Zidovudine
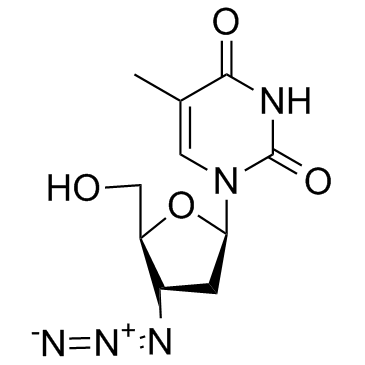
Zidovudine structure
|
Common Name | Zidovudine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 30516-87-1 | Molecular Weight | 267.241 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H13N5O4 | Melting Point | 113-115 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of ZidovudineZidovudine is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI), widely used to treat HIV infection. Zidovudine increases CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing frequency. |
| Name | zidovudine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Zidovudine is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI), widely used to treat HIV infection. Zidovudine increases CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing frequency. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
HIV-1 CRISPR/Cas9 |
| In Vitro | Zidovudine inhibits SVG, Primary human fetal astrocytes (PFA), peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC), and monocyte-derived macrophages (MDM) with EC50 of 17, 1311, 8, and 5 nM, respectively. Zidovudine inhibits SVG, PFA, PBMC, and MDM with EC90 of 0.205 μM, 44.157 μM, 0.481 μM, and 0.219 μM, respectively[1]. Genome editing via CRISPR/Cas9 has become an efficient and reliable way to make precise, targeted changes to the genome of living cells. CXCR4 is a co-receptor for the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection and has been considered as an important therapeutic target for AIDS. CXCR4 mediates viral entry into human CD4+ cells by binding to envelope protein, gp120. Human CXCR4 gene is efficiently disrupted by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing, leading to HIV-1 resistance of human primary CD4+ T cells. The Cas9-mediated ablation of CXCR4 demonstrated high specificity and negligible off-target effects without affecting cell division and propagation[2]. |
| In Vivo | Intravitrous injection of the NRTIs Lamivudine (3TC), Zidovudine (AZT), or Abacavir (ABC) suppresses the laser-induced choroidal neovascularization (CNV) in wild-type mice compared to PBS vehicle. The mean level of VEGF-A in the RPE/choroid, which peaks on day 3 after laser injury, is significantly reduced in 3TC-, AZT- and ABC-treated eyes compared with control eyes in wild-type mice, but not inP2rx7-/- mice[3]. |
| Cell Assay | Assays are performed in all cell types in the presence of titrating concentrations of ARV. 5,000 SVG, 2,500 PFA, 200,000 PBMC, or 50,000 MDM cells/well are seeded into triplicate wells of 96-well plates. Twenty-four hours later, the culture medium is removed and replaced with medium containing the ARV or DMSO (0.5% vol/vol), and equivalent TCID50 infectious units of luciferase reporter virus are added to the cells. After a 16 h incubation at 37°C, the initial viral inoculum is removed and replaced with culture medium containing the same antiretroviral drug (ARV) or DMSO (0.5% vol/vol) concentrations. At 72 h post infection, the medium is aspirated, the cells are lysed and HIV-1 infection measured using the Luciferase Assay System. Luminescence is measured using a FLUOStar Optima microplate reader. Inhibition curves and the 50% (EC50) and 90% (EC90) effective concentrations are determined by nonlinear regression analysis, using GraphPad Prism software[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] C57BL/6J (wild-type) and P2rx7-/- mice are used. The Nlrp3-/- mice are used. The NRTIs 3TC, AZT, and ABC or the P2X7 antagonist A438079 hydrochloride are dissolved in PBS. For CNV, each group of mice is injected once with 1 μL of NRTIs (3TC, 125 ng/μL; ABC, 183 ng/μL; AZT, 146 ng/μL), 1 μL of A438079 hydrochloride (3, 30, or 300 ng/μL), or the same volume of vehicle (PBS) into the vitreous humor using a 33-gauge needle immediately after laser injury. Another group of mice is injected with 3TC (125 ng) in combination with an anti-mouse VEGF polyclonal antibody (10 ng). Goat whole IgG (10 ng) is used as a biological control for the anti-mouse VEGF antibody. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 113-115 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H13N5O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 267.241 |
| Exact Mass | 267.096741 |
| PSA | 134.07000 |
| LogP | -0.53 |
| Index of Refraction | 47 ° (C=1, H2O) |
| Water Solubility | 1-5 g/100 mL at 17 ºC |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H351 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R40 |
| Safety Phrases | S36/37/39-S45 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | XP2072000 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
| Precursor 5 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Xenobiotics that affect oxidative phosphorylation alter differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells at concentrations that are found in human blood.
