Niranthin
Modify Date: 2024-01-11 19:36:19
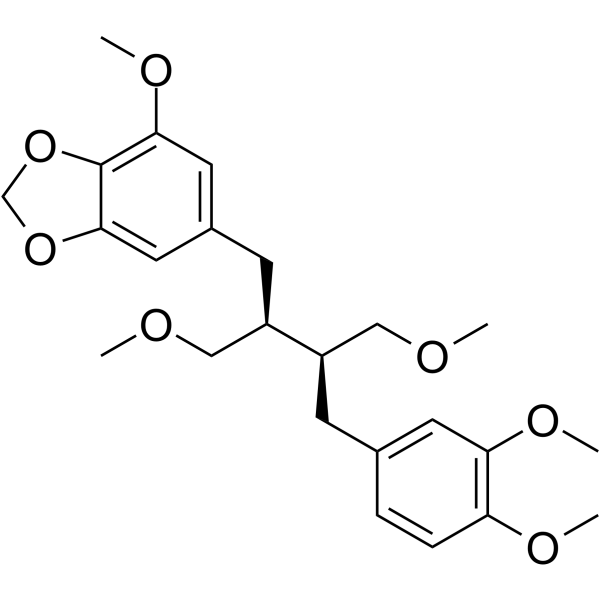
Niranthin structure
|
Common Name | Niranthin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 50656-77-4 | Molecular Weight | 432.507 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 559.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C24H32O7 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 221.8±30.0 °C | |
Use of NiranthinNiranthin, a lignan with a wide spectrum of pharmacological activities. Niranthin is a potent and non-competitive inhibitor of heterodimeric type IB topoisomerase of L. donovani. Niranthin can be used for the research of drug-resistant leishmaniasis treatment[1]. |
| Name | Niranthin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Niranthin, a lignan with a wide spectrum of pharmacological activities. Niranthin is a potent and non-competitive inhibitor of heterodimeric type IB topoisomerase of L. donovani. Niranthin can be used for the research of drug-resistant leishmaniasis treatment[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Topoisomerase |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 559.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C24H32O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 432.507 |
| Flash Point | 221.8±30.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 432.214813 |
| PSA | 64.61000 |
| LogP | 4.40 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.534 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
| 1,3-Benzodioxole, 6-[(2R,3R)-4-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2,3-bis(methoxymethyl)butyl]-4-methoxy- |
| 6-[(2R,3R)-3-(3,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)-4-methoxy-2-(methoxymethyl)butyl]-4-methoxy-1,3-benzodioxole |

