L-arginine
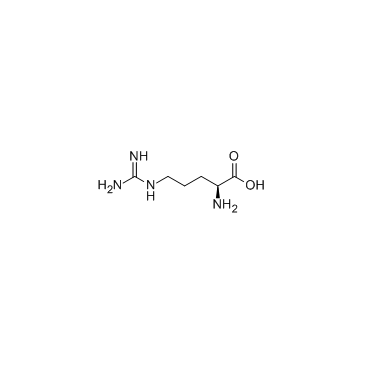
L-arginine structure
|
Common Name | L-arginine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 74-79-3 | Molecular Weight | 174.201 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 367.6±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H14N4O2 | Melting Point | 222 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 176.1±30.7 °C | |
Use of L-arginineL-Arginine is the nitrogen donor for synthesis of nitric oxide, a potent vasodilator that is deficient during times of sickle cell crisis.Target: OthersL-Arginine is an α-amino acid. It was first isolated in 1886. The L-form is one of the 20 most common natural amino acids. At the level of molecular genetics, in the structure of the messenger ribonucleic acid mRNA, CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA, and AGG, are the triplets of nucleotide bases or codons that code for arginine during protein synthesis. In mammals, arginine is classified as a semiessential or conditionally essential amino acid, depending on the developmental stage and health status of the individual.L-Arginine is associated with a decrease in cardiac index while stroke index is maintained in patients with severe sepsis. Resolution of shock at 72 hours is achieved by 40% and 24% of the patients in the L-Arginine and placebo cohorts, respectively. L-Arginine (450 mg/kg during a 15-minute period) amplifies and sustains the hyperemia (38%) and increases absolute brain blood flow after eNOS upregulation by chronic simvastatin treatment (2 mg/kg subcutaneously, daily for 14 days) in SV-129 mice. |
| Name | L-arginine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-Arginine is the nitrogen donor for synthesis of nitric oxide, a potent vasodilator that is deficient during times of sickle cell crisis.Target: OthersL-Arginine is an α-amino acid. It was first isolated in 1886. The L-form is one of the 20 most common natural amino acids. At the level of molecular genetics, in the structure of the messenger ribonucleic acid mRNA, CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA, and AGG, are the triplets of nucleotide bases or codons that code for arginine during protein synthesis. In mammals, arginine is classified as a semiessential or conditionally essential amino acid, depending on the developmental stage and health status of the individual.L-Arginine is associated with a decrease in cardiac index while stroke index is maintained in patients with severe sepsis. Resolution of shock at 72 hours is achieved by 40% and 24% of the patients in the L-Arginine and placebo cohorts, respectively. L-Arginine (450 mg/kg during a 15-minute period) amplifies and sustains the hyperemia (38%) and increases absolute brain blood flow after eNOS upregulation by chronic simvastatin treatment (2 mg/kg subcutaneously, daily for 14 days) in SV-129 mice. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
[1]. Tapiero H, et al. I. Arginine. Biomed Pharmacother. 2002 Nov;56(9):439-45. |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 367.6±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 222 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H14N4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 174.201 |
| Flash Point | 176.1±30.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 174.111679 |
| PSA | 125.22000 |
| LogP | -1.79 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.601 |
| Water Solubility | 148.7 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R36 |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | CF1934200 |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2925290090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2925290090 other imines and their derivatives; salts thereof。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) protease: a chymotrypsin-like enzyme that processes both non-structural (pORF1) and capsid (pORF2) protein.
J. Gen. Virol. 95(Pt 8) , 1689-700, (2014) Hepatitis E virus (HEV), a major cause of acute viral hepatitis across the world, is a non-enveloped, plus-strand RNA virus. Its genome codes three proteins, pORF1 (multifunctional polyprotein), pORF2... |
|
|
Mechanistic studies on the flavin-dependent N⁶-lysine monooxygenase MbsG reveal an unusual control for catalysis.
Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 550-551 , 58-66, (2014) The mechanism of Mycobacterium smegmatis G (MbsG), a flavin-dependent l-lysine monooxygenase, was investigated under steady-state and rapid reaction conditions using primary and solvent kinetic isotop... |
|
|
Sustained Arginase 1 Expression Modulates Pathological Tau Deposits in a Mouse Model of Tauopathy.
