Anisomycin
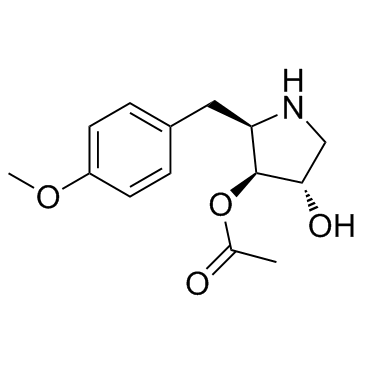
Anisomycin structure
|
Common Name | Anisomycin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 22862-76-6 | Molecular Weight | 265.305 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 398.7±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H19NO4 | Melting Point | 140-141ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 194.9±27.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of AnisomycinAnisomycin is a potent protein synthesis inhibitor which interferes with protein and DNA synthesis by inhibiting peptidyl transferase or the 80S ribosome system. |
| Name | (-)-anisomycin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Anisomycin is a potent protein synthesis inhibitor which interferes with protein and DNA synthesis by inhibiting peptidyl transferase or the 80S ribosome system. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
DNA synthesis[1] |
| In Vitro | To examine whether JNK has a core role in colistin-induced neurotoxicity in PC-12 cells, an SP600125 (a highly selective inhibitor of JNK) and Anisomycin (a potent activator) are used in this study. In order to select an appropriate concentration, PC-12 cells are treated with a range of SP600125 (0-80 μM) and Anisomycin (0-20 μM) respectively for 24 h. The results show that the cells viability significantly decreases by SP600125 treatment in a concentration-dependent manner, observed at the concentrations greater than 20 μM (p<0.01). Similarly the cells viability is inhibited by Anisomycin treatment (≥8 μM) (p<0.05) [1]. |
| In Vivo | Disruption of TNFRp55/p75 attenuates Anisomycin-induced ventricular functional improvements. Anisomycin results in an improvement in left ventricular developed pressure (LVDP), which disappears in animals with disruption of TNFR p55/p75. In addition, the Anisomycin-induced improvement in LVEDP in wild-type animals is eliminated by deletion of TNFR p55/p75. Likewise, disruption of TNFR p55/p75 abrogates the recovery of rate pressure product (RPP) elicited by pretreatment of Anisomycin. TNFR p55/p75-/- mice without Anisomycin treatment do not show differences in cardiac functional recovery compared with the control wild-type mice. There are no significant differences in heart rate between wild-type and TNFR p55/p75-deficient mice. To see whether Nox2 is involved in Anisomycin-induced myocardial protection, Nox2-deficient mice are treated with Anisomycin. The improvement in the LVEDP in Anisomycin-treated mice is eliminated in Nox2-/- mice compared with wild-type mice. In addition, recovery of RPP in wild-type mice treated with Anisomycin is mitigated in Nox2-/- mice. Nox2-/- mice without Anisomycin treatment do not show the difference in cardiac functional recovery compared with wild-type control mice[2]. |
| Cell Assay | PC-12 cells are seeded in 96-well plates at a concentration of 1×104 cells/well and cultured in an incubator at 37°C with 5% CO2 for at least 12 h prior to exposure to different concentrations of SP600125 (0-80 μM) or Anisomycin (0-20 μM) for 24 h. Subsequently, the culture medium is added to 20 μL of 5 mg/mL MTT working solution and the plate is incubated for 2 h at 37°C. The culture supernatant is removed and the formazan crystals are dissolved in 150 μL DMSO. Finally, the absorbance of each well is measured at 490 nm by a microplate reader. Cell viability is expressed as the percentage of the control group, which is set to 100%[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] Adult male TNFRp55/p75 mice, adult male wild-type C57/BL and homozygous Nox2-/- mice are used in this study. Mice are randomized into six experimental groups that undergo the following treatments,. Animals are divided into six groups: group 1: control ischemia/reperfusion, wild-type mice are injected with DMSO (0.1 mL); group 2: Anisomycin+wild-type mice, wild-type mice are injected with Anisomycin (0.1 mg/kg ip); group 3: Anisomycin+TNFR p55/p75-/- mice, TNFR p55/75-/- mice are injected with Anisomycin (0.1 mg/kg ip); group 4: TNFR p55/p75-/- mice, TNFR p55/75-/- mice are not injected with Anisomycin; group 5: Anisomycin+Nox2-/- mice, Nox2-/- mice are injected with Anisomycin (0.1 mg/kg ip); and group 6: Nox2-/- mice, Nox2-/- mice are not injected with Anisomycin. Later (24 h), the hearts are subjected to 30 min of ischemia followed by 30 min of reperfusion[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 398.7±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 140-141ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C14H19NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 265.305 |
| Flash Point | 194.9±27.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 265.131409 |
| PSA | 67.79000 |
| LogP | 0.42 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.558 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T: Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R25 |
| Safety Phrases | 45-36-26 |
| RIDADR | UN 3462 6 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | BZ9800000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Thousands of chemical starting points for antimalarial lead identification.
Nature 465 , 305-10, (2010) Malaria is a devastating infection caused by protozoa of the genus Plasmodium. Drug resistance is widespread, no new chemical class of antimalarials has been introduced into clinical practice since 19... |
|
|
Analysis of physico-chemical properties of substrates of ABC and MFS multidrug transporters of pathogenic Candida albicans.
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45 , 4813-26, (2010) In this study, we have explored the structure activity relationships of substrates of two major, promiscuous, multidrug transporters of an opportunistic human pathogen Candida albicans namely, CaCdr1p... |
|
|
Trophic factor-induced activity 'signature' regulates the functional expression of postsynaptic excitatory acetylcholine receptors required for synaptogenesis.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 9523, (2015) Highly coordinated and coincidental patterns of activity-dependent mechanisms ("fire together wire together") are thought to serve as inductive signals during synaptogenesis, enabling neuronal pairing... |
| antibioticpa-106 |
| (2S,3R,4R)-4-Hydroxy-2-(4-methoxybenzyl)-3-pyrrolidinyl acetate |
| (2S,3R,4R)-4-Hydroxy-2-(4-methoxybenzyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl acetate |
| [2R-(2a,3a,4b)]-2-[(4-Methoxyphenyl)methyl]-3,4-pyrrolidinediol 3-Acetate |
| ANISOMYCIN,STREPTOMYCES GRISEOLUS |
| EINECS 245-269-7 |
| MFCD00077650 |
| Anisomycin |
| Anisomycin,(2R,3S,4S)-2-[(4-Methoxyphenyl)methyl]-3,4-pyrrolidinediol3-acetate |
| FLAGECIDIN |
| Anisomycin from Streptomyces griseolus |
| 2-p-methoxyphenylmethyl-3-acetoxy-4-hydroxypyrrolidine |
| 3,4-Pyrrolidinediol, 2-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-, 3-acetate, (2S,3R,4R)- |
| (2R,3S,4S)-2-(4-Methoxybenzyl)-3,4-pyrrolidinediol 3-Acetate |
 CAS#:27958-08-3
CAS#:27958-08-3 CAS#:180081-83-8
CAS#:180081-83-8 CAS#:87796-46-1
CAS#:87796-46-1 CAS#:87796-29-0
CAS#:87796-29-0 CAS#:87796-27-8
CAS#:87796-27-8 CAS#:87796-40-5
CAS#:87796-40-5
