(S,R,S)-AHPC-C5-COOH
Modify Date: 2024-04-04 00:05:08
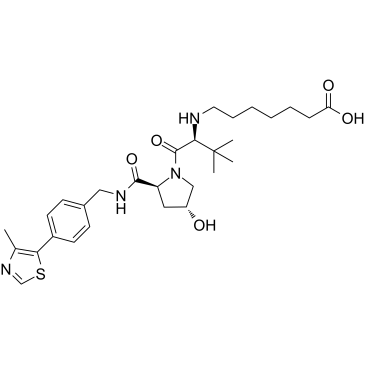
(S,R,S)-AHPC-C5-COOH structure
|
Common Name | (S,R,S)-AHPC-C5-COOH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2267282-19-7 | Molecular Weight | 558.73 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C29H42N4O5S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of (S,R,S)-AHPC-C5-COOH(S,R,S)-AHPC-C5-COOH (VH032-C5-COOH) is a synthesized E3 ligase ligand-linker conjugate, contains the VH032 VHL-based ligand and a linker to form PROTACs. VH-032 is a selective and potent inhibitor of VHL/HIF-1α interaction with a Kd of 185 nM, has the potential for the study of anemia and ischemic diseases[1]. |
| Name | (S,R,S)-AHPC-C5-COOH |
|---|
| Description | (S,R,S)-AHPC-C5-COOH (VH032-C5-COOH) is a synthesized E3 ligase ligand-linker conjugate, contains the VH032 VHL-based ligand and a linker to form PROTACs. VH-032 is a selective and potent inhibitor of VHL/HIF-1α interaction with a Kd of 185 nM, has the potential for the study of anemia and ischemic diseases[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
VHL |
| In Vitro | PROTACs contain two different ligands connected by a linker; one is a ligand for an E3 ubiquitin ligase and the other is for the target protein. PROTACs exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins.The von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor protein is the substrate-binding subunit of the VHL E3 ubiquitin ligase, it targets hydroxylated α subunit of HIFs for ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C29H42N4O5S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 558.73 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|