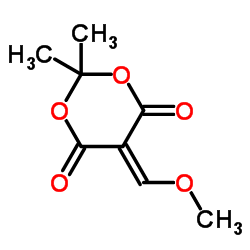
Flumequine
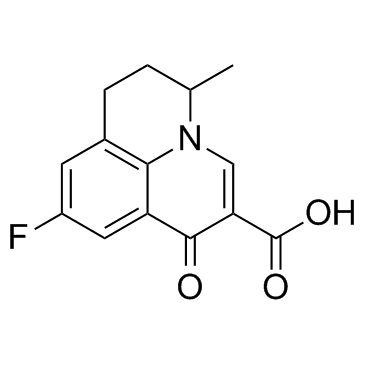
Flumequine structure
|
Common Name | Flumequine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 42835-25-6 | Molecular Weight | 261.248 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 439.7±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H12FNO3 | Melting Point | 253-255°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 219.7±28.7 °C | |
Use of FlumequineFlumequine is a quinolone antibiotic, and acts as a topoisomerase II inhibitor, with an IC50 of 15 μM (3.92 μg/mL). |
| Name | Flumequine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Flumequine is a quinolone antibiotic, and acts as a topoisomerase II inhibitor, with an IC50 of 15 μM (3.92 μg/mL). |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Topoisomerase II:15 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Flumequine is a topoisomerase II inhibitor, with an IC50 of 3.92 μg/mL, and less potently inhibits Gyrase, with an IC50 of 1764 μg/mL. Flumequine (0-625 μg/mL) increases migration of nuclear DNA from CHL cells[1]. Flumequine inhibits Spanish field isolates of B. hyodysenteriae with MIC50 and MIC90 of 50 and 100 μg/mL, and MBC50 and MBC90 of 50, 200 μg/mL, respectively[2]. Flumequine suppresses A. salmonicida isolates with MIC ranging from 0.06 to 32 μg/mL[3]. |
| In Vivo | Flumequine (0-500 mg/kg, p.o.) causes dose-related DNA damage in the stomach, colon, and urinary bladder of mice, 1 and 3 h but not 24 h after its administration[1]. |
| Kinase Assay | Twenty μL of reaction mixture containing 0.4 μg of kinetoplast DNA with 1 U of topoisomerase II and serial dilutions of each antibacterial agent (including Flumequine) are incubated for 5 min at 37°C in buffer containing 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 120 mM KCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM ATP, 0.5 mM dithiothreitol, and 30 μg/mL of bovine serum albumin. After stopping the reaction by adding sarcosyl with gel-loading buffer, catenated and decatenated kDNAs are separated by agarose gel electrophoresis. The gels are stained with ethidium bromide and photographed using UV light (302 nm) with a Gel Print 200i/VGA, and the brightness of bands is traced with an Image Analyzer. Each band is quantified and the amount of DNA treated with each concentration of quinolone is measured to determine the 50% inhibitory concentration against DNA gyrase and topoisomerase II[1]. |
| Cell Assay | The Chinese hamster lung cell line CHL/IU is routinely maintained in monolayer culture in Dulbecco's modified MEM medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37°C under a 5% CO2 atmosphere. Exponentially growing cells are treated with Flumequine dissolved in DMSO for 1 h. The dose range is chosen in order to obtain both damaged and highly damaged cells. Following Flumequine treatment, cells are embedded in GP42 agarose dissolved in saline at 1%. Cell number and cell viability are determined for each dose[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Infant and young-adult male ddY mice at 4 and 7 weeks of age, respectively, are used after 1 week of acclimatization. Groups are treated once orally with Flumequine at <500 mg/kg. Adult mice are sacrificed at 3 and 24 h after treatment, and 8 organs, the stomach, colon, liver, kidney, urinary bladder, lung, brain, and bone marrow, are removed. Infant mice are sacrificed 3 and 24 h after treatment, and the livers are excised. In another study, the genotoxicity of Flumequine is studied in the regenerating liver of adult mice. For this purpose, male mice at 8 weeks-of-age are anesthetized with ether and 3 major lobes of the liver, left lateral lobe, left medial lobe, and right lateral lobe, are removed. Four days after the hepatectomy, mice are subjected to oral administration of Flumequine once. They are sacrificed 3 h after FL-treatment and regenerated livers are sampled. Slides for the comet assay are prepared at each set time[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 439.7±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 253-255°C |
