Flufenamic Acid
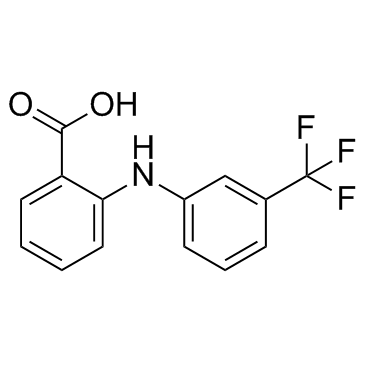
Flufenamic Acid structure
|
Common Name | Flufenamic Acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 530-78-9 | Molecular Weight | 281.230 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 373.9±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H10F3NO2 | Melting Point | 132-135 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 179.9±27.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Flufenamic AcidFlufenamic acid is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent, inhibits cyclooxygenase (COX), activates AMPK, and also modulates ion channels, blocking chloride channels and L-type Ca2+ channels, modulating non-selective cation channels (NSC), activating K+ channels. |
| Name | flufenamic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Flufenamic acid is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent, inhibits cyclooxygenase (COX), activates AMPK, and also modulates ion channels, blocking chloride channels and L-type Ca2+ channels, modulating non-selective cation channels (NSC), activating K+ channels. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
COX, Chloride Channel, Calcium Channel, Potassium Channel[1], AMPK[2] |
| In Vitro | Flufenamic acid is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent, inhibits cyclooxygenase (COX), and also modulates ion channels, blocking chloride channels and L-type Ca2+ channels, modulating non-selective cation channels (NSC), activating K+ channels. Flufenamic acid inhibits a wide spectrum of TRP channels, including: C3, C7, M2, M3, M4, M5, M7, M8, V1, V3, and V4 but activates at least two TRP channels (C6 and A1)[1]. Flufenamic acid induces AMPK activation in T84 cells, and such an effect is via a direct stimulation of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase beta (CaMKKβ) activity[2]. Moreover, Flufenamic acid (FFA; 5-50 μM) dose-dependently inhibits cAMP-dependent Cl- secretion in intact T84 cells, suppresses CFTR-mediated apical ICl-, and blocks the Ca2+-dependent Cl- secretion in a dose-dependent manner with IC50 of appr 10 μM and near complete inhibition at 100 μM in T84 cell monolayers, but shows no effect on Na+-K+ ATPase or NKCC in T84 cells[3]. |
| In Vivo | Flufenamic acid (50 mg/kg, i.p.) has anti-inflammatory effect in a mouse model of Vibrio cholerae El Tor variant (EL)-induced diarrhea and significantly abrogates EL-induced intestinal fluid secretion and barrier disruption at 20 mg/kg. Furthermore, Flufenamic acid suppresses NF-κB nuclear translocation and expression of proinflammatory mediators and promotes AMPK phosphorylation in the EL-infected mouse intestine[2]. |
| Cell Assay | In brief, apical and basolateral chambers are filled symmetrically with Kreb's solutions. Thereafter, DMSO or Flufenamic acid is added into the basolateral chamber followed by apical membrane permealization by amphotericin B. After the amphotericin B-elicited Isc is stabilized, ouabain is added into the basolateral chamber. The ouabain sensitive Isc is used as an indicator of Na+-K+ ATPase activity[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats[2] Six-week-old male ICR outbred mice (weight 30-35 g) are fasted for 24 h before anesthesia using an intraperitoneal injection of nembutal (60 mg/kg). Following abdominal incision, the ileum is ligated (appr 3-4 cm long) and inoculated with 100 µL of PBS or PBS containing V. cholerae (105 CFU/loop) with or without a concomitant intraperitoneal injection of Flufenamic acid or metformin. Twelve hours post-inoculation, ileal loops are removed for weight/length ratio measurement, biochemical analysis and ultrastructural evaluation[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 373.9±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 132-135 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C14H10F3NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 281.230 |
| Flash Point | 179.9±27.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 281.066376 |
| PSA | 49.33000 |
| LogP | 5.62 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.585 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
| Water Solubility | 0.0265 g/L (37 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H315-H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | CB4375000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 5 | |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2922499990 other amino-acids, other than those containing more than one kind of oxygen function, and their esters; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Purinergic signaling via P2Y receptors up-mediates IL-6 production by liver macrophages/Kupffer cells.
J. Toxicol. Sci. 39(3) , 413-23, (2014) Resident macrophages in the liver (Kupffer cells) produce various cytokines and chemokines, and have important roles in hepatitis and liver fibrosis. The cells are activated by various factors, for ex... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental... |
|
|
Convenient QSAR model for predicting the complexation of structurally diverse compounds with β-cyclodextrins
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 896-904, (2009) This paper reports a QSAR study for predicting the complexation of a large and heterogeneous variety of substances (233 organic compounds) with beta-cyclodextrins (beta-CDs). Several different theoret... |
| 2-(3-Trifluoromethylanilino)benzoic Acid |
| N-(3-Trifluoromethylphenyl)anthranilic Acid |
| 2-{[3-(Trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino}benzoic acid |
| Meralen |
| N-(a,a,a-Trifluoro-m-tolyl)anthranilic Acid |
| Paraflu |
| 2-[(3-Trifluoromethylphenyl)amino]benzoic Acid |
| Alfenamin |
| Flufenamic Acid |
| EINECS 208-494-1 |
| Surika |
| Sastridex |
| 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)anilino]benzoic acid |
| Opyrin |
| Achless |
| Benzoic acid, 2-[[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino]- |
| Tecramine |
| 2-[[3-(Trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino]benzoic acid |
| Arlef |
| MFCD00002422 |
| Ristogen |
| Parlef |
| 2-((3-(Trifluoromethyl)phenyl)amino)benzoic acid |
![methyl 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)anilino]benzoate Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/273/2765-91-5.png) CAS#:2765-91-5
CAS#:2765-91-5 CAS#:98-16-8
CAS#:98-16-8 CAS#:118-91-2
CAS#:118-91-2![Benzoic acid, 2-[[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]oxy]-, Methyl ester Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/344/17763-70-1.png) CAS#:17763-70-1
CAS#:17763-70-1![sodium 2-[[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino]benzoate Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/008/1977-00-0.png) CAS#:1977-00-0
CAS#:1977-00-0![1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-4-one Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/152/32509-03-8.png) CAS#:32509-03-8
CAS#:32509-03-8 CAS#:137488-39-2
CAS#:137488-39-2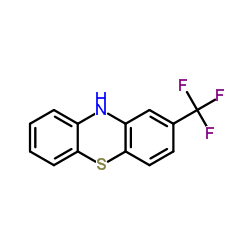 CAS#:92-30-8
CAS#:92-30-8![acetyloxymethyl 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)anilino]benzoate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/165/29098-19-9.png) CAS#:29098-19-9
CAS#:29098-19-9![benzoyloxymethyl 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)anilino]benzoate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/098/29261-37-8.png) CAS#:29261-37-8
CAS#:29261-37-8
