Wortmannin
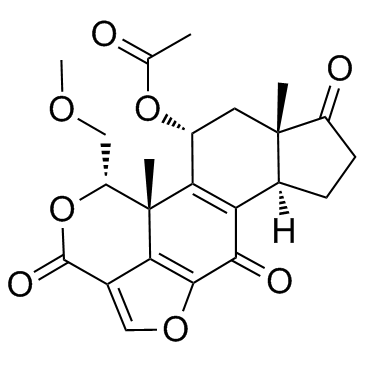
Wortmannin structure
|
Common Name | Wortmannin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 19545-26-7 | Molecular Weight | 428.432 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 615.6±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C23H24O8 | Melting Point | 234-240ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 326.1±31.5 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of WortmanninWortmannin is a multi-target inhibitor of PI3K and MLCK with IC50s of 3 nM and 200 nM, respectively. Wortmannin is also a potent inhibitor of DNA-PK (IC50, 16 nM) and ATM (IC50, 150 nM). Wortmannin is also a potent inhibitor of Polo-like kinase (Plk). |
| Name | wortmannin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Wortmannin is a multi-target inhibitor of PI3K and MLCK with IC50s of 3 nM and 200 nM, respectively. Wortmannin is also a potent inhibitor of DNA-PK (IC50, 16 nM) and ATM (IC50, 150 nM). Wortmannin is also a potent inhibitor of Polo-like kinase (Plk). |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
PI3K:3 nM (IC50) ATM:150 nM (IC50) ATR:1.8 μM (IC50) DNA-PK:16 nM (IC50) MLCK:200 nM (IC50) Plk3:48 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Wortmannin irreversibly inhibits phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-kinase) activity with binding to the 110-kDa protein (IC50 of 3 nM) and has no effect PI4-kinase in RBL-2H3 cells. Wortmannin also inhibits both Fc epsilon RI-mediated histamine secretion and leukotriene release, with no effect on the activation of the tyrosine kinase Lyn[1]. In intact A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells, wortmannin inhibits both DNA-PK and ATM at concentrations that correlated closely with those required for radiosensitization. Furthermore, pretreatment of A549 cells with wortmannin results in radioresistant DNA synthesis, a characteristic abnormality of ATM-deficient cells[2]. The inhibition of MLCK by Wortmannin is not affected by calmodulin or peptide substrat, while reduced by high concentration of ATP. Wortmannin directly interacts with the catalytic domain of MLCK and leads to an irreversible loss of the enzyme activity. Wortmannin has no inhibitory to cAMP-dependent protein kinase, cGMP-dependent protein kinase, and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, and has little effect on protein kinase C activity[3]. Wortmannin is also a potent inhibitor of Polo-like kinase 3 (Plk3). Wortmannin potently inhibits the activity of purified Plk3 with an IC50 of 48 nM. Wortmannin is a potent inhibitor of Plk1 and AX7503, a tetramethylrhodamine-Wortmannin conjugate, is an activity-dependent probe for labeling Plk1. Wortmannin inhibits Plk1-AX7503 reactivity with a IC50 of 5.8 nM. Wortmannin inhibits Plk3 reacting with AX7503 in a dose-dependent manner. The IC50 value of Wortmannin for inhibiting labeling of Plk3 by AX7503 is determined to be 49 nM. Wortmannin covalently labels Plk1 and Plk3 by targeting conserved lysine residues in their ATP binding sites. Wortmannin inhibits Plk1 and Plk3 with a potency similar to its inhibition of PI3K. Wortmannin also inhibits Plk2 and Plk4[6]. |
| In Vivo | Wortmannin inhibits phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase-protein kinase B (PKB)/Akt phosphorylation in both normal tissues (lung, heart and brain homogenates) and tumor tissue in mice, without mortality or acute toxicity at 0.7 mg/kg. Combination with LY188011, wortmannin significantly increases apoptosis and inhibits tumor growth in orthotopic tumor, while both monotherapy can not[4]. Wortmannin (1 mg/kg) inhibits peritoneal metastasis of SW1990 in mice, without any weight loss[5]. |
| Kinase Assay | MLCK activity is assayed with peptide substrate (KKRPQRATSNVFS-NH2) or myosin light chain. The peptide substrate (24 μM) is phosphorylated in a reaction mixture containing 25 mM Tris-HC1 (pH 7.5), 0.5 mg/mL bovine serum albumin, 4 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM CaCl2, 2.6 nM calmodulin, 1.5 nM MLCK, and 400 μM ATP in a final volume of 0.25 mL. After a 10-min preincubation at 28°C without ATP, the reaction is started by addition of ATP at 28°C and terminated by the addition of 0.1 mL of 10% (v/v) acetic acid after 30 min. The mixture is analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography: column, Unisil Pack 5C18 4.6 X 150 mm; solvent, 18% (v/v) acetonitrile, 0.1% (v/v) trifluoroacetic acid in water; flow rate, 1.0 mL/min; temperature, 40°C; detection, absorbance at 220 nm. Percent of reaction is calculated from the ratio of peak areas of phosphorylated form to those of unphosphorylated form. Specific activity measured under the conditions described above is 0.81 μmol/min/mg. Myosin light chain (108 μg/mL) is