Cineole
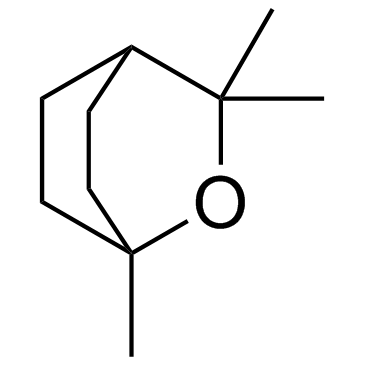
Cineole structure
|
Common Name | Cineole | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 470-82-6 | Molecular Weight | 154.249 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 174.0±8.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H18O | Melting Point | 1.5ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 50.9±15.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS02 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of CineoleEucalyptol is an inhibitor of 5-HT3 receptor ,potassium channel, TNF-α and IL-1β. |
| Name | 1,8-cineole |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Eucalyptol is an inhibitor of 5-HT3 receptor ,potassium channel, TNF-α and IL-1β. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
5-HT3 Receptor IL-1β TNF-α potassium channel |
| In Vitro | Eucalyptol inhibits 5-HT-evoked currents in oocytes expressing 5-HT3 receptors with an IC50 of 258 µM[1]. Eucalyptol (Cin) treatment significantly decreases the ROS level in Aβ25-35 treated cells in a dose dependent manner. Eucalyptol treatment significantly decreases the NO level in Aβ25-35 treated cells in a dose dependent manner (p<0.05 and p<0.01). Eucalyptol treatment also significantly decreases IL-1βlevel in Aβ25-35 treated cells in a dose dependent manner (p<0.05 and p<0.01) as compare to Aβ25-35 treated PC12 cells. IL-6 level is also attenuated by Eucalyptol in dose dependent manner (p<0.05 and p<0.01) as compare to Aβ25-35 treated cells[3]. |
| In Vivo | Results show that male and female rats treated with Eucalyptol (CIN) at the highest doses, 500 and 1000 mg/kg, have shown lower body weight than control group from the 7th to 50th day of treatment. The administration of Eucalyptol significantly reduces body weight gain of male rats (Eucalyptol 500 and 1000 mg/kg) and female rats (Eucalyptol 1000 mg/kg) in the first week of treatment. However, this reduction is followed by an increase in body weight of rats males and females treated with all doses of the second week until the end of treatment. For male rats, there is a significant increase of 6.93% in mean corpuscular volume (MCV) (Eucalyptol 1000 mg/kg) and of 43.54 and 38.98% in the platelet count (Eucalyptol 500 and 1000 mg/kg, respectively) and a decrease of 6.74 and 6.67% in mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) (Eucalyptol 500 and 1000 mg/kg) and mean platelet volume (MPV) of 10.40, 10.60 and 15.73% (Eucalyptol 100, 500 and 1000 mg/kg, respectively), when compare to the control group[4]. |
| Cell Assay | The protective dose of Eucalyptol (Cineole) is determined by MTT dye-uptake method. In brief, cells (1×104 per well) are seeded in 96-well tissue culture plates and allowed to adhere for 24 h in CO2 incubator at 37°C. Cells are differentiated for the indicated time period. Thereafter, the medium is replaced with the medium containing Eucalyptol (0 to 10 μM) in different experiments for a period up to 24 h. Tetrazolium bromide salt (5 mg/mL of stock in PBS) 10 μL/well is added in 100 mL of cell suspension and plate is incubated for 4 h. At the end of incubation period, the reaction mixture is carefully taken out and 200 μL of DMSO is added to each well by pipetting up and down several times until the content gets homogenized. The plates are kept on rocker shaker for 10 min at room temperature and then read at 550 nm using microplate reader[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Swiss mice are used in this experiment. The animals are randomly divided into two groups (n=5) and fasted overnight with free access to water. The group control receives a 1% Tween-80 aqueous solution (0.1 mL/10 g) and the other group is treated with Eucalyptol a single 2000 mg/kg dose by oral route. The animals are observed at 30, 60, 120, 180 and 240 min after oral treatment and daily for 14 days. Behavioral changes, weight, food and water consumption, clinical signs of toxicity or mortality are recorded daily[4]. |
| References |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 174.0±8.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 1.5ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C10H18O |
| Molecular Weight | 154.249 |
| Flash Point | 50.9±15.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 154.135757 |
| PSA | 9.23000 |
| LogP | 2.82 |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.6±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.461 |
| Stability | Stable. Flammable. Incompatible with acids, bases, strong oxidizing agents. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS02 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H226 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P370 + P378 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R10;R37/38;R41 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S39 |
| RIDADR | UN 1993 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | OS9275000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 3.0 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
|
Combined effects of drying methods, extract concentration, and film thickness on efficacy of antimicrobial chitosan films.
