Doxorubicin Hydrochloride
Doxorubicin Hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Doxorubicin Hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 25316-40-9 | Molecular Weight | 579.980 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 810.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C27H30ClNO11 | Melting Point | 216ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 443.8ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Doxorubicin HydrochlorideDoxorubicin hydrochloride is a cytotoxic anthracycline antibiotic for the treatment of multiple cancers. The possible mechanisms by which doxorubicin acts in the cancer cell are intercalation into DNA and disruption of topoisomerase-II-mediated DNA repair. |
| Name | adriamycin, hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Doxorubicin hydrochloride is a cytotoxic anthracycline antibiotic for the treatment of multiple cancers. The possible mechanisms by which doxorubicin acts in the cancer cell are intercalation into DNA and disruption of topoisomerase-II-mediated DNA repair. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Topoisomerase II |
| In Vitro | Combination of Doxorubicin and Simvastatin in the highest tested concentrations (2 μM and 10 μM, respectively) kills 97% of the Hela cells[2]. |
| In Vivo | Mice bearing PC3 xenografts are injected with 2, 4 or 8 mg/kg Doxorubicin and tumor volume is measured over time. A dose of 2 mg/kg does not affect tumor growth while higher dosages delay tumor growth initially (p<0.05 at days 18 and 22), 4 mg/kg or 8 mg/kg Doxorubicin significantly reduces levels of c-FLIP in PC3 xenografts[3]. A single intraperitoneal injection 10 mg/kg (Doxorubicin 1) is administered in rats, 10 daily intraperitoneal injections of 1 mg/kg (Doxorubicin 2), or in 5 weekly intraperitoneal injections of 2 mg/kg (Doxorubicin 3). An 80% mortality rate is observed at day 28 in Doxorubicin 1, whereas Doxorubicin 2 and Doxorubicin 3 reached 80% mortality at days 107 and 98, respectively. Fractional shortening decreased by 30% at week 2 in Doxorubicin DOX1, 55% at week 13 in Doxorubicin 2, and 42% at week 13 in Doxorubicin 3[4]. |
| Cell Assay | 160 μL of Hela cells suspension (3×104 cell/mL) is dispensed into three 96-well U-bottom microplates and incubated for 24 h at 37°C in a fully humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2. In plate 1, serial dilutions of Doxorubicin (20 μL; final concentration, 0.1-2 μM) and Simvastatin (20 μL; final concentration, 0.25-2 μM) are added to a final volume of 200 μL and incubated for another 72 h. In plates 2 and 3 serial dilutions of each drug (Simvastatin or Doxorubicin, 40 μL) are added. After an incubation period of 24 h, the medium is aspirated and the cells are washed in PBS. Then, serial dilutions of other drug (40 μL) are added and supplemented with culture medium to a final volume of 200 μL, and incubated for 48 h. Doxorubicin and Simvastatin are used individually as positive controls (40 μL in each well), and the cells treated only with solvent are considered as negative controls. To evaluate cell survival, 20 μL of MTT solution (5 mg/mL in PBS) is added to each well and incubated for 3 h. Then the media is replaced with 150 μL of DMSO, and complete solubilization of formazan crystals is achieved by repeated pipetting of the solution. Absorbance is then determined at 540 nm by an ELISA plate reader. Each drug concentration is assayed in 4 or 8 wells and repeated 3 times. The cytotoxic/cytostatic effect of Doxorubicin is expressed as the relative viability (% control) and calculated. Percentage of cell survival in the negative control is assumed as 100. Relative viability=(experimental absorbance-background absorbance)/ (absorbance of untreated controls-background absorbance)×100 %[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] Athymic male nude mice (3-4 weeks old) are used. PC3 cells (4×106) are injected subcutaneously into the flanks of mice. Animals bearing tumors are randomly assigned to treatment groups (five or six mice per group) and treatment initated when xenografts reached volumes of about 100 mm3. Tumors are measured using digital calipers and volume calculated using the formula: Volume=Width2×Length×0.52, where width represents