Anidulafungin
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 19:43:13
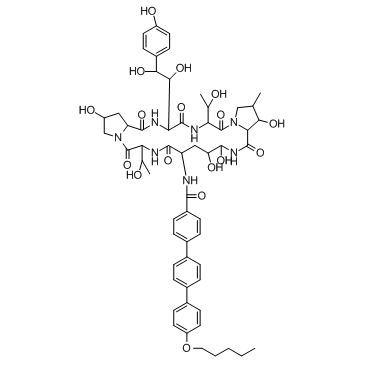
Anidulafungin structure
|
Common Name | Anidulafungin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 166663-25-8 | Molecular Weight | 1140.237 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 1477.0±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C58H73N7O17 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 847.0±34.3 °C | |
Use of AnidulafunginAnidulafungin is a new semisynthetic echinocandin with antifungal potency. |
| Name | anidulafungin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Anidulafungin is a new semisynthetic echinocandin with antifungal potency. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Antifungal[1] |
| In Vitro | Anidulafungin (LY-303366) has MICs of ≤0.32 μg/mL for all Candida albicans (n=99), Candida glabrata (n=18), and Candida tropicalis (n=10) isolates tested. Anidulafungin is also active against Aspergillus species (minimum effective concentration at which 90% of the isolates are inhibited, 0.02 μg/mL) (n=20), is less active against Candida parapsilosis (MIC at which 90% of the isolates are inhibited [MIC90], 5.12 μg/mL) (n=10), and is inactive against C. neoformans (MIC90 >10.24 μg/mL) (n=15) and B. dermatitidis (MIC90, 16 μg/mL) (n=29).The MICs of Fluconazole for three strains of C. tropicalis, seven strains of C. glabrata, and two strains of Candida krusei are ≥16 μg/mL. The MICs of Anidulafungin for 11 of these 12 strains range from 0.08 to 0.32 mg/mL. The twelfth strain is a C. krusei strain (Fluconazole MIC, 32 μg/mL) for which the Anidulafungin MIC is 1.28 mg/mL. The MIC at which 90% of the isolates are inhibited (MIC90) for these 12 strains is 0.32 μg/mL. The Anidulafungin MIC90 for the remaining 18 C. glabrata isolates and C. tropicalis isolates for which the Fluconazole MICs are ≥ 8 μg/mL is also 0.32 mg/mL. Anidulafungin appeares equally active against Candida species for which the fluconazole MICs are ≥16 mg/mL and against those for which the fluconazole MICs are ≥ 8 μg/mL. Anidulafungin has significantly less activity against C. neoformans and B. dermatitidis than against C. albicans, C. glabrata, and C. tropicalis. Ketoconazole and amphotericin B are the most active antifungal agents tested for both C. neoformans and B. dermatitidis. Anidulafungin demonstrated potent in vitro activity against Aspergillus species with a MEC90 of 0.02 μg/mL. MICs of Anidulafungin for the control strain yeast isolates are 0.02 μg/mL for C. albicans ATCC 90028, 0.16 mg/mL for C. glabrata ATCC 90030, and >10.24 μg/mL for C. neoformans ATCC 90112[1]. Strains selected with CD101 that have a 2-fold or greater CD101 MIC increase also have at least a 2-fold MIC increase for Anidulafungin (ANF) and/or Caspofungin (CSF)[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Stocks of CD101 (formerly SP 3025, biafungin, AF-025) are prepared fresh in 100% DMSO prior to use. The comparator antifungals Anidulafungin (ANF), Caspofungin (CSF), and Amphotericin B (AMB) are also prepared in 100% DMSO. MIC assays are performed via broth microdilution in accordance with CLSI guidelines, with the exception that test compounds are made up at a 50× final assay concentration and 100 μL assay mixture volumes are used (2 μL added to 98 μL of broth containing cells at 0.5×103 to 2.5×103 CFU/mL). All MIC assays are run at least three times, and a representative data set is shown. Quality control (QC) is assessed throughout the study via comparison of MIC values derived for WT C. krusei strain ATCC 6258 for AMB, CSF, and ANF with previously reported CLSI 24-h broth microdilution QC ranges[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1477.0±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C58H73N7O17 |
| Molecular Weight | 1140.237 |
| Flash Point | 847.0±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 1139.506348 |
| PSA | 377.42000 |
| LogP | -3.86 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.688 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| V-Echinocandin |
| Anidulafungin |
| N-{(2R,6S,9S,11R,12R,14aS,15S,16S,20S,23S,25aS)-23-[(1S,2S)-1,2-Dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl]-2,11,12,15-tetrahydroxy-6,20-bis[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-16-methyl-5,8,14,19,22,25-hexaoxotetracosahydro-1H-dipyrrolo[2,1-c:2',1'-l][1,4,7,10,13,16]hexaazacyclohenicosin-9-yl}-4''-(pentyloxy)-1,1':4',1''-terphenyl-4-carboxamide |
| VER-002 |
| Ecalta |
| [1,1':4',1''-Terphenyl]-4-carboxamide, N-[(2R,6S,9S,11R,12R,14aS,15S,16S,20S,23S,25aS)-23-[(1S,2S)-1,2-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl]tetracosahydro-2,11,12,15-tetrahydroxy-6,20-bis[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-16-methyl-5,8,14,19,22,25-hexaoxo-1H-dipyrrolo[2,1-c:2',1'-l][1,4,7,10,13,16]hexaazacycloheneicosin-9-yl]-4''-(pentyloxy)- |
| Eraxis |
| LY 303366 |
 CAS#:619-44-3
CAS#:619-44-3 CAS#:63619-51-2
CAS#:63619-51-2![[1,1':4',1''-Terphenyl]-4-carboxylic acid, 4''-(pentyloxy)- Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/222/158938-08-0.png) CAS#:158938-08-0
CAS#:158938-08-0