| Molecular Formula | C14H12FNO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 261.248 |
| Flash Point | 219.7±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 261.080109 |
| PSA | 59.30000 |
| LogP | 2.41 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.646 |
| Storage condition | 0-6°C |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|
~% 
Flumequine CAS#:42835-25-6 |
| Literature: Minnesota Mining and Manufacturing Company Patent: US4301289 A1, 1981 ; Title/Abstract Full Text Show Details Minnesota Mining and Manufacturing Company Patent: US4301291 A1, 1981 ; |
|
~% 
Flumequine CAS#:42835-25-6 |
| Literature: S P A SOCIETA' PRODOTTI ANTIBIOTICI S.p.a. Patent: EP310849 A1, 1989 ; |
|
~69% 
Flumequine CAS#:42835-25-6 |
| Literature: Balint, Jozsef; Egri, Gabriella; Fogassy, Elemer; Boecskei, Zsolt; Simon, Kalman; Gajary, Antal; Friesz, Antal Tetrahedron Asymmetry, 1999 , vol. 10, # 6 p. 1079 - 1087 |
|
~% 
Flumequine CAS#:42835-25-6 |
| Literature: S P A SOCIETA' PRODOTTI ANTIBIOTICI S.p.a. Patent: EP310849 A1, 1989 ; |
|
~% 
Flumequine CAS#:42835-25-6 |
| Literature: Balint, Jozsef; Egri, Gabriella; Fogassy, Elemer; Boecskei, Zsolt; Simon, Kalman; Gajary, Antal; Friesz, Antal Tetrahedron Asymmetry, 1999 , vol. 10, # 6 p. 1079 - 1087 |
|
~% 
Flumequine CAS#:42835-25-6 |
| Literature: Balint, Jozsef; Egri, Gabriella; Fogassy, Elemer; Boecskei, Zsolt; Simon, Kalman; Gajary, Antal; Friesz, Antal Tetrahedron Asymmetry, 1999 , vol. 10, # 6 p. 1079 - 1087 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Calculating virtual log P in the alkane/water system (log P(N)(alk)) and its derived parameters deltalog P(N)(oct-alk) and log D(pH)(alk).
J. Med. Chem. 48 , 3269-79, (2005) Growing interest in the use of both the logarithm of the partition coefficient of the neutral species in the alkane/water system (log P(N)(alk)) and the difference between log P(N)(oct) (the logarithm... |
|
|
QSAR-based solubility model for drug-like compounds.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 18 , 7078-84, (2010) Solubility plays a very important role in the selection of compounds for drug screening. In this context, a QSAR model was developed for predicting water solubility of drug-like compounds. First, a se... |
|
|
gyrA and parC Mutations and associated quinolone resistance in Vibrio anguillarum serotype O2b strains isolated from farmed Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) in Norway.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51 , 2597-9, (2007) MIC testing of Vibrio anguillarum isolates recovered from diseased farmed Atlantic cod revealed oxolinic acid MICs of < or =0.001, 0.06, and 16 microg ml(-1). Single gyrA Ser-Ile substitutions were id... |
| Apurone |
| UNII:UVG8VSP2SJ |
| Quinolone |
| 9-Fluoro-5-methyl-1-oxo-1,5,6,7-tetrahydropyrido[3,2,1-ij]quinoline-2-carboxylic acid |
| FLUMEQUIN |
| Flumeguine |
| EINECS 255-962-6 |
| 1H,5H-Benzo[ij]quinolizine-2-carboxylic acid, 9-fluoro-6,7-dihydro-5-methyl-1-oxo- |
| 9-Fluoro-5-methyl-1-oxo-6,7-dihydro-1H,5H-pyrido[3,2,1-ij]quinoline-2-carboxylic acid |
| MFCD00079298 |
| Imequyl |
| 9-Fluoro-1,5,6,7-tetrahydro-5-methyl-1-oxopyrido[3,2,1-ij]quinoline-2-carboxylic Acid |
| Flumural |
| Flumequine |
| Aoyribe |
| Fantacin |
| R 802 |

![5- [1-(6-fluoro-2-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolyl)] -methylene-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxan-4,6-dione structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/123/123400-74-8.png)
![9-fluoro-5-methyl-1-oxo-6,7-dihydro-1H,5H-pyrido[3,2,1-ij]quinoline-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/001/42835-47-2.png)