the shorter dimension of the tumor. Treatments are administered as indicated using vehicle (PBS containing 0.1% BSA), Doxorubicin (2-8 mg/kg), Apo2L/TRAIL (500 μg/animal), or a combination of 4 mg/kg Doxorubicin followed by 500 μg Apo2L/TRAIL. Doxorubicin is administered systemically whereas Apo2L/TRAIL is given either intra-tumorally or systemically. All treatments are given once. Mice are monitored daily for signs of adverse effects (listlessness and scruffy apparance). Treatments seemed to be well tolerated. The mean±SEM is calculated for each data point. Differences between treatment groups are analyzed by the student t-test. Differences are considered significant when P<0.05. Rats[4] Thirty male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 250 to 300 g are randomly assigned to 1 of 3 experimental groups: Doxorubicin schedule 1 (Doxorubicin 1, n=10), Doxorubicin schedule 2 (Doxorubicin 2, n=10), or Doxorubicin schedule 3 (Doxorubicin 3, n=10). For all Doxorubicin treatment schedules, the cumulative dose of Doxorubicin is 10 mg/kg. Schedule 1 involves a single bolus intraperitoneal injection of Doxorubicin at 10 mg/kg. Schedule 2 involves 10 intraperitoneal injections of Doxorubicin at 1 mg/kg for 10 consecutive days. Schedule 3 involves 5 intraperitoneal injections of Doxorubicin at 2 mg/kg, once each week, for 5 wk. Immediately before the first Doxorubicin treatment and at weekly intervals after beginning Doxorubicin treatment, blood pressure and cardiac function are assessed in all surviving animals as long as there are at least 3 rats per group. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 810.3ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 216ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C27H30ClNO11 |
| Molecular Weight | 579.980 |
| Flash Point | 443.8ºC |
| Exact Mass | 579.150757 |
| PSA | 206.07000 |
| LogP | 1.50360 |
| Vapour Pressure | 9.64E-28mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | H2O: 10 mg/mL, clear, red-orange |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H350 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P305 + P351 + P338-P308 + P313 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T: Toxic;T+: Very toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R45;R22 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S45-S36/37/39-S22-S7/9 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | QI9295900 |
| HS Code | 2941909000 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 8 | |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2932999099. other heterocyclic compounds with oxygen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
SSX2 is a novel DNA-binding protein that antagonizes polycomb group body formation and gene repression.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42(18) , 11433-46, (2014) Polycomb group (PcG) complexes regulate cellular identity through epigenetic programming of chromatin. Here, we show that SSX2, a germline-specific protein ectopically expressed in melanoma and other ... |
|
|
Loading and release mechanism of red clover necrotic mosaic virus derived plant viral nanoparticles for drug delivery of doxorubicin.
Small 10(24) , 5126-36, (2014) Loading and release mechanisms of Red clover necrotic mosaicvirus (RCNMV) derived plant viral nanoparticle (PVN) are shown for controlled delivery of the anticancer drug, doxorubicin (Dox). Previous s... |
|
|
Fast, Stable Induction of P-Glycoprotein-mediated Drug Resistance in BT-474 Breast Cancer Cells by Stable Transfection of ABCB1 Gene.
Anticancer Res. 35 , 2531-8, (2015) Patients with P-glycoprotein and HER2/neu (HER2) receptor-overexpressing breast cancer usually have poor clinical outcomes. However, there exist no commercially available breast cancer cell lines that... |
| ADM hydrochloride |
| DOX HCl |
| Adriamycin hydrochloride |
| (1S,3S)-3,5,12-trihydroxy-3-(hydroxyacetyl)-10-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydrotetracen-1-yl 3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranoside hydrochloride |
| 5,12-naphthacenedione, 10-[(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,8,11-trihydroxy-8-(hydroxyacetyl)-1-methoxy-, (8S,10S)-, hydrochloride |
| ADRIACIN |