J. Neurosci. 35 , 14842-60, (2015) Tau accumulation remains one of the closest correlates of neuronal loss in Alzheimer's disease. In addition, tau associates with several other neurodegenerative diseases, collectively known as tauopat... |
| L-Arginine |
| L-ornithine, N-(diaminomethylene)- |
| MFCD00002635 |
| H-L-ARG-OH |
| L-Argnie |
| (L)-Arginine |
| L-ARG-OH |
| L-arginie |
| AGRININE |
| arginine |
| L(+)-Arginine |
| L-Arginine (9CI) |
| QVYZ3MYZUM &&L or S Form |
| FEMA 3819 |
| Pentanoic acid, 2-amino-5-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]-, (S)- |
| EINECS 200-811-1 |
| ARGININE, L- |
| L-a-Amino-d-guanidinovaleric Acid |
| L-Norvaline, 5-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]- |
| (2S)-2-Amino-5-carbamimidamidopentanoic acid |
| H-ARG-OH |
| S-(+)-2-Amino-5-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]pentanoic acid |
| l-arginin |
| Arginine, L- (8CI) |
| Arginine (VAN) |
| l-arg |
| 5-[(Aminoiminomethyl)amino]-L-norvaline |
| Arg |
| N5-(Aminoiminomethyl)-L-ornithine |
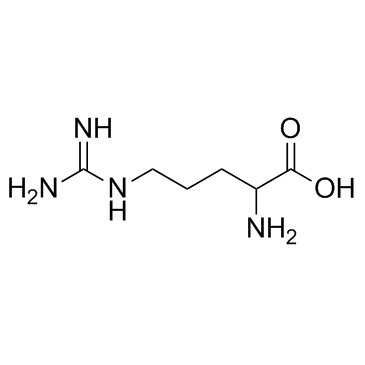 CAS#:7200-25-1
CAS#:7200-25-1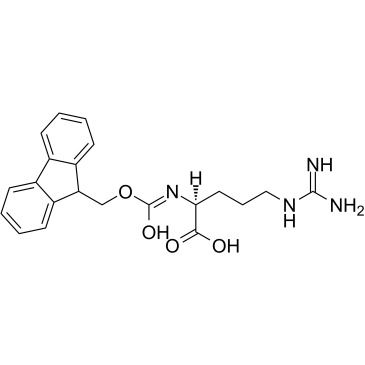 CAS#:91000-69-0
CAS#:91000-69-0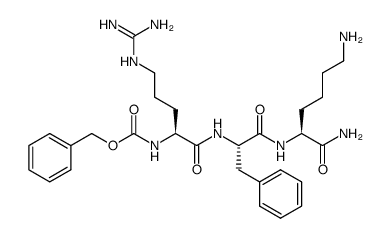 CAS#:1432516-48-7
CAS#:1432516-48-7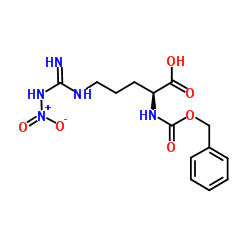 CAS#:2304-98-5
CAS#:2304-98-5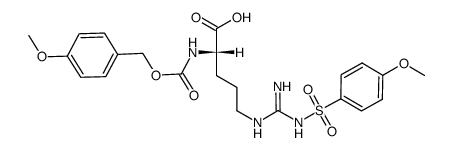 CAS#:67320-28-9
CAS#:67320-28-9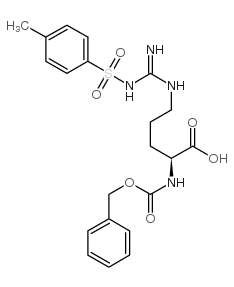 CAS#:13650-38-9
CAS#:13650-38-9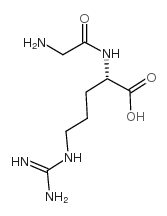 CAS#:18635-55-7
CAS#:18635-55-7![(5S)-5-[(Dimethylamino)methyl]-1-{[hydroxy(methoxy)phosphoryl]oxy }-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-amine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/232/103170-78-1.png) CAS#:103170-78-1
CAS#:103170-78-1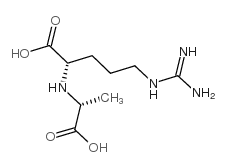 CAS#:34522-32-2
CAS#:34522-32-2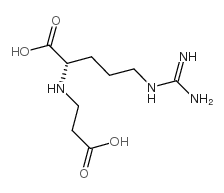 CAS#:63358-47-4
CAS#:63358-47-4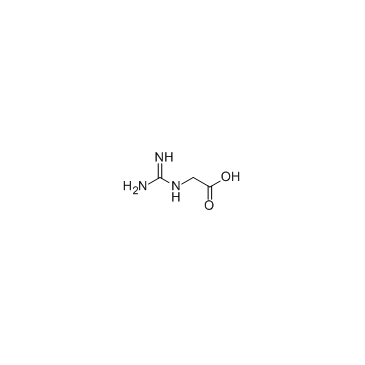 CAS#:352-97-6
CAS#:352-97-6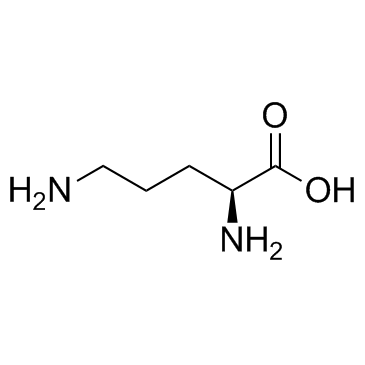 CAS#:70-26-8
CAS#:70-26-8 CAS#:372-75-8
CAS#:372-75-8 CAS#:14279-64-2
CAS#:14279-64-2 CAS#:463-00-3
CAS#:463-00-3 CAS#:14049-14-0
CAS#:14049-14-0 CAS#:110-15-6
CAS#:110-15-6
