Bonducellpin D
Modify Date: 2024-01-09 10:49:53
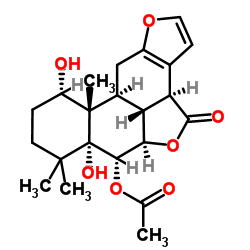
Bonducellpin D structure
|
Common Name | Bonducellpin D | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 197781-85-4 | Molecular Weight | 404.453 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 518.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H28O7 | Melting Point | 216-217℃ | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 267.4±30.1 °C | |
Use of Bonducellpin DBonducellpin D is a furanoditerpenoid lactone isolated from Caesalpinia minax. Bonducellpin D exhibits broad-spectrum inhibition potential against SARS-CoV Mpro and MERS-CoV Mpro, with an Ki of 467.11 and 284.86 nM, respectively. Bonducellpin D also exhibits moderate anti-cancer activity in vitro[1][2][3]. |
| Name | (3bS,3b1R,5aR,6S,6aR,10S,10aS,10bS)-6a,10-dihydroxy-7,7,10a-trimethyl-4-oxo-3b,3b1,5a,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10a,10b,11-dodecahydro-4H-phenanthro[3,2-b:10,1-b'c']difuran-6-yl acetate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Bonducellpin D is a furanoditerpenoid lactone isolated from Caesalpinia minax. Bonducellpin D exhibits broad-spectrum inhibition potential against SARS-CoV Mpro and MERS-CoV Mpro, with an Ki of 467.11 and 284.86 nM, respectively. Bonducellpin D also exhibits moderate anti-cancer activity in vitro[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Ki: 467.11 nM (SARS-CoV Mpro), 284.86 nM (MERS-CoV Mpro)[1] |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 518.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 216-217℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C22H28O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 404.453 |
| Flash Point | 267.4±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 404.183502 |
| PSA | 106.20000 |
| LogP | 1.61 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.598 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
| Bonducellpin D |
| 4H-Phenanthro[3,2-b:10,1-b'c']difuran-4-one, 6-(acetyloxy)-3b,5a,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10a,10b,10c,11-dodecahydro-6a,10-dihydroxy-7,7,10a-trimethyl-, (3bS,5aR,6S,6aR,10S,10aS,10bS,10cR)- |
| (3bS,5aR,6S,6aR,10S,10aS,10bS,10cR)-6a,10-Dihydroxy-7,7,10a-trimethyl-4-oxo-3b,5a,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10a,10b,10c,11-dodecahydro-4H-furo[3',2':2,3]phenanthro[10,1-bc]furan-6-yl acetate |