Ac-Lys-Ome HCl
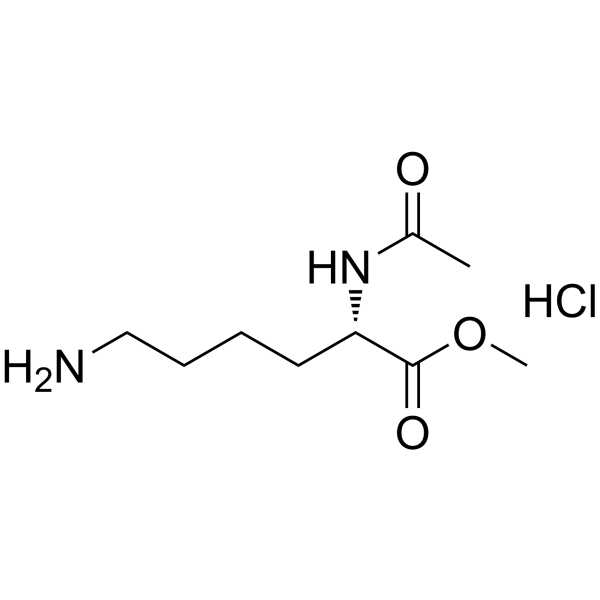
Ac-Lys-Ome HCl structure
|
Common Name | Ac-Lys-Ome HCl | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 20911-93-7 | Molecular Weight | 238.712 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 354.6ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H19ClN2O3 | Melting Point | 108-114ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 168.2ºC | |
Use of Ac-Lys-Ome HClMethyl acetyl-L-lysinate hydrochloride is a lysine derivative[1]. |
| Name | ac-lys-ome hcl |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Methyl acetyl-L-lysinate hydrochloride is a lysine derivative[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Amino acids and amino acid derivatives have been commercially used as ergogenic supplements. They influence the secretion of anabolic hormones, supply of fuel during exercise, mental performance during stress related tasks and prevent exercise induced muscle damage. They are recognized to be beneficial as ergogenic dietary substances[1]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 354.6ºC at 760mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 108-114ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H19ClN2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 238.712 |
| Flash Point | 168.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 238.108414 |
| PSA | 81.42000 |
| LogP | 1.68630 |
| Vapour Pressure | 3.32E-05mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Safety Phrases | 24/25 |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
DNA-protein cross-links between guanine and lysine depend on the mechanism of oxidation for formation of C5 vs C8 guanosine adducts.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130(2) , 703-9, (2008) The reaction between N(alpha)-acetyllysine methyl ester (Lys) and 2'-deoxyguanosine (dGuo) was used to study structural aspects of DNA-protein cross-link (DPC) formation. The precise structure of DPCs... |
|
|
Antifibrinolytic activities of alpha-N-acetyl-L-lysine methyl ester, epsilon-aminocaproic acid, and tranexamic acid. Importance of kringle interactions and active site inhibition.
Arterioscler. Thromb. 12(6) , 708-16, (1992) alpha-N-acetyl-L-lysine methyl ester (NALME) is a lysine analogue that reportedly binds to low-affinity lysine binding sites in plasmin(ogen) and miniplasmin(ogen). In the studies presented here, we s... |
|
|
Characterization of antibodies to advanced glycosylation end products on protein.
J. Immunol. Methods 140(1) , 119-25, (1991) Antibodies directed against advanced glycosylation end products (AGEs) formed during a Maillard reaction have been generated and characterized. Since protein-bound AGEs recognized by the antibodies we... |
| Na-Acetyl-L-lysine methyl ester hydrochloride |
| EINECS 244-111-4 |
| Methyl N-acetyl-L-lysinate hydrochloride (1:1) |
| Ac-Lys-Ome.HCl |
| L-ALME |
| L-Lysine, N-acetyl-, methyl ester, hydrochloride (1:1) |
| ACETYL-L-LYSINE METHYL ESTER HCL |
| ACETYL-L-LYSINE METHYL ESTER HYDROCHLORIDE |
| MFCD00003570 |
| Ac-L-Lys-OMe*HCl |
| AC-LYSINE-OME HCL |
| Ac-Lys-OMe |
| Methyl N-acetyl-6-ammonio-L-norleucinate chloride |