Dis. Model Mech. 8 , 1441-55, (2015) Adipogenesis is accompanied by differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells to adipocytes. As part of this differentiation, biogenesis of the oxidative phosphorylation system occurs. Many chem... |
|
|
Evaluation of the in vitro/in vivo potential of five berries (bilberry, blueberry, cranberry, elderberry, and raspberry ketones) commonly used as herbal supplements to inhibit uridine diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 72 , 13-9, (2014) In this study, we evaluated inhibitory potentials of popularly-consumed berries (bilberry, blueberry, cranberry, elderberry, and raspberry ketones) as herbal supplements on UGT1A1, UGT1A4, UGT1A6, UGT... |
|
|
Evaluation of thein vitro/in vivodrug interaction potential of BST204, a purified dry extract of ginseng, and its four bioactive ginsenosides through cytochrome P450 inhibition/induction and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase inhibition
Food Chem. Toxicol. 68 , 117-27, (2014) • BST204 is a purified dry extract of ginseng containing high amounts of Rh2 and Rg3. • BST204 had only weak inhibitory effects on nine CYPs and five UGTs. • It is unlikely that BST204 alter pharmacok... |
| Retrovis |
| bwa509u |
| Azitidin |
| BW-A509U |
| 1-(3-Azido-2,3-dideoxy-β-D-glycero-pentofuranosyl)-5-methylpyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione |
| 1-(3-Azido-2,3-dideoxy-β-D-ribofuranosyl)thymine |
| Thymidine, 3'-azido-3'-deoxy- |
| ZVD |
| 3'-azido-3'-droxythymidine |
| retrovir |
| Timazid |
| ZDV |
| 1-(3-Azido-2,3-Dideoxy-Beta-D-Ribofuranosyl)Thymine |
| BE-AS09U |
| Azidothymidine |
| 1-[(2R,4S,5S)-4-Azido-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]-5-methylpyrimidin-2,4(1H,3H)-dion |
| 3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine |
| 1-[(2R,4S,5S)-4-azido-5-(hydroxyméthyl)tétrahydrofuran-2-yl]-5-méthylpyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione |
| AZT |
| MFCD00006536 |
| 2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione, 1-(3-azido-2,3-dideoxy-β-D-glycero-pentofuranosyl)-5-methyl- |
| Zidovudine |
 CAS#:29706-84-1
CAS#:29706-84-1 CAS#:7288-28-0
CAS#:7288-28-0 CAS#:106060-78-0
CAS#:106060-78-0 CAS#:134485-31-7
CAS#:134485-31-7 CAS#:134485-32-8
CAS#:134485-32-8![2-amino-1-[(2R,4S,5S)-4-azido-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-5-methylpyrimidin-4-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/060/108441-50-5.png) CAS#:108441-50-5
CAS#:108441-50-5 CAS#:141039-00-1
CAS#:141039-00-1 CAS#:19047-85-9
CAS#:19047-85-9![1-[(2R,4S,5S)-4-azido-5-(dichlorophosphoryloxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-5-methylpyrimidine-2,4-dione structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/022/188426-77-9.png) CAS#:188426-77-9
CAS#:188426-77-9 CAS#:56-89-3
CAS#:56-89-3 CAS#:65-71-4
CAS#:65-71-4 CAS#:52450-18-7
CAS#:52450-18-7 CAS#:110-00-9
CAS#:110-00-9 CAS#:67-56-1
CAS#:67-56-1
