L-AP4

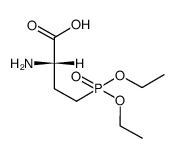
L-AP4 structure
|
Common Name | L-AP4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 23052-81-5 | Molecular Weight | 183.100 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 491.7±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H10NO5P | Melting Point | 207-215 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 251.2±31.5 °C | |
Use of L-AP4L-APB is a potent and specific agonist for the group III mGluRs, with EC50s of 0.13, 0.29, 1.0, 249 μM for mGlu4, mGlu8, mGlu6 and mGlu7 receptors, respectively. |
| Name | L-(+)-2-Amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-APB is a potent and specific agonist for the group III mGluRs, with EC50s of 0.13, 0.29, 1.0, 249 μM for mGlu4, mGlu8, mGlu6 and mGlu7 receptors, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
mGlu4:0.13 μM (EC50) mGlu8:0.29 μM (EC50) mGlu6:1.0 μM (EC50) mGlu7:249 μM (EC50) |
| In Vivo | Paw withdrawal threshold in response to application of von Frey filaments before spinal nerve ligation is 22.6±2.4 g. The mechanical threshold decreases significantly (2.3±0.5 g, P<0.05) within 10 days after nerve ligation and remains stable for at least 8 weeks. Intrathecal injection of 5 to 30 μg of L-APB significantly increases the paw withdrawal threshold in response to application of von Frey filaments in eight nerve-ligated rats in a dose-dependent manner. The maximal effect of L-APB appears within 45 min and gradually subsided in 120 min following intrathecal administration[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats[2] The effect of L-APB (L-AP4: 5, 10, and 50 μM) on identified ascending dorsal horn neurons is studied in 20 L5 and L6 spinal nerve ligated rats. L-APB, starting with the lowest concentration, is applied topically onto the exposed spinal cord. Five to 10 min following L-APB application, the response of neurons to graded mechanical stimuli is re-examined. To ensure that the effect of L-APB on dorsal horn neurons is through group III mGluRs, the inhibitory effect of 50 μM L-APB is tested before and after topical application of 100 μM MAP4, a specific antagonist for group III mGluRs, in another 12 dorsal horn neurons. MAP4 is applied to the recording site 10 min before application of 50 μM L-APB. In addition, to determine whether topical application of L-APB affects ascending dorsal horn neurons in normal rats, the effect of 50 μM L-APB on spontaneous and evoked responses to graded mechanical stimuli is examined in 11 dorsal horn neurons from eight normal rats. Also, the effect of topical spinal application of 100 μM MAP4 alone on these cells is tested 15 to 20 min after washout of L-APB solution from the recording site[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 491.7±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 207-215 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C4H10NO5P |
| Molecular Weight | 183.100 |
| Flash Point | 251.2±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 183.029663 |
| PSA | 130.66000 |
| LogP | -2.39 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.546 |
| Storage condition | 0-6°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | ES7191700 |
| HS Code | 2931900090 |
|
~63% 
L-AP4 CAS#:23052-81-5 |
| Literature: Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci. Div. Chem. Sci. (Engl. Transl.), , vol. 41, # 2 p. 397 - 402,311 - 315 |
|
~% 
L-AP4 CAS#:23052-81-5 |
| Literature: Synthetic Communications, , vol. 22, # 8 p. 1179 - 1186 |
|
~% 
L-AP4 CAS#:23052-81-5 |
| Literature: Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, , vol. 60, p. 1761 - 1766 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 2931900090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2931900090. other organo-inorganic compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward). MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
The rat retina has five types of ganglion-cell photoreceptors.
Exp. Eye Res. 130 , 17-28, (2014) Intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs) are inner retinal photoreceptors that mediate non-image-forming visual functions, e.g. pupillary constriction, regulation of pineal melaton... |
|
|
Examination of VLC-PUFA-deficient photoreceptor terminals.
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 55(7) , 4063-72, (2014) Juvenile-onset autosomal dominant Stargardt-like macular dystrophy (STGD3) is caused by mutations in ELOVL4 (elongation of very long fatty acids-4), an elongase necessary for the biosynthesis of very ... |
|
|
Adenosine modulates light responses of rat retinal ganglion cell photoreceptors througha cAMP-mediated pathway.
J. Physiol. 592(Pt 19) , 4201-20, (2014) Adenosine is an established neuromodulator in the mammalian retina, with A1 adenosine receptors being especially prevalent in the innermost ganglion cell layer. Activation of A1 receptors causes inhib... |
| L-AP4 |
| l-ap-4,l-ap4 |
| 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid |
| (S)-2-amino-4-phosphonobutanoic acid |
| MFCD00083244 |
| 2S-amino-4-phosphono-butanoic acid |
| L-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid |
| Butanoic acid, 2-amino-4-phosphono-, (2S)- |
| l-ap-4 l-ap4 |
| (2S)-2-Amino-4-phosphonobutanoic acid |
| L-(+)-2-Amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid |