1,5-Isoquinolinediol
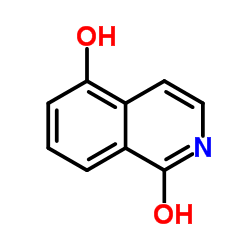
1,5-Isoquinolinediol structure
|
Common Name | 1,5-Isoquinolinediol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 5154-02-9 | Molecular Weight | 161.157 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 501.1±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H7NO2 | Melting Point | 270-275 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 256.8±24.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 1,5-Isoquinolinediol1,5-Isoquinolinediol is a potent PARP inhibitor, with an IC50 of 0.18-0.37 µM. 1,5-Isoquinolinediol attenuates diabetes-induced NADPH oxidase-derived oxidative stress in retina[1][2]. |
| Name | isoquinoline-1,5-diol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 1,5-Isoquinolinediol is a potent PARP inhibitor, with an IC50 of 0.18-0.37 µM. 1,5-Isoquinolinediol attenuates diabetes-induced NADPH oxidase-derived oxidative stress in retina[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
PARP:0.18-0.37 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | 1,5-isoquinolinediol leads to an increase up to 8-fold in the absolute frequency of gene targeting in the correction of the mutation at the stable integrated HSV tk gene[1]. 1,5-Isoquinolinediol is a potent PARP antagonist and decreases cleaved PARP in diabetic retina.1,5-Isoquinolinediol (500 μM H2O2; 24 hours) attenuates H2O2-induced upregulation of cleaved PARP-1 expression in retinal Muller cells. 1,5-Isoquinolinediol attenuates diabetes-induced upregulation of retinal nitrated protein expression. 1,5-Isoquinolinediol attenuates diabetes-induced activation of NADPH oxidase in the retina[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 501.1±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 270-275 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C9H7NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 161.157 |
| Flash Point | 256.8±24.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 161.047684 |
| PSA | 53.35000 |
| LogP | -0.17 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.743 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: >36 mg/mL |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2933499090 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 3 | |
| HS Code | 2933499090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933499090. other compounds containing in the structure a quinoline or isoquinoline ring-system (whether or not hydrogenated), not further fused. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Inhibitors of poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase protect rat cardiomyocytes against oxidant stress.
Cardiovasc. Res. 41(1) , 126-34, (1999) Inhibitors of poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase (PARS) activity reduce the infarct size caused by regional myocardial ischaemia and reperfusion in the rabbit and rat in vivo. The mechanism of action of the... |
|
|
Prevention of the degeneration of human dopaminergic neurons in an astrocyte co-culture system allowing endogenous drug metabolism.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 172 , 4119-32, (2015) Few neuropharmacological model systems use human neurons. Moreover, available test systems rarely reflect functional roles of co-cultured glial cells. There is no human in vitro counterpart of the wid... |
|
|
Modulation of the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor response and DNA recombination in breast cancer cells by drugs affecting endogenous wild-type p53.
Carcinogenesis 35(10) , 2273-82, (2014) Synthetic lethal interactions between poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) and homologous recombination (HR) repair pathways have been exploited for the development of novel mono- and combination cance... |
| isoquinoline-1,5-diol |
| 5-Hydroxyisocarbostyril |
| 5-Hydroxy-1(2H)-isoquinolinone |
| 5-Hydroxyisoquinoline-1(2H)-one |
| 1(2H)-Isoquinolinone, 5-hydroxy- |
| 1,5-Dihydroxyisoquinoline 5-Hydroxy-1(2H)-isoquinolinone DiQ |
| 5-hydroxy-2H-isoquinolin-1-one |
| MFCD00006900 |
| 5-Hydroxyisoquinolin-1(2H)-one |
| 1,5-Isoquinolinediol |
 CAS#:56469-02-4
CAS#:56469-02-4 CAS#:762236-09-9
CAS#:762236-09-9 CAS#:129075-87-2
CAS#:129075-87-2