capsaicin
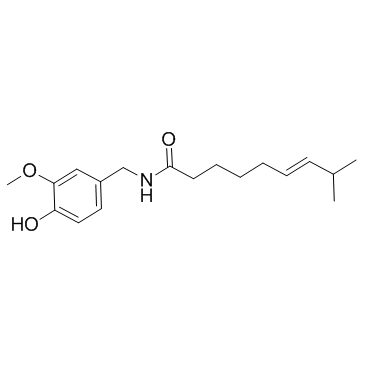
capsaicin structure
|
Common Name | capsaicin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 404-86-4 | Molecular Weight | 305.412 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 469.7±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H27NO3 | Melting Point | 62-65 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 237.9±31.5 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of capsaicinCapsaicin is a TRPV1 agonist with an EC50 of 0.29 μM in HEK293 cells. |
| Name | capsaicin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Capsaicin is a TRPV1 agonist with an EC50 of 0.29 μM in HEK293 cells. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
EC50: 290 nM (hTRPV1, in HEK293 cell)[1] |
| In Vitro | Capsaicin is an agonist of transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 (TRPV1), which is expressed in nociceptive sensory neurons and a range of secretory epithelia, including salivary glands. Capsaicin activates TRPV1, which modulates the permeability of tight junctions (TJ) by regulating the expression and function of putative intercellular adhesion molecules in an ERK-dependent manner[2]. Capsaicin is found to inhibit the growth and proliferation of FaDu cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Cells treated with 50, 100, 200, and 300 µM Capsaicin show an augmented decrease in cell growth as the Capsaicin dose increases. In addition, the percentage of viable cells decreases as the incubation time increases. The observed IC50 value is around 150 µM[3]. |
| In Vivo | Capsaicin (CAP)-treated animals (Group IV) show increased DNA fragmentation suggesting apoptosis when compare with B(a)P-induced lung cancer-bearing animals (Group II) that show reduced DNA fragmentation. CAP-treated Group IV animals show markedly increased expressions of p53, Bax and caspase-3 with remarkable decrease in the levels of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2, when compare with B(a)P-administered lung cancer animals of Group II[4]. Capsaicin causes a dose-dependent reduction of tear secretion in female Wistar/ST rats. Significant effects are observed at doses of 20, 50 and 100 mg/kg. In addition, Capsaicin also causes corneal lesions, and significant effects are observed at doses of 50 and 100 mg/kg[5]. |
| Cell Assay | FaDu cells are plated at a density of 1×105 cells/well on 24-well plate. After overnight growth, the cells are treated with various concentrations of Capsaicin (0 μM, 50 μM, 100 μM, 150 μM, 200 μM, 250 μM, 300 μM, and 350 μM) for 24, 48 and 72 hours, with medium replacement every 24 hours. At the end of treatment, 30 µL of the tetrazolium compound MTT, and 270 µL of fresh medium are added. After further incubation for 4 hours at 37°C, 200 µL of 0.1 N HCl in 10% SDS is added into each well to dissolve the tetrazolium crystals. Finally, the absorbance at a wavelength of 540 nm is recorded using an ELISA plate reader[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[4] Healthy male Swiss albino mice weighing 20-25 g (8-10 weeks old) are divided into four groups of six mice each as follows. Group I: control animals receive olive oil throughout the course of the experiment. Group II: animals are administered with Benzo(a)pyrene (B(a)P) (50 mg/kg body weight dissolved in olive oil) orally twice a week for four successive weeks. Group III: animals receive Capsaicin alone (10 mg/kg body weight dissolved in olive oil) intraperitoneally once in a week for 14 weeks to assess the cytotoxicity (if any) induced by Capsaicin. Group IV: animals receive B(a)P (as in Group II) along with Capsaicin (10 mg/kg b.wt dissolves in olive oil) intraperitoneally. Capsaicin treatment is started one week prior to the first dose of B(a)P administration and continued for 14 weeks. Rats[5] Female Wistar/ST rats, 4 d of age, are used. On postnatal day 4, rats are given a single subcutaneous injection of Capsaicin at a dose of 50 mg/kg (or 20 and 100 mg/kg for the dose-response test) dissolved in physiological saline containing 10% ethanol and 10% Tween 80. Vehicle-treated rats receive the vehicle solution alone. The injected rats are housed with their mothers, who are fed standard rat chow and maintained under normal conditions. At 4 weeks of age, the injected rats are separated and housed in cages, and maintained under normal conditions until the initiation of experiments. |
| References |
[2]. Shin YH, et al. The Effect of Capsaicin on Salivary Gland Dysfunction. Molecules. 2016 Jun 25;21(7). |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 469.7±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 62-65 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C18H27NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 305.412 |
| Flash Point | 237.9±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 305.199097 |
| PSA | 58.56000 |
| LogP | 4.27 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.508 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H315-H317-H319-H334-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P301 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338-P342 + P311 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic |
| Risk Phrases | R25;R37/38;R41;R42/43 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S26-S28-S36/39-S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | RA8530000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 4 | |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924299090. other cyclic amides (including cyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Unbiased classification of sensory neuron types by large-scale single-cell RNA sequencing.
Nat. Neurosci. 18(1) , 145-53, (2015) The primary sensory system requires the integrated function of multiple cell types, although its full complexity remains unclear. We used comprehensive transcriptome analysis of 622 single mouse neuro... |
|
|
TCF4 Is a Molecular Target of Resveratrol in the Prevention of Colorectal Cancer.
