Escitalopram oxalate
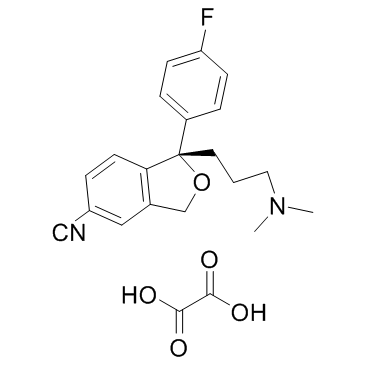
Escitalopram oxalate structure
|
Common Name | Escitalopram oxalate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 219861-08-2 | Molecular Weight | 414.427 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 428.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H23FN2O5 | Melting Point | 152-153ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 212.8ºC | |
Use of Escitalopram oxalateEscitalopram is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) with Ki of 0.89 nM.Target: SSRIsEscitalopram, the S-enantiomer of citalopram, belongs to a class of antidepressant agents known as selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). Escitalopram may be used to treat major depressive disorder (MDD) and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). Escitalopram has no significant affinity for adrenergic (alpha1, alpha2, beta), cholinergic, GABA, dopaminergic, histaminergic, serotonergic (5HT1A, 5HT1B, 5HT2), or benzodiazepine receptors; antagonism of such receptors has been hypothesized to be associated with various anticholinergic, sedative, and cardiovascular effects for other psychotropic drugs. The chronic administration of escitalopram is found to downregulate brain norepinephrine receptors, as has been observed with other drugs effective in the treatment of major depressive disorder. Escitalopram does not inhibit monoamine oxidase. |
| Name | Escitalopram oxalate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Escitalopram is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) with Ki of 0.89 nM.Target: SSRIsEscitalopram, the S-enantiomer of citalopram, belongs to a class of antidepressant agents known as selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). Escitalopram may be used to treat major depressive disorder (MDD) and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). Escitalopram has no significant affinity for adrenergic (alpha1, alpha2, beta), cholinergic, GABA, dopaminergic, histaminergic, serotonergic (5HT1A, 5HT1B, 5HT2), or benzodiazepine receptors; antagonism of such receptors has been hypothesized to be associated with various anticholinergic, sedative, and cardiovascular effects for other psychotropic drugs. The chronic administration of escitalopram is found to downregulate brain norepinephrine receptors, as has been observed with other drugs effective in the treatment of major depressive disorder. Escitalopram does not inhibit monoamine oxidase. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 428.3ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 152-153ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C22H23FN2O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 414.427 |
| Flash Point | 212.8ºC |
| Exact Mass | 414.159088 |
| PSA | 110.86000 |
| LogP | 2.96858 |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer, Under Inert Atmosphere |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
|
The effect of combined treatment with risperidone and antidepressants on the MK-801-induced deficits in the social interaction test in rats.
Pharmacol. Rep. 67 , 1183-7, (2015) Several clinical reports have suggested that augmentation of atypical antipsychotics' activity by antidepressants may efficiently improve the treatment of negative and some cognitive symptoms of schiz... |
|
|
Prolonged administration of antidepressant drugs leads to increased binding of [(3)H]MPEP to mGlu5 receptors.
Neuropharmacology 84 , 46-51, (2014) Metabotropic glutamate 5 (mGlu5) receptors are functionally connected with NMDA receptors. The antidepressant activity of the NMDA receptor antagonist ketamine in both preclinical and clinical studies... |
|
|
Prenatal stress, regardless of concurrent escitalopram treatment, alters behavior and amygdala gene expression of adolescent female rats.
Neuropharmacology 97 , 251-8, (2015) Depression during pregnancy has been linked to in utero stress and is associated with long-lasting symptoms in offspring, including anxiety, helplessness, attentional deficits, and social withdrawal. ... |
| Lexapro (TN) |
| MFCD06407826 |
| Lu-26-054-0 |
| (1S)-1-[3-(diméthylamino)propyl]-1-(4-fluorophényl)-1,3-dihydro-2-benzofurane-5-carbonitrile oxalate |
| Ethandisäure--(1S)-1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-1-(4-fluorphenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2-benzofuran-5-carbonitril(1:1) |
| ESCIFALOPRAMOXALATE |
| (S)-Citalopram Oxalate |
| (1S)-1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2-benzofuran-5-carbonitrile ethanedioate |
| (1S)-1-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2-benzofuran-5-carbonitrile ethanedioate (1:1) |
| Escitalopram oxalate (USAN) |
| Lexapro |
| escitalopram oxalic acid |
| Escitalopram Oxalate |
| Cipralex |
| (1S)-1-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2-benzofuran-5-carbonitrile oxalate |
| 5-Isobenzofurancarbonitrile, 1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-, (1S)-, ethanedioate (1:1) |
| (S)-Escitalopram Oxalate |
| Citalopram Impurity 2 |
| Escitalopram (oxalate) |
 CAS#:144-62-7
CAS#:144-62-7 CAS#:128196-01-0
CAS#:128196-01-0 CAS#:50-00-0
CAS#:50-00-0 CAS#:488787-59-3
CAS#:488787-59-3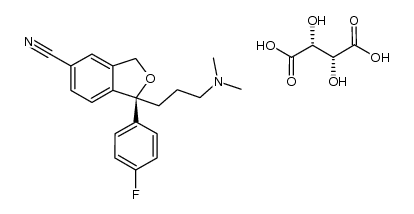 CAS#:1073819-95-0
CAS#:1073819-95-0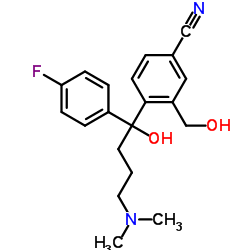 CAS#:103146-25-4
CAS#:103146-25-4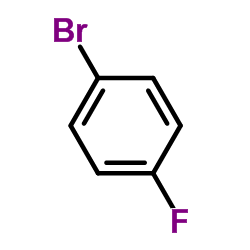 CAS#:460-00-4
CAS#:460-00-4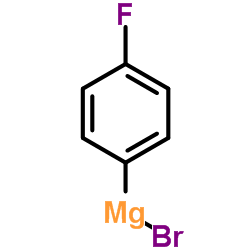 CAS#:352-13-6
CAS#:352-13-6 CAS#:5407-04-5
CAS#:5407-04-5 CAS#:19070-16-7
CAS#:19070-16-7
