Diphyllin
Modify Date: 2024-01-08 10:47:54
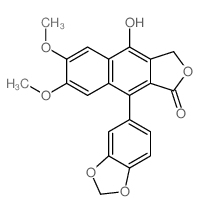
Diphyllin structure
|
Common Name | Diphyllin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 22055-22-7 | Molecular Weight | 380.34800 | |
| Density | 1.445g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 638.8ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H16O7 | Melting Point | 290 ºC (methanol ) | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 232.4ºC | |
Use of DiphyllinDiphyllin is an arylnaphthalene lignan isolated from Justicia procumbens and is a potent HIV-1 inhibitor with an IC50 of 0.38 μM. Diphyllin is active against vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) and influenza virus[1]. Diphyllin is a vacuolar type H+-ATPase (V-ATPase) inhibitor with an IC50 value of 17 nM and inhibits lysosomal acidification in human osteoclasts[2]. Diphyllin inhibits NO production with an IC50 of 50 μM and has anticancer and anti-inflammatory activities[3]. |
| Name | 9-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-4-hydroxy-6,7-dimethoxy-3H-benzo[f][2]benzofuran-1-one |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Diphyllin is an arylnaphthalene lignan isolated from Justicia procumbens and is a potent HIV-1 inhibitor with an IC50 of 0.38 μM. Diphyllin is active against vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) and influenza virus[1]. Diphyllin is a vacuolar type H+-ATPase (V-ATPase) inhibitor with an IC50 value of 17 nM and inhibits lysosomal acidification in human osteoclasts[2]. Diphyllin inhibits NO production with an IC50 of 50 μM and has anticancer and anti-inflammatory activities[3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
HIV-1:0.38 μM (IC50) Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) Vacuolar type H+-ATPase:17 nM (IC50) |
| References |
| Density | 1.445g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 638.8ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 290 ºC (methanol ) |
| Molecular Formula | C21H16O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 380.34800 |
| Flash Point | 232.4ºC |
| Exact Mass | 380.09000 |
| PSA | 83.45000 |
| LogP | 3.62870 |
| Vapour Pressure | 6.53E-17mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.679 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| Water Solubility | Insuluble (2.4E-3 g/L) (25 ºC) |
| HMS1607M09 |
| 7-hydroxyjusticidin B |
| Bio-0182 |
| Diphyllin |
![4-acetoxy-6,7-dimethoxy-9-(1,3- benzodioxol-5-yl)naphtho[2,3-c]furan-1(3H)-one Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/182/25001-54-1.png) CAS#:25001-54-1
CAS#:25001-54-1 CAS#:120-57-0
CAS#:120-57-0 CAS#:105875-33-0
CAS#:105875-33-0 CAS#:5392-10-9
CAS#:5392-10-9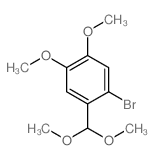 CAS#:70461-33-5
CAS#:70461-33-5![benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-4,5-dimethoxyphenyl)methanol Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/444/74879-19-9.png) CAS#:74879-19-9
CAS#:74879-19-9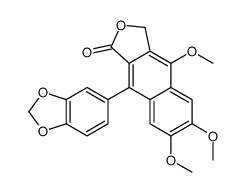 CAS#:25001-57-4
CAS#:25001-57-4