| (1S,3S)-3-Glycoloyl-3,5,12-trihydroxy-10-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydro-1-tetracenyl 3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranoside hydrochloride (1:1) |
| MFCD00077757 |
| 5,12-Naphthacenedione, 10-[(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,8,11-trihydroxy-8-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-1-methoxy-, (8S,10S)-, hydrochloride (1:1) |
| Doxorubicin Hydrochloride |
| DOX,Hydroxydaunorubicin hydrochloride |
| Dox hydrochloride |
| ADR |
| (1S,3S)-3-Glycoloyl-3,5,12-trihydroxy-10-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydrotetracen-1-yl 3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranoside hydrochloride (1:1) |
| Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) HCl |
| 5,12-naphthacenedione, 10-[(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-a-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,8,11-trihydroxy-8-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-1-methoxy-, (8S,10S)-, hydrochloride (1:1) |
| Lipodox |
| FI 106 |
| (1S,3S)-3,5,12-trihydroxy-3-(hydroxyacetyl)-10-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydrotetracen-1-yl 3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-a-L-lyxo-hexopyranoside hydrochloride (1:1) |
| 14-hydroxydaunomycin hydrochloride |
| Adriamycin HCl |
| fi6804 |
| (8S-cis)-10-((3-Amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy)-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,8,11-trihydroxy-8-(hydroxyacetyl)-1-methoxynaphthacene-5,12-dione hydrochloride |
| Rubex |
| Adriamycin RDF |
| Caely |
| DOX |
| (1S,3S)-3-glycoloyl-3,5,12-trihydroxy-10-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydrotetracen-1-yl 3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-a-L-lyxo-hexopyranoside hydrochloride |
| (8S,10S)-10-((3-Amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-a-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy)-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,8,11-trihydroxy-8-(hydroxyacetyl)-1-methoxy-5,12-naphthacenedione hydrochloride |
| CAELYX |
| EINECS 246-818-3 |
| Adriamycin, hydrochloride |
| 5,12-Naphthacenedione, 10-((3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-l-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy)-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,8,11-trihydroxy-8-(hydroxyacetyl)-1-methoxy-, hydrochloride, (8S-cis)- |
| Ardriamycin |
| Adriamycin PFS |
| Adriblastin |
| Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) |
| (8S,10S)-10-((3-Amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy)-8-glycoloyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,8,11-trihydroxy-1-methoxy-5,12-naphthacenedione hydrochloride |
| (8S-cis)-10-[(3-Amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-a-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,8,11-trihydroxy-8-(hydroxyacetyl)-1-methoxy-5,12-naphthacenedione hydrochloride |
| doxorubicin HCl |
| (8S,10S)-10-{[(2R,4S,5S,6S)-4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-6,8,11-trihydroxy-8-(hydroxyacetyl)-1-methoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrotetracene-5,12-dione hydrochloride |
| Hydroxydaunorubicin hydrochloride |
| Doxorubicin (hydrochloride) |
| Daunorubicin Impurity 4 |
![5,12-Naphthacenedione, 10-[(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-8-(2-bromoacetyl)-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,8,11-trihydroxy-1-methoxy-, hydrochloride (1:1), (8S,10S) Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/135/29742-67-4.png) CAS#:29742-67-4
CAS#:29742-67-4 CAS#:23541-50-6
CAS#:23541-50-6 CAS#:26295-56-7
CAS#:26295-56-7 CAS#:23214-92-8
CAS#:23214-92-8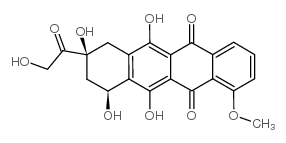 CAS#:24385-10-2
CAS#:24385-10-2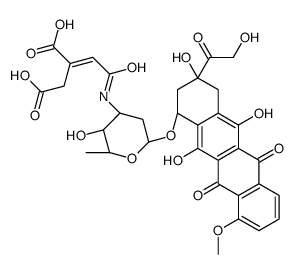 CAS#:114390-31-7
CAS#:114390-31-7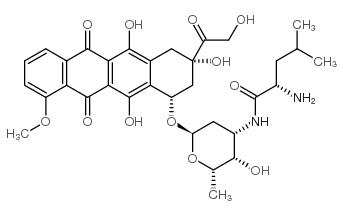 CAS#:70774-25-3
CAS#:70774-25-3 CAS#:80875-73-6
CAS#:80875-73-6 CAS#:80790-68-7
CAS#:80790-68-7![5,12-Naphthacenedione,10-[[3-(3-cyano-4-morpholinyl)-2,3,6-trideoxy-a-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,8,11-trihydroxy-8-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-1-methoxy-,(8S,10S)- structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/221/88254-07-3.png) CAS#:88254-07-3
CAS#:88254-07-3
