D(-)-Norvaline
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 18:39:52
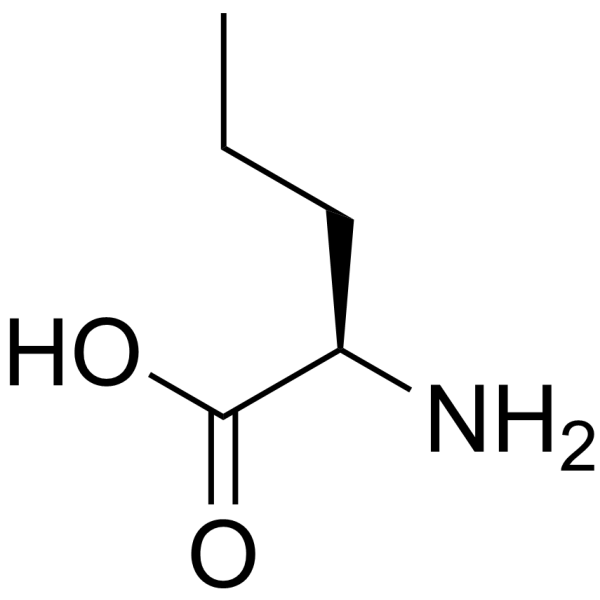
D(-)-Norvaline structure
|
Common Name | D(-)-Norvaline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2013-12-9 | Molecular Weight | 117.146 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 222.9±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H11NO2 | Melting Point | 300ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 88.6±22.6 °C | |
Use of D(-)-NorvalineD-Norvaline is a valine derivative[1]. |
| Name | (2R)-2-aminopentanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | D-Norvaline is a valine derivative[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Amino acids and amino acid derivatives have been commercially used as ergogenic supplements. They influence the secretion of anabolic hormones, supply of fuel during exercise, mental performance during stress related tasks and prevent exercise induced muscle damage. They are recognized to be beneficial as ergogenic dietary substances[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 222.9±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 300ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C5H11NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 117.146 |
| Flash Point | 88.6±22.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 117.078979 |
| PSA | 63.32000 |
| LogP | 0.38 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.464 |
| Precursor 5 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 8 | |
|
Three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship analyses of substrates of the human proton-coupled amino acid transporter 1 (hPAT1).
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 19 , 6409-18, (2011) The proton-coupled amino acid transporter hPAT1 has recently gained much interest due to its ability to transport small drugs thereby allowing their oral administration. A three-dimensional quantitati... |
| (R)-(−)-2-Aminopentanoic acid |
| D-Nva |
| H-D-Nva-OH |
| D-2-amino-pentanoate |
| NORVALINE, D- |
| D-2-Aminopentanoic acid |
| D(-)-Norvaline |
| D-norVal-OH |
| D-Norvaline |
| (R)-2-Aminopentanoic acid,(R)-2-Aminovaleric acid |
| (R)-(-)-2-Aminopentanoic acid |
| Norvaline |
| MFCD00008097 |
| (R)-2-Aminopentanoic acid |
| (2R)-2-aminopentanoic acid |
| (R)-2-Aminovaleric Acid |
| EINECS 217-936-2 |
| (R)-norvaline |
| D-2-Aminovaleric acid |
| D-Ape |
 CAS#:338-69-2
CAS#:338-69-2 CAS#:1821-02-9
CAS#:1821-02-9 CAS#:105816-58-8
CAS#:105816-58-8 CAS#:760-78-1
CAS#:760-78-1 CAS#:108341-16-8
CAS#:108341-16-8![N-[(Benzyloxy)carbonyl]norvaline structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/019/42918-89-8.png) CAS#:42918-89-8
CAS#:42918-89-8![2-[(2-aminoacetyl)amino]pentanoic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/445/1999-38-8.png) CAS#:1999-38-8
CAS#:1999-38-8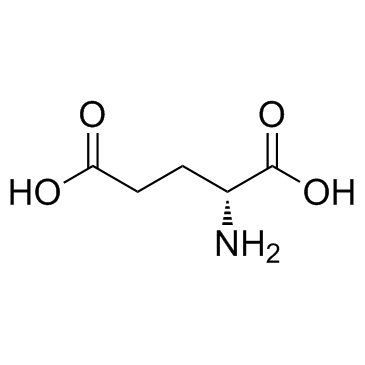 CAS#:6893-26-1
CAS#:6893-26-1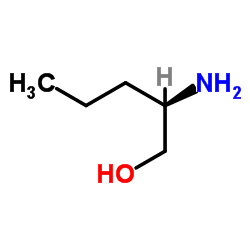 CAS#:80696-30-6
CAS#:80696-30-6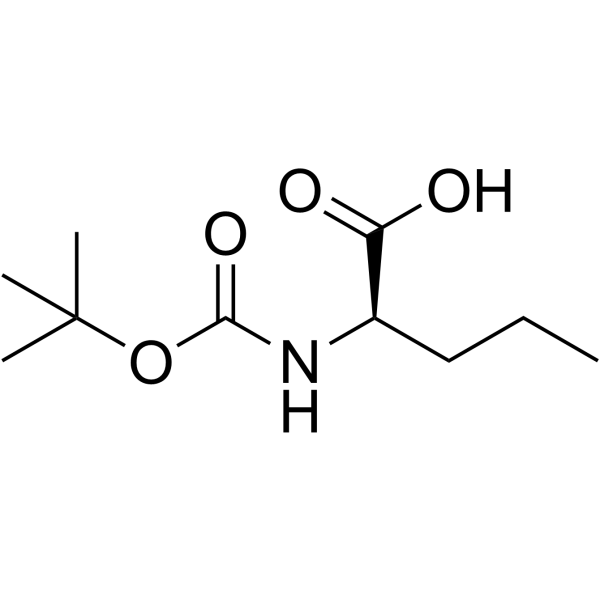 CAS#:57521-85-4
CAS#:57521-85-4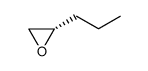 CAS#:123731-68-0
CAS#:123731-68-0 CAS#:62421-33-4
CAS#:62421-33-4