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16 , 10411-25, (2015) The Wnt/β-catenin pathway plays an essential role in the tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer. T-cell factor-4 (TCF4) is a member of the TCF/LEF (lymphoid enhancer factor) family of transcription factor... |
|
|
Pituitary Adenylate Cyclase-Activating Polypeptide Is Upregulated in Murine Skin Inflammation and Mediates Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid-1-Induced Neurogenic Edema.
J. Invest. Dermatol. 135 , 2209-18, (2015) Although pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) was described as a key vasoregulator in human skin, little is known about its expression in mouse skin. As it is important to invest... |
| (E)-Capsaicin |
| 8-Methyl-N-vanillyl-trans-6-nonenamide |
| (E)-8-Methyl-N-vanillyl-6-nonenamide |
| (6E)-N-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)-8-methyl-6-nonenamide |
| (E)-N-((4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl)-8-methyl-6-nonenamide |
| MFCD00017259 |
| CAPSAICINE |
| Zostrix |
| trans-Capsaicin |
| Qutenza |
| (E)-N-[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-8-methylnon-6-enamide |
| 8-Methyl-N-vanillyl-6-nonenamide |
| 6-Nonenamide, N-((4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl)-8-methyl-, (E)- |
| capsaicin |
| (E)-N-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)-8-methylnon-6-enamide |
| 6-Nonenimidic acid, N-[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-8-methyl-, (1Z,6E)- |
| Transacin |
| Capsaicin (Natural) |
| trans-8-methyl-n-vanillyl-6-nonenamide |
| (6E)-N-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)-8-methylnon-6-enamide |
| N-vanillyl-8-methyl-non-6-enamide |
| (1Z,6E)-N-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)-8-methyl-6-nonenimidic acid |
| Styptysat |
| N-[(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-8-methyl-6-nonenamide |
| Axsain |
| Capsidol |
| 6-Nonenamide, N-[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-8-methyl-, (6E)- |
| 8-Methyl-N-vanillyl-trans-6-nonenamide,Capsaicin |
| 8-Methyl-N-vanillyl-6-nonenamide, (E)- |
| 8-methyl N-vanillyl-6-nonenamide |
| EINECS 206-969-8 |
| Capsaicin, (6E)- |
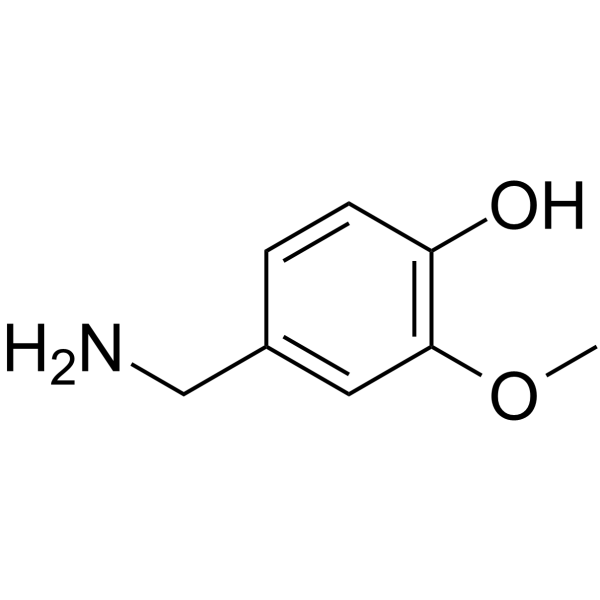 CAS#:1196-92-5
CAS#:1196-92-5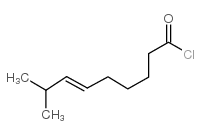 CAS#:95636-02-5
CAS#:95636-02-5 CAS#:59320-77-3
CAS#:59320-77-3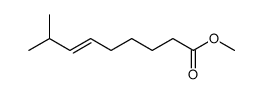 CAS#:112375-54-9
CAS#:112375-54-9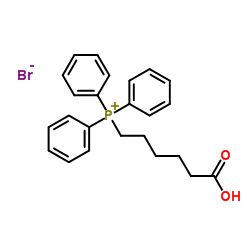 CAS#:50889-29-7
CAS#:50889-29-7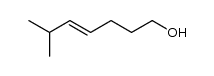 CAS#:59721-82-3
CAS#:59721-82-3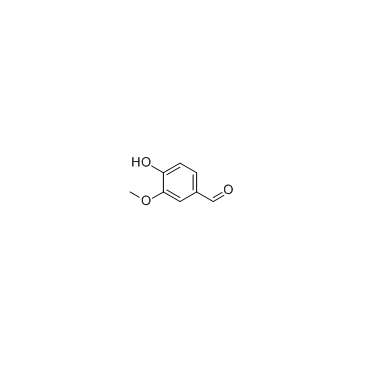 CAS#:121-33-5
CAS#:121-33-5 CAS#:31467-60-4
CAS#:31467-60-4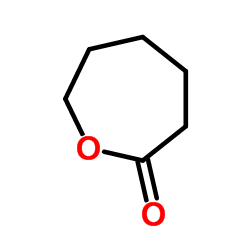 CAS#:502-44-3
CAS#:502-44-3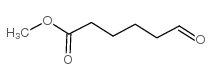 CAS#:6654-36-0
CAS#:6654-36-0 CAS#:19408-84-5
CAS#:19408-84-5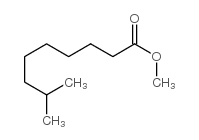 CAS#:5129-54-4
CAS#:5129-54-4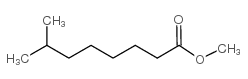 CAS#:5129-53-3
CAS#:5129-53-3
