Decamethonium Bromide
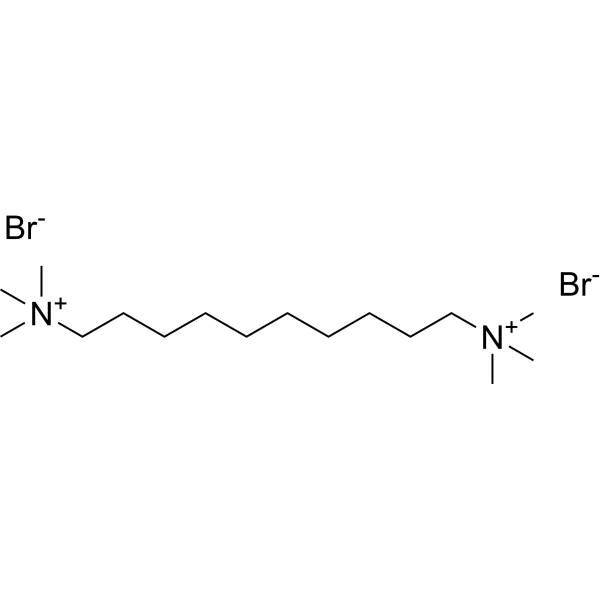
Decamethonium Bromide structure
|
Common Name | Decamethonium Bromide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 541-22-0 | Molecular Weight | 418.294 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H38Br2N2 | Melting Point | 263-267 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Decamethonium BromideDecamethonium Bromide is a nicotinic AChR partial agonist and neuromuscular blocking agent.Target: nAChRDecamethonium (Syncurine) is a depolarizing muscle relaxant or neuromuscular blocking agent, and is used in anesthesia to induce paralysis. Decamethonium, which has a short action time, is similar to acetylcholine and acts as a partial agonist of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. In the motor endplate, it causes depolarization, preventing further effects to the normal release of acetylcholine from the presynaptic terminal, and therefore preventing the neural stimulus from affecting the muscle. In the process of binding, decamethonium actually activates (depolarizes) the motor endplate, but since the decamethonium itself is not degraded, the membrane remains depolarized and unresponsive to normal acetylcholine release [1]. |
| Name | decamethonium bromide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Decamethonium Bromide is a nicotinic AChR partial agonist and neuromuscular blocking agent.Target: nAChRDecamethonium (Syncurine) is a depolarizing muscle relaxant or neuromuscular blocking agent, and is used in anesthesia to induce paralysis. Decamethonium, which has a short action time, is similar to acetylcholine and acts as a partial agonist of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. In the motor endplate, it causes depolarization, preventing further effects to the normal release of acetylcholine from the presynaptic terminal, and therefore preventing the neural stimulus from affecting the muscle. In the process of binding, decamethonium actually activates (depolarizes) the motor endplate, but since the decamethonium itself is not degraded, the membrane remains depolarized and unresponsive to normal acetylcholine release [1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Melting Point | 263-267 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H38Br2N2 |
| Molecular Weight | 418.294 |
| Exact Mass | 416.140167 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P301 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T |
| Risk Phrases | R25;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | BP5950000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
|
~53% 
Decamethonium B... CAS#:541-22-0 |
| Literature: Tischer, Maximilian; Sologub, Ludmilla; Pradel, Gabriele; Holzgrabe, Ulrike Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry, 2010 , vol. 18, # 9 p. 2998 - 3003 |
|
~0% 
Decamethonium B... CAS#:541-22-0 |
| Literature: Baer, Andrew J.; Macartney, Donal H. Organic and Biomolecular Chemistry, 2005 , vol. 3, # 8 p. 1448 - 1453 |
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain canc... |
|
|
Genetic mapping of targets mediating differential chemical phenotypes in Plasmodium falciparum.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 5 , 765-71, (2009) Studies of gene function and molecular mechanisms in Plasmodium falciparum are hampered by difficulties in characterizing and measuring phenotypic differences between individual parasites. We screened... |
|
|
Development of a phospholipidosis database and predictive quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) models.
Toxicol. Mech. Methods 18 , 217-27, (2008) ABSTRACT Drug-induced phospholipidosis (PL) is a condition characterized by the accumulation of phospholipids and drug in lysosomes, and is found in a variety of tissue types. PL is frequently manifes... |
| dekamethoniumbromid |
| Decane-1,10-bis(trimethylammonium Bromide) |
| decacuran |
| syncurine |
| N,N,N,N',N',N'-Hexamethyl-1,10-decanediaminium dibromide |
| decamethoniumdibromide |
| hexa-N-methyl-N,N'-decanediyl-di-ammonium,dibromide |
| N,N,N,N',N',N'-Hexamethyldecane-1,10-diaminium dibromide |
| decamethylenebis[trimethylammonium bromide] |
| 1,10-Decanediaminium, N,N,N,N',N',N'-hexamethyl-, dibromide |
| Decamethylene bis(trimethylammonium bromide) (Decane-1,10-bis(trimethylammonium bromide) |
| MFCD00011779 |
| Hexa-N-methyl-N,N'-decandiyl-di-ammonium,Dibromid |
| Decamethonium dibromide |
| Decamethylene bis(trimethylammonium bromide) |
| 1,10-Decanediaminium, N,N,N,N,N,N-hexamethyl-, bromide (1:2) |
| Decamethonium Bromide |
| EINECS 208-772-2 |
| UNII-55C6RK944K |
| decamethylene-1,10-bistrimethylammoniumdibromide |
| Decamethonium (Bromide) |