Nivalenol
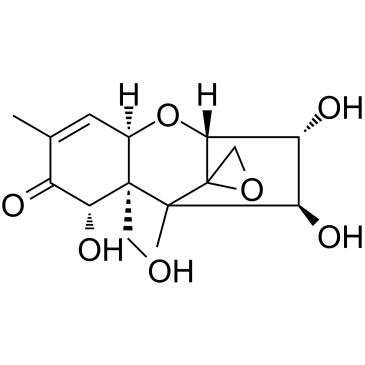
Nivalenol structure
|
Common Name | Nivalenol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 23282-20-4 | Molecular Weight | 312.315 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 585.1±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H20O7 | Melting Point | 222-223ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 221.9±23.6 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of NivalenolNivalenol, classified as type B trichotecenes toxins produced by Fusarium graminearum, is a fungal metabolite present in agricultural product[1]. Nivalenol induces cell death through caspase-dependent mechanisms and via the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. Nivalenol affects the immune system, causes emesis, growth retardation, reproductive disorders and has a haematotoxic/myelotoxic effect[2]. |
| Name | nivalenol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Nivalenol, classified as type B trichotecenes toxins produced by Fusarium graminearum, is a fungal metabolite present in agricultural product[1]. Nivalenol induces cell death through caspase-dependent mechanisms and via the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. Nivalenol affects the immune system, causes emesis, growth retardation, reproductive disorders and has a haematotoxic/myelotoxic effect[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Caspase |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 585.1±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 222-223ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C15H20O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 312.315 |
| Flash Point | 221.9±23.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 312.120911 |
| PSA | 119.75000 |
| LogP | -0.75 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.658 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H302 + H332-H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | T+: Very toxic;Xn: Harmful;F: Flammable; |
| Risk Phrases | R26/27/28 |
| Safety Phrases | S22;S26;S28;S45;S36/S37;S36/S37/S39 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | YD0165000 |
| Packaging Group | I |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |
| HS Code | 38220090 |
|
~% 
Nivalenol CAS#:23282-20-4 |
| Literature: Lauren, Denis R.; Smith, Wendy A.; Wilkins, Alistair L. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 1994 , vol. 42, # 3 p. 828 - 833 |
|
Low toxicity of deoxynivalenol-3-glucoside in microbial cells.
Toxins (Basel.) 7(1) , 187-200, (2015) Host plants excrete a glucosylation enzyme onto the plant surface that changes mycotoxins derived from fungal secondary metabolites to glucosylated products. Deoxynivalenol-3-glucoside (DON3G) is synt... |
|
|
Toxicity induced by F. poae-contaminated feed and the protective effect of Montmorillonite supplementation in broilers.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 74 , 120-30, (2014) The T-2 and HT-2 toxins, the main metabolites of Fusarium poae, induce toxicity in broilers and accumulate in tissues. Consequently, during the breeding process of broilers, diets are frequently suppl... |
|
|
Pathogenicity, symptom development, and mycotoxin formation in wheat by Fusarium species frequently isolated from sugar beet.
Phytopathology 101(11) , 1338-45, (2011) Crop rotations with putative non-host crops such as sugar beet are often recommended to reduce Fusarium head blight (FHB) in cereals. However, recent observations have shown pathogenic, endophytic, an... |
| Nivalenol from Fusarium nivale |
| Trichothec-9-en-8-one, 12,13-epoxy-3,4,7,15-tetrahydroxy-, (2α,3α,4β,6β,7β,11β,12ξ)- |
| MFCD10567355 |
| 12,13-epoxy-3,4,7,15-tetrahydroxytrichothec-9-en-8-one |
| Nivalenol hydrate |
| fusarenon-X |
| NIV |
| Nivalenol in acetonitrile |
| (3β,4α,7α,12ξ)-3,4,7,15-Tetrahydroxy-12,13-epoxytrichothec-9-en-8-one |
| nivalenol solution |
