| In Vivo |
A liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry method has been developed and validated for identification and quantification of four major bioactive saponins in rat plasma after oral administration of extraction of saponins from Flos Lonicerae, i.e., Macranthoidin B, Macranthoidin A, Dipsacoside B, and Macranthoside B. The retention time of Macranthoidin B, Macranthoidin A, Dipsacoside B, Macranthoside B and IS are 10.65, 12.11, 13.81, 23.31 and 5.47 min, respectively[1]. Taking Macranthoidins A, B, Dipsacoside B (saponins), sweroside (iridoids), and luteolin-7-O-d-glucoside (flavonoids) as markers, a method of ultra high performance liquid chromatography with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry is employed to determine their amounts in Lonicerae Flos, Lonicerae Japonicae Flos, and Lonicerae Japonicae Flos preparations[2].
|
| Animal Admin |
Mice[1] Sprague-Dawley rats (220-250 g) are used. To calculate the administered dose of Macranthoidin B, Macranthoidin A, Dipsacoside B, and Macranthoside B, their contents in saponins extraction are quantitatively determined. One hundred milligrams of the dry powder is suspended in 100 mL 50% methanol (v/v), ultrasonically extracted for 40 min, and then cooled at room temperature; 50% methanol is added to compensate for the lost weight. Finally, 5 μL of this solution is injected into the HPLC system for analysis after filtration through a 0.45 μm membrane. The contents of Macranthoidin B, Macranthoidin A, Dipsacoside B, and Macranthoside B are found as 36.7, 6.59, 23.3 and 0.506 g/100 g extraction, respectively.
|
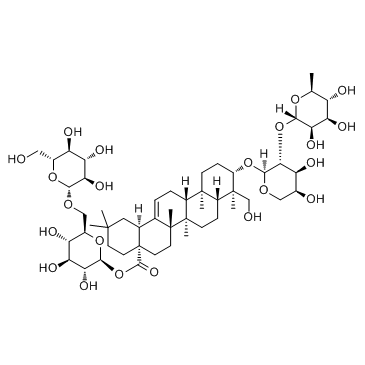
 CAS#:14216-03-6
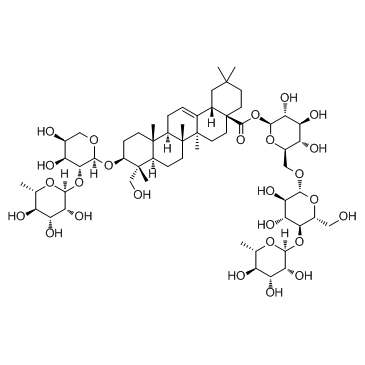
CAS#:14216-03-6![3-O-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1->2)-α-L-arabinopyranosyl]-28-O-[6-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1->6)-β-D-glucopyranosyl]hederagenin Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/465/120481-41-6.png) CAS#:120481-41-6
CAS#:120481-41-6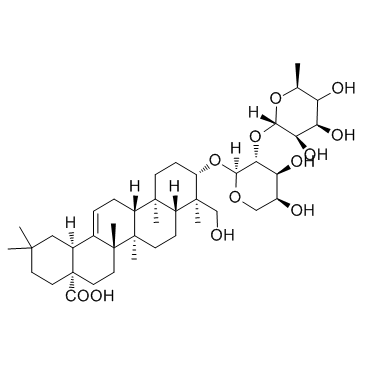 CAS#:27013-91-8
CAS#:27013-91-8
