Boc-Gly-OH
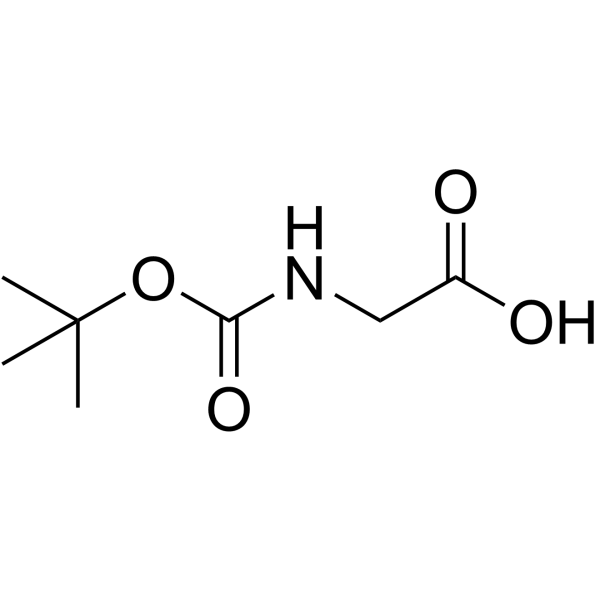
Boc-Gly-OH structure
|
Common Name | Boc-Gly-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4530-20-5 | Molecular Weight | 175.182 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 315.9±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H13NO4 | Melting Point | 86-89 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 144.9±23.2 °C | |
Use of Boc-Gly-OHBoc-Glycine is a Glycine (HY-Y0966) derivative[1]. |
| Name | t-Butoxycarbonylglycine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Boc-Glycine is a Glycine (HY-Y0966) derivative[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Amino acids and amino acid derivatives have been commercially used as ergogenic supplements. They influence the secretion of anabolic hormones, supply of fuel during exercise, mental performance during stress related tasks and prevent exercise induced muscle damage. They are recognized to be beneficial as ergogenic dietary substances[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 315.9±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 86-89 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C7H13NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 175.182 |
| Flash Point | 144.9±23.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 175.084457 |
| PSA | 75.63000 |
| LogP | 0.75 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.460 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R41 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39-S39 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924199090. other acyclic amides (including acyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
In situ fabrication of cleavable peptide arrays on polydimethylsiloxane and applications for kinase activity assays.
Anal. Chim. Acta 865 , 53-9, (2015) Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) is widely used for microfabrication and bioanalysis; however, its surface functionalization is limited due to the lack of active functional groups and incompatibility with ... |
|
|
Accumulation of cell-penetrating peptides in large unilamellar vesicles: A straightforward screening assay for investigating the internalization mechanism.
Biopolymers 104 , 533-43, (2015) The internalization of cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) into liposomes (large unilamellar vesicles, LUVs) was studied with a rapid and robust procedure based on the quenching of a small fluorescent pr... |
|
|
Optimization of the Ugi reaction using parallel synthesis and automated liquid handling.
J. Vis. Exp. (21) , doi:10.3791/942, (2008) The optimization of a Ugi reaction involving the mixing of furfurylamine, benzaldehyde, boc-glycine and t-butylisocyanide is described. Triplicate runs of 48 parallel experiments are reported, varying... |
| N-(tert-Butoxycarbonyl)glycin |
| Glycine, N-[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]- |
| Boc-glycine |
| N-Boc-protected glycine |
| n-boc-glycine |
| boc-gly |
| N-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)glycine |
| Boc-Gly-OH |
| MFCD00002690 |
| N-{[(2-Methyl-2-propanyl)oxy]carbonyl}glycine |
| N-Boc-L-glycine |
| 2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl)amino)acetic acid |
| ({[(2-Methyl-2-propanyl)oxy]carbonyl}amino)acetic acid |
| Glycine, N-carboxy-, N-tert-butyl ester |
| N-Boc glycine |
| EINECS 224-864-5 |
 CAS#:24424-99-5
CAS#:24424-99-5 CAS#:56-40-6
CAS#:56-40-6 CAS#:17790-86-2
CAS#:17790-86-2 CAS#:98015-52-2
CAS#:98015-52-2 CAS#:31954-27-5
CAS#:31954-27-5 CAS#:1080004-01-8
CAS#:1080004-01-8 CAS#:58632-95-4
CAS#:58632-95-4 CAS#:130384-98-4
CAS#:130384-98-4 CAS#:3303-34-2
CAS#:3303-34-2 CAS#:34306-42-8
CAS#:34306-42-8 CAS#:33507-63-0
CAS#:33507-63-0 CAS#:35150-09-5
CAS#:35150-09-5![[Nle11]-Substance P structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/019/57462-42-7.png) CAS#:57462-42-7
CAS#:57462-42-7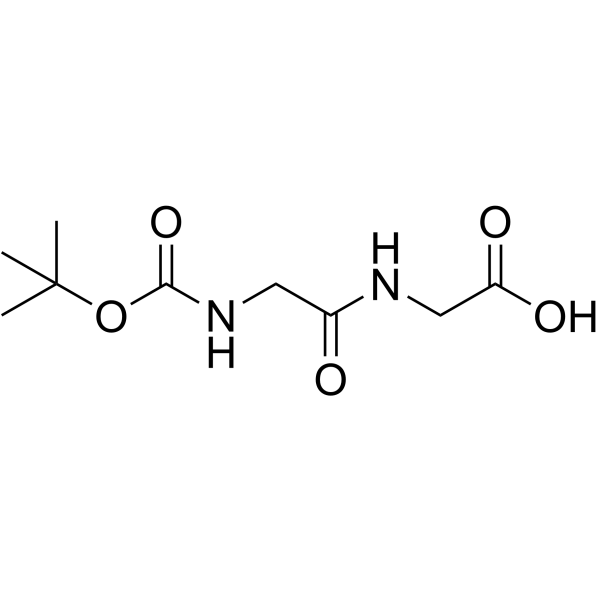 CAS#:31972-52-8
CAS#:31972-52-8 CAS#:39968-33-7
CAS#:39968-33-7![N-[4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)phenyl]-2-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)acetamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/244/880545-43-7.png) CAS#:880545-43-7
CAS#:880545-43-7![tert-butyl N-[3-[methoxy(methyl)amino]-3-oxopropyl]carbamate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/425/142570-56-7.png) CAS#:142570-56-7
CAS#:142570-56-7
