Chinese gallotannin
Modify Date: 2024-01-05 22:23:00
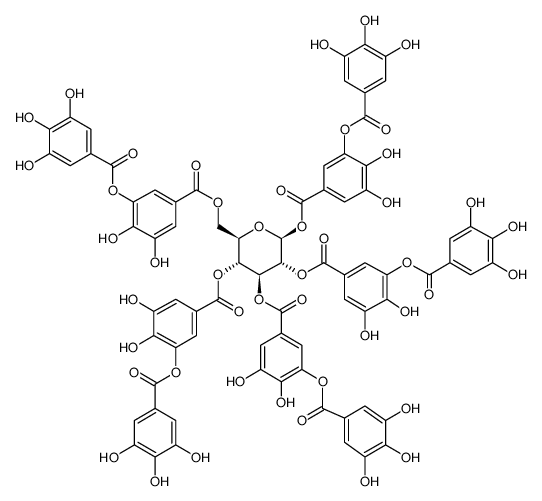
Chinese gallotannin structure
|
Common Name | Chinese gallotannin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 5424-20-4 | Molecular Weight | 1701.20 | |
| Density | 2.12 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 198ºC | |
| Molecular Formula | C76H52O46 | Melting Point | 218ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 198 °C | |
Use of Chinese gallotanninChinese gallotannin is a non-specific promiscuous α-amylase inhibitor with a Ki of 0.82 μg/mL for human salivary α-amylase. Chinese gallotannin can be used for the research of diabetes[1]. |
| Name | tannic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Chinese gallotannin is a non-specific promiscuous α-amylase inhibitor with a Ki of 0.82 μg/mL for human salivary α-amylase. Chinese gallotannin can be used for the research of diabetes[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Ki: 0.82 μg/mL (Human Salivary α-Amylase)[1] IC50: 2.3 μg/mL (Porcine Pancreatic α-Amylase), 128.9 nM (Telomerase), 3.0 μM (Fatty acid synthase), 6.9 μM (α-Ketoglutarate-Dependent Dioxygenase AlkB), 7.8 μM (5α-Reductase), 24.2 μM (Poly(ADP-ribose) Glycohydrolase)[1] |
| References |
| Density | 2.12 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 198ºC |
| Melting Point | 218ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C76H52O46 |
| Molecular Weight | 1701.20 |
| Flash Point | 198 °C |
| Exact Mass | 1700.17000 |
| PSA | 777.98000 |
| LogP | 4.83810 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.927 |
| Safety Phrases | 24/25 |
|---|---|
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | WW5075000 |
| HS Code | 3201909000 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
| HS Code | 3201909000 |
|---|
| Quebracho extract |
| DSSTox_CID_6076 |
| gallotannin |
| Gallotannic acid |
| penta-m-digalloyl-glucose |
| gallotanine |
| Tanninum |
| decagalloyl glucose |
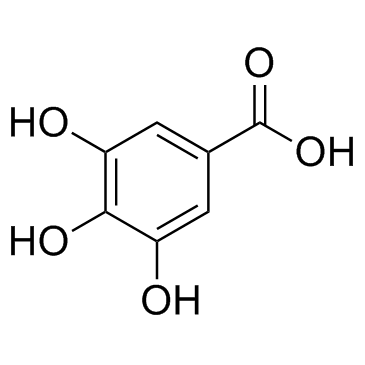 CAS#:149-91-7
CAS#:149-91-7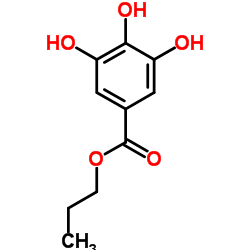 CAS#:121-79-9
CAS#:121-79-9