelial dysfunction in... |
|
|
Simultaneous determination of 18 D-amino acids in rat plasma by an ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method: application to explore the potential relationship between Alzheimer's disease and D-amino acid level alterations.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 408 , 141-50, (2016) D-Amino acids are increasingly being recognized as important signaling molecules, and abnormal levels of D-amino acids have been implicated in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. To evaluate the ... |
| (R)-2-Amino-5-guanidinopentanoic acid |
| EINECS 205-866-5 |
| H-D-Arg-OH |
| D-ARGININE BASE |
| R-(-)-ARGININE |
| D-ornithine, N-(diaminomethylene)- |
| (2R)-2-amino-5-guanidinopentanoic acid |
| D-Arg-OH |
| D-ARG.FREE BASE |
| D-2-Amino-5-guanidinovalerate |
| ARGININE,D |
| D-Arginine |
| N-(diaminomethylidene)-D-ornithine |
| D-(-)-ARGININE |
| MFCD00063116 |
| D-Arg |
| D(-)-Arginine |
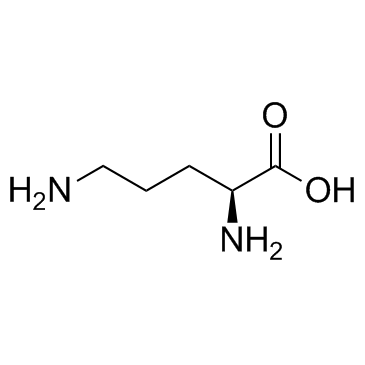 CAS#:70-26-8
CAS#:70-26-8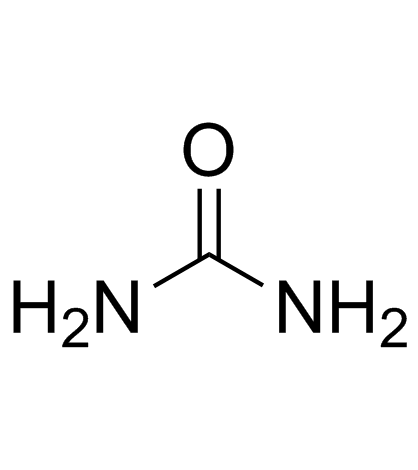 CAS#:57-13-6
CAS#:57-13-6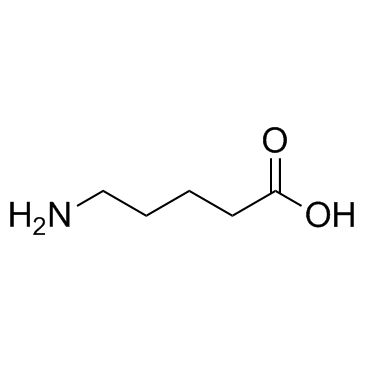 CAS#:660-88-8
CAS#:660-88-8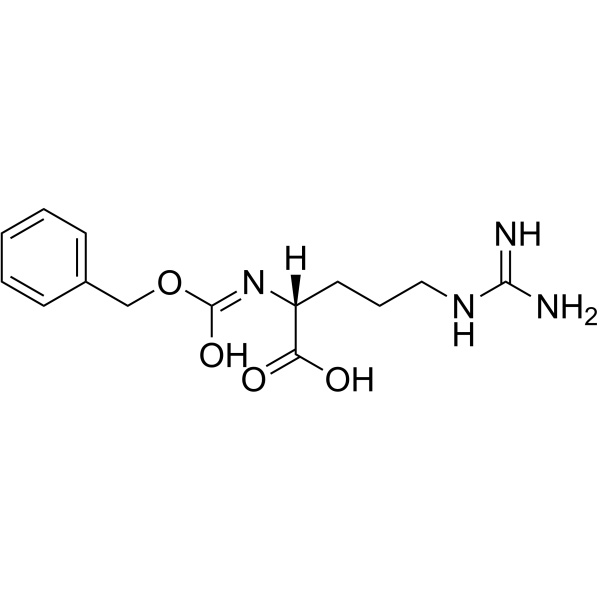 CAS#:6382-93-0
CAS#:6382-93-0 CAS#:2149-70-4
CAS#:2149-70-4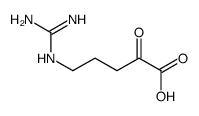 CAS#:3715-10-4
CAS#:3715-10-4