J. Food Sci. 79(6) , E1150-8, (2014) An idea of using a suitable drying method to minimize the loss of added antimicrobial agent and, at the same time, to modify the structure, and hence the release characteristics of chitosan films was ... |
|
|
Identification of odorants in frankincense (Boswellia sacra Flueck.) by aroma extract dilution analysis and two-dimensional gas chromatography-mass spectrometry/olfactometry.
Phytochemistry 109 , 66-75, (2014) Frankincense has been known, traded and used throughout the ages for its exceptional aroma properties, and is still commonly used in both secular and religious settings to convey a pleasant odor. Surp... |
|
|
Identification of olfactory receptor neurons in Uraba lugens (Lepidoptera: Nolidae) and its implications for host range.
J. Insect Physiol. 78 , 33-46, (2015) Phytophagous insects detect volatile compounds produced by host and non-host plants, using species-specific sets of olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs). To investigate the relationship between the range... |
| 2-Oxa-1,3,3-trimethylbicyclo(2.2.2)octane |
| eucalyptol (cineole) |
| Terpan |
| 2-Oxabicyclo[2.2.2]octane, 1,3,3-trimethyl- |
| 2,2,4-trimethyl-3-oxabicyclo[2.2.2]octane |
| Eucapur |
| Zineol |
| Eukalyptol [Czech] |
| p-Menthane, 1,8-epoxy- |
| Eucalyptol |
| Eucalyptole |
| MFCD00167977 |
| 1,8-Cineol |
| 1,3,3-Trimethyl-2-oxabicyclo[2.2.2]octane,1,8-Cineole,1,8-Epoxy-p-menthane |
| EINECS 207-431-5 |
| 1,3,3-Trimethyl-2-oxabicyclo(2.2.2)octane |
| cineole |
| Cajeputol |
| 1,3,3-Trimethyl-2-oxabicyclo[2.2.2]octane |
| 1,8-cineole |
| 1,8-Epoxy-p-menthane |
| limonene oxide |
| p-Cineole |
![2,2,4-trimethyl-5-phenylselanyl-3-oxabicyclo[2.2.2]octane Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/288/92691-96-8.png) CAS#:92691-96-8
CAS#:92691-96-8 CAS#:71208-23-6
CAS#:71208-23-6 CAS#:107553-94-6
CAS#:107553-94-6 CAS#:917-64-6
CAS#:917-64-6 CAS#:43103-57-7
CAS#:43103-57-7 CAS#:99-86-5
CAS#:99-86-5 CAS#:98-55-5
CAS#:98-55-5 CAS#:203719-53-3
CAS#:203719-53-3 CAS#:2451-01-6
CAS#:2451-01-6![1,5-Dimethyl-8-oxatricyclo[3.2.1.02.7]octan-6-one Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/016/107553-95-7.png) CAS#:107553-95-7
CAS#:107553-95-7 CAS#:107149-16-6
CAS#:107149-16-6 CAS#:491-09-8
CAS#:491-09-8 CAS#:494-90-6
CAS#:494-90-6![1-Isopropyl-4-methyl-7-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/319/470-67-7.png) CAS#:470-67-7
CAS#:470-67-7 CAS#:108-38-3
CAS#:108-38-3 CAS#:138-86-3
CAS#:138-86-3 CAS#:138-87-4
CAS#:138-87-4 CAS#:67-64-1
CAS#:67-64-1 CAS#:108-88-3
CAS#:108-88-3