phosphorylated in a reaction mixture containing 25 mM Tris-HC1 (pH 7.5), 0.5 mg/mL bovine serum albumin, 4 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM CaCl2, 4.2 nM calmodulin, 0.92 nM enzyme, and 10 μM[γ-32P]ATP (100-900 cpm/pmol) in a final volume of 0.25 mL. After a 3-min preincubation at 30°C without ATP, the reaction is started by the addition of [γ-32P]ATP at 30°C and stopped by the addition of 0.125 mL of trichloroacetic acid after 5 min. The acid-precipitable materials are collected on a nitrocellulose membrane filter and washed with four 1-mL aliquots of 5% (v/v) trichloroacetic acid. The radioactivity on the filter is measured in a toluene scintillation fluid, using a Packard Tri-Carb liquid scintillation spectrometer Model 4530. The specific activity measured under the conditions is 1.23 μmol/min/mg. |
| Animal Admin | Specific pathogen-free athymic BALB/c male mice (5 weeks) are kept under sterile conditions in a laminar flow room in cages with filter bonnets and fed a sterilized mouse diet and water. In order to induce peritoneal metastasis, the mice are anesthetized by inhalation administration of sevoflurane, and SW1990 cells (1×106 cells/mouse) in 100 μL of PBS are injected into the peritoneal cavity using a 23-gauge needle after incubation without FBS for 24 h to inactivate Akt. To examine the effect of PI3K inhibitor, the mice are treated with the intraperitoneal treatment of wortmannin at 1.0, 0.5, or 0.25 mg/kg/day or vehicle (PBS + dimethyl sulfoxide) immediately after cancer cells are inoculated. The treatment is continued for 20 consecutive days. Twenty days later, mice are sacrificed and body weight, ascites, number, and total weight of peritoneal metastatic tumors are examined. The weight exceeding the mean weight of mesenterium and greater omentum of normal nude mice of the same age (in weeks) is regarded as the net weight of metastatic tumors in order to minimize the interfusion of blood or tissues. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 615.6±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 234-240ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C23H24O8 |
| Molecular Weight | 428.432 |
| Flash Point | 326.1±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 428.147125 |
| PSA | 109.11000 |
| LogP | 0.81 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.591 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H300-H310-H330 |
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P264-P280-P284-P302 + P350-P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T+: Very toxic;T: Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R26/27/28 |
| Safety Phrases | 28-36/37-45 |
| RIDADR | UN 3462 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | CB9641000 |
| Packaging Group | I |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
|
Pro-apoptotic and pro-autophagic effects of the Aurora kinase A inhibitor alisertib (MLN8237) on human osteosarcoma U-2 OS and MG-63 cells through the activation of mitochondria-mediated pathway and inhibition of p38 MAPK/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.
Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 9 , 1555-84, (2015) Osteosarcoma (OS) is the most common malignant bone tumor occurring mostly in children and adolescents between 10 and 20 years of age with poor response to current therapeutics. Alisertib (ALS, MLN823... |
|
|
SUMO1 promotes Aβ production via the modulation of autophagy.
Autophagy 11(1) , 100-12, (2015) Autophagy is one of the main mechanisms in the pathophysiology of neurodegenerative disease. The accumulation of autophagic vacuoles (AVs) in affected neurons is responsible for amyloid-β (Aβ) product... |
|
|
Unmethylated CpG motifs in the L. donovani DNA regulate TLR9-dependent delay of programmed cell death in macrophages.
J. Leukoc. Biol. 97(2) , 363-78, (2015) Regulation of macrophage PCD plays an important role in pathogenesis of leishmaniasis. However, the precise involvement of any parasite molecule in this process remains uncertain. In the current study... |
| EINECS 214-538-0 |
| Wartmannin |
| MFCD00133927 |
| 3H-Furo[4,3,2-de]indeno[4,5-h]-2-benzopyran-3,6,9-trione, 11-(acetyloxy)-1,6b,7,8,9a,10,11,11b-octahydro-1-(methoxymethyl)-9a,11b-dimethyl-, (1S,6bR,9aS,11R,11bR)- |
| (1S,6BR,9AS,11R,11BR)-9A,11B-DIMETHYL-1-[(METHYLOXY)METHYL]-3,6,9-TRIOXO-1,6,6B,7,8,9,9A,10,11,11B-DECAHYDRO-3H-FURO[4,3,2-DE]INDENO[4,5-H][2]BENZOPYRAN-11-YL ACETATE |
| Wortmannin |
| SL-2052 |
| Antibiotic SL-2052 |
| (1S,6bR,9aS,11R,11bR)-1-(Methoxymethyl)-9a,11b-dimethyl-3,6,9-trioxo-1,6,6b,7,8,9,9a,10,11,11b-decahydro-3H-furo[4,3,2-de]indeno[4,5-h]isochromen-11-yl acetate |
 CAS#:58053-83-1
CAS#:58053-83-1 CAS#:382-44-5
CAS#:382-44-5 CAS#:1035-69-4
CAS#:1035-69-4 CAS#:2899-95-8
CAS#:2899-95-8
