Crotaline

Crotaline structure
|
Common Name | Crotaline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 315-22-0 | Molecular Weight | 325.357 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 537.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H23NO6 | Melting Point | 204ºC (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 278.7±30.1 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of CrotalineMonocrotaline is an pyrrolizidine alkaloid extracted from the seeds of the Crotalaria spectabilis plant to induce pulmonary hypertension in rodents. |
| Name | monocrotaline |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Monocrotaline is an pyrrolizidine alkaloid extracted from the seeds of the Crotalaria spectabilis plant to induce pulmonary hypertension in rodents. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Monocrotaline (MCT) is an 11-membered macrocyclic pyrrolizidine alkaloid (PA) derived from the seeds of the Crotalaria spectabilis plant[1]. Monocrotaline a natural ligand exhibits dose-dependent cytotoxicity with potent antineoplastic activity. The in vitro cytotoxicity of monocrotaline is proved at IC50 24.966 µg/mL and genotoxicity at 2 X IC50 against HepG2 cells[2]. |
| In Vivo | MCT causes a pulmonary vascular syndrome in rats characterized by proliferative pulmonary vasculitis, pulmonary hypertension (PH), and cor pulmonale[3]. Among preclinical models of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), monocrotaline animal model offers the advantage of mimic several key aspects of human PAH, including vascular remodeling, proliferation of smooth muscle cells, endothelial dysfunction, upregulation of inflammatory cytokines, and right ventricle failure, requiring a single drug injection[4]. Changes in multiple pathways associated with the development of PH, including activated glycolysis, increased markers of proliferation, disruptions in carnitine homeostasis, increased inflammatory and fibrosis biomarkers, and a reduction in glutathione biosynthesis are observed with the injection of monocrotaline[5]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: A total of 20 male Sprague Dawley rats (SD; 220-270g) are used in this study (n=10 per group). Control group received vehicle for monocrotaline (MCT). Pre-pulmonary hypertension (PH) group received a single injection of MCT (60 mg/kg i.p.) to induce and are sacrificed after 14 days[5]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 537.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 204ºC (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C16H23NO6 |
| Molecular Weight | 325.357 |
| Flash Point | 278.7±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 325.152527 |
| PSA | 96.30000 |
| LogP | -0.37 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.586 |
| Storage condition | 2~8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H351 |
| Precautionary Statements | P281-P301 + P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T: Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R25 |
| Safety Phrases | 36/37/39-45 |
| RIDADR | UN 1544 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | QB3140000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 29399990 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 8 | |
|
The Japanese toxicogenomics project: application of toxicogenomics.
Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 54 , 218-27, (2010) Biotechnology advances have provided novel methods for the risk assessment of chemicals. The application of microarray technologies to toxicology, known as toxicogenomics, is becoming an accepted appr... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals ... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predicti... |
| Monocrotaline/crotaline |
| Monccrotalire |
| Bulbus Lilii |
| CROTALINE |
| (13a,14a)-14,19-Dihydro-12,13-dihydroxy-20-norcrotolanan-11,15-dione |
| Monocrotaline |
| 2H-[1,6]Dioxacycloundecino[2,3,4-gh]pyrrolizine-2,6(3H)-dione, 4,5,8,10,12,13,13a,13b-octahydro-4,5-dihydroxy-3,4,5-trimethyl-, (3R,4R,5R,13aR,13bR)- |
| (3R,4R,5R,13aR,13bR)-4,5-Dihydroxy-3,4,5-trimethyl-4,5,8,10,12,13,13a,13b-octahydro-2H-[1,6]dioxacycloundecino[2,3,4-gh]pyrrolizine-2,6(3H)-dione |
| MONOCRATALINE |
| MFCD00084656 |
| A 6080 |
| MONOCROTALIN |
| CROTALIN |
| Crotaline,Monocrotaline |
 CAS#:110121-56-7
CAS#:110121-56-7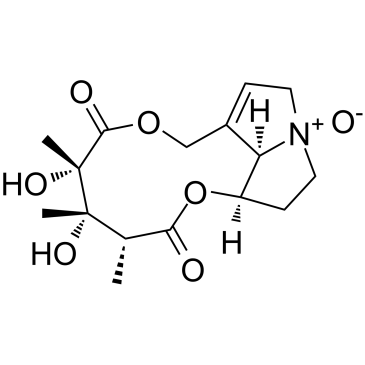 CAS#:35337-98-5
CAS#:35337-98-5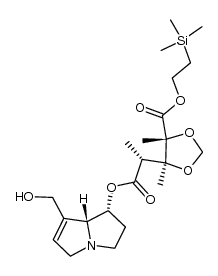 CAS#:109391-29-9
CAS#:109391-29-9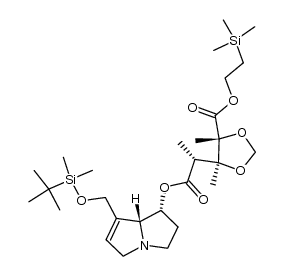 CAS#:109432-25-9
CAS#:109432-25-9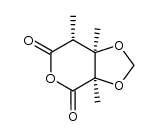 CAS#:109391-24-4
CAS#:109391-24-4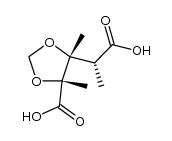 CAS#:109494-78-2
CAS#:109494-78-2![(2'R,3R,4S)-5-[2'-methoxy-2'-(trifluoromethyl)phenylacetoxy]-2,3,4-trimethyl-3,4-methylenedioxy-2-pentene Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/082/121719-94-6.png) CAS#:121719-94-6
CAS#:121719-94-6![(2'R,2S,3R,4S)-5-[2'-methoxy-2'-(trifluoromethyl)phenylacetoxy]-2,3,4-trimethyl-3,4-methylenedioxypentanoic acid Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/006/121719-96-8.png) CAS#:121719-96-8
CAS#:121719-96-8 CAS#:23107-12-2
CAS#:23107-12-2 CAS#:23291-96-5
CAS#:23291-96-5 CAS#:608-40-2
CAS#:608-40-2 CAS#:520-55-8
CAS#:520-55-8 CAS#:25490-68-0
CAS#:25490-68-0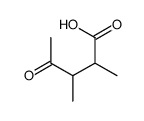 CAS#:526-79-4
CAS#:526-79-4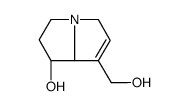 CAS#:480-85-3
CAS#:480-85-3
