Terbinafine lactate
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 22:04:59
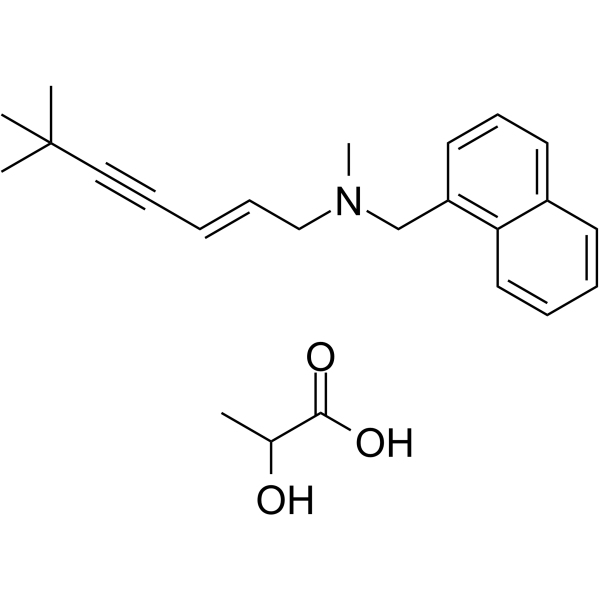
Terbinafine lactate structure
|
Common Name | Terbinafine lactate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 335276-86-3 | Molecular Weight | 381.51 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C24H31NO3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Terbinafine lactateTerbinafine lactate (TDT 067 lactate) is an orally active and potent antifungal agent. Terbinafine lactate is a potent non-competitive inhibitor of squalene epoxidase from Candida, with a Ki of 30 nM. Terbinafine lactate also shows antibacterial activity against certain Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria[1][2][3]. |
| Name | Terbinafine lactate |
|---|
| Description | Terbinafine lactate (TDT 067 lactate) is an orally active and potent antifungal agent. Terbinafine lactate is a potent non-competitive inhibitor of squalene epoxidase from Candida, with a Ki of 30 nM. Terbinafine lactate also shows antibacterial activity against certain Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Terbinafine has a primary fungicidal action in vitro against most fungal pathogens, including dermatophytes, and dimorphic and filamentous fungi. Terbinafine specifically inhibits fungal ergosterol biosynthesis at the point of squalene epoxidation. The treated fungal cells rapidly accumulate tlic intermediate squalene and become deficient in the end-product of the pathway, ergosterol[1]. |
| In Vivo | Terbinafine is not only active after topical application but is very effective in experimental dermatophytoses following oral administration. In fungi infected guinea-pigs, the skin temperature dropps dramatically after the fourth treatment of terbinafine[2]. |
| References |
[3]. Ciftci E, et al. Mupirocin vs terbinafine in impetigo.Indian J Pediatr. 2002 Aug;69(8):679-82. |
| Molecular Formula | C24H31NO3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 381.51 |