Tetrahydrocurcumin
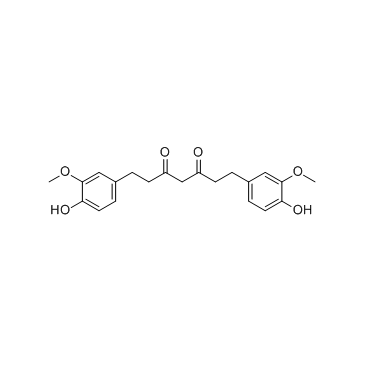
Tetrahydrocurcumin structure
|
Common Name | Tetrahydrocurcumin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 36062-04-1 | Molecular Weight | 372.412 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 564.1±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H24O6 | Melting Point | 95-97ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 196.2±22.2 °C | |
Use of TetrahydrocurcuminTetrahydrocurcumin is a Curcuminoid found in turmeric (Curcuma longa) that is produced by the reduction of Curcumin. Tetrahydrocurcumin inhibit CYP2C9 and CYP3A4. |
| Name | tetrahydrocurcumin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Tetrahydrocurcumin is a Curcuminoid found in turmeric (Curcuma longa) that is produced by the reduction of Curcumin. Tetrahydrocurcumin inhibit CYP2C9 and CYP3A4. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
CYP2C9 CYP3A4 Human Endogenous Metabolite Autophagy |
| In Vitro | Tetrahydrocurcumin (THC) has a number of attractive properties not shared with Curcumin that may make it superior. Tetrahydrocurcumin inhibited lipoxygenase as low as 1 μM. Tetrahydrocurcumin is tested for its ability to inhibit CYP2C9, CYP3A4, CYP1A2 and CYP2D6. Tetrahydrocurcumin yields dose-dependent inhibition of CYP2C9, and to a lesser extent, CYP3A4. Tetrahydrocurcumin exhibits maximum inhibition of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 at 50 to 100 μM. Tetrahydrocurcumin does not show a consistent dose-response inhibition of CYP1A2 or CYP2D6 over the range of concentrations tested. In some cases, the percent inhibition exceeds 100%. The effect of Tetrahydrocurcumin on cancer cell viability is measured. Sup-T1 cells, T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma cells, are treated with Tetrahydrocurcumin to determine its ability to induce growth inhibition using an MTS assay, and the corresponding IC50 values are in the mid-to-high micromolar range[1]. |
| In Vivo | The serum Tetrahydrocurcumin (THC) concentration versus time curve shows that more than one absorption and distribution phase is present. Initially, a rapid absorption phase with an average Tmax of 6.8 μg/mL at 1 h is observed, followed by a short elimination phase. This is followed by two redistributions with two smaller Tetrahydrocurcumin maxima at 6 and 24 h. Both redistribution phases has similar maxima of about 1 μg/mL. The total amount of Tetrahydrocurcumin excrets unchanged in urine was up to 8 μg at 24 h[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Sup-T1 cells are cultured in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% FBS and 1% Penicillin/Streptomycin at 37°C and 5% CO22. 2×105 cells/mL are seeded in each well and Tetrahydrocurcumin, Curcumin and Calebin-A, at 0.1, 0.5, 1.0, 5.0, 10.0, 50.0 and 100.0 μM dissolved in DMSO, are added to their respective wells and incubated for 24, 48 and 72 h. The MTS reagent is added and incubated for 4 h. Absorbance is recorded at 490 nm in Synergy HT multi-well plate reader and Gen5 data analysis software[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats[1] Surgically-modified, exposed jugular vein-catheterized, adult male CD Sprague-Dawley rats (250–300 g) ared used. Each rat is placed in a separate metabolic cage and fasted for 12 h prior to dosing with free access to water. On the day of experiment, the animals (N=3) receive a single dose of Tetrahydrocurcumin by oral gavage (500 mg/kg) in a volume not exceeding 1 mL. Animals have free access to water pre- and post-dosing, and food is provided 2 hours post-dosing. A series of blood samples (0.3 mL) are collected at 0, 15 and 30 min, and 1, 2, 4, 6, 12, 24, 48 and 72 h post-dose. At 72 h after administration, the animals are euthanized and exsanguinated. Immediately after each blood collection time point (except the terminal point), the cannula is flushed with 0.3 mL of 0.9% saline to replenish the collected blood volume. The dead volume of the cannula is replaced with sterile heparin/50% dextrose catheter lock solution to maintain the patency of the cannula as advised in the technical sheet supplied with the animals from Charles River. Following centrifugation of blood samples at 15,000 rpm for 5 min, serum is collected and placed into 2 mL tubes at -20°C until further analysis. Urine samples are collected at 0, 2, 6, 12, 24, 48 and 72 h post-dose and placed in 15 mL tubes. The exact urine volume of each sample is recorded then stored at -20°C until further analysis[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 564.1±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 95-97ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C21H24O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 372.412 |
| Flash Point | 196.2±22.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 372.157288 |
| PSA | 96.22000 |
| LogP | 2.13 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.575 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| HS Code | 2914509090 |
| HS Code | 2914509090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2914509090 other ketones with other oxygen function VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:5.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Structure-activity relationship analysis of curcumin analogues on anti-influenza virus activity.
FEBS J. 280(22) , 5829-40, (2013) Curcumin (Cur) is a commonly used colouring agent and spice in food. Previously, we reported that Cur inhibits type A influenza virus (IAV) infection by interfering with viral haemagglutination (HA) a... |
|
|
Differential cellular uptake and metabolism of curcuminoids in monocytes/macrophages: regulatory effects on lipid accumulation.
Br. J. Nutr. 112(1) , 8-14, (2014) We have previously shown that curcumin (CUR) may increase lipid accumulation in cultured human acute monocytic leukaemia cell line THP-1 monocytes/macrophages, but that tetrahydrocurcumin (THC), an in... |
|
|
Synthesis of quinoline derivatives of tetrahydrocurcumin and zingerone and evaluation of their antioxidant and antibacterial attributes.
Food Chem. 136(2) , 650-8, (2013) Tetrahydrocurcumin (THC, 1) and zingerone (2) are biologically active molecules originating from the important spices turmeric and ginger, respectively. Novel quinoline derivatives of THC and zingeron... |
| 1OR BQ E2V1V2R DQ CO1 |
| 1,7-Bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)heptane-3,5-dione |
| 3,5-Heptanedione, 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)- |
| 1,7-Bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-3,5-heptanedione |
| Tetrahydro Curcumin |
| Tetrahydrocurcumin |
 CAS#:458-37-7
CAS#:458-37-7 CAS#:121-33-5
CAS#:121-33-5 CAS#:123-54-6
CAS#:123-54-6 CAS#:36062-05-2
CAS#:36062-05-2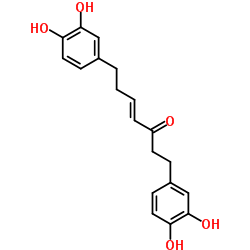 CAS#:41137-87-5
CAS#:41137-87-5
