MPP+ iodide
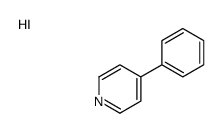
MPP+ iodide structure
|
Common Name | MPP+ iodide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 36913-39-0 | Molecular Weight | 283.10800 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H10IN | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of MPP+ iodideMPP+ iodide, a toxic metabolite of the neurotoxin MPTP, causes symptom of Parkinson's disease in animal models by selectively destroying dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra. MPP+ iodide is taken up by the dopamine transporter into dopaminergic neurons where it exerts its neurotoxic action on mitochondria by affecting complex I of the respiratory chain. MPP+ iodide is also a high affinity substrate for the serotonin transporter (SERT)[1][2]. |
| Name | 1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium iodide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | MPP+ iodide, a toxic metabolite of the neurotoxin MPTP, causes symptom of Parkinson's disease in animal models by selectively destroying dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra. MPP+ iodide is taken up by the dopamine transporter into dopaminergic neurons where it exerts its neurotoxic action on mitochondria by affecting complex I of the respiratory chain. MPP+ iodide is also a high affinity substrate for the serotonin transporter (SERT)[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | MPP+ (1-3 mM; 24 hours) remarkably decreases the viability of cells[1]. MPP+ also inhibits the activity of nicotinamide adenosine dinucleotide (NADH)-linked respiration in mitochondrial preparations and impairs aerobic glycolysis, leading to the present belief that the inhibition of NADH-linked cell respiration may constitute the final molecular mechanism of MPP+ neurotoxicity[3]. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Line: SH-SY5Y cells Concentration: 1, 2, 3 mM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: SH-SY5Y cells were treated with MPP+, mimicking the progress of dopaminergic neurons loss in PD; Reduced cell viability in both dose-dependent (1, 2, 3 mM for 24 h) and time dependent (1 mM) manner. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C11H10IN |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 283.10800 |
| Exact Mass | 282.98600 |
| PSA | 12.89000 |
| LogP | 3.74680 |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 + H311 + H331-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P301 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338-P311 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T+ |
| Risk Phrases | 23/24/25-36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36-45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 2 |
| RTECS | UU6580000 |
| HS Code | 2933399090 |
| HS Code | 2933399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933399090. other compounds containing an unfused pyridine ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
A new dopaminergic nigro-olfactory projection.
Acta Neuropathol. 130 , 333-48, (2015) Parkinson disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by massive loss of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Whereas onset of motor impairments reflects a rather advanced stage of the disord... |
|
|
The contribution of human OCT1, OCT3, and CYP3A4 to nitidine chloride-induced hepatocellular toxicity.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 42(7) , 1227-34, (2014) Nitidine chloride (NC), a quaternary ammonium alkaloid, has numerous pharmacological effects, such as anticancer activity. However, it was found that NC also has hepatocellular toxicity. Because organ... |
|
|
Nucleoside transporters and human organic cation transporter 1 determine the cellular handling of DNA-methyltransferase inhibitors.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 171(16) , 3868-80, (2014) Inhibitors of DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), such as azacytidine, decitabine and zebularine, are used for the epigenetic treatment of cancer. Their action may depend upon their translocation across t... |
| MFCD00055096 |
 CAS#:28289-54-5
CAS#:28289-54-5 CAS#:939-23-1
CAS#:939-23-1 CAS#:2065-66-9
CAS#:2065-66-9 CAS#:127382-80-3
CAS#:127382-80-3 CAS#:127382-75-6
CAS#:127382-75-6