Caroverine HCl
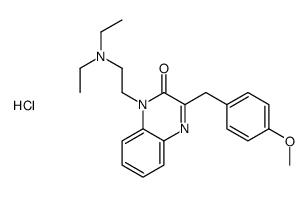
Caroverine HCl structure
|
Common Name | Caroverine HCl | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 55750-05-5 | Molecular Weight | 401.93000 | |
| Density | 1.11g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 521.2ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H28ClN3O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 269ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Caroverine HClCaroverine hydrochloride is a potent, competitive and reversible antagonist of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptor. Caroverine hydrochloride is also an antioxidant and calcium-blocking agent that exhibits vasorelaxant action. Caroverine hydrochloride can be used for the research of inner ear tinnitus[1][2][3]. |
| Name | 1-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-3-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]quinoxalin-2-one,hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Caroverine hydrochloride is a potent, competitive and reversible antagonist of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptor. Caroverine hydrochloride is also an antioxidant and calcium-blocking agent that exhibits vasorelaxant action. Caroverine hydrochloride can be used for the research of inner ear tinnitus[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
NMDA[1] AMPA[1] |
| In Vitro | Caroverine (1 μM; pretreated for 10 min) inhibits the pressor response to KCl (80 mM) and noradrenaline (1 μM) in the rat hindquarter preparation. Caroverine markedly suppresses the contraction caused by KCl (40 mM) in the rat isolated aorta[3]. |
| In Vivo | Caroverine (1.44 mg/rat; s.c; 1.0 mL/h for 72 h) attenuates impulse noise-induced hearing loss in the rat[4]. Animal Model: Sprague-Dawley rats of either sex (250-300 g) received impulse noise exposure[4] Dosage: 1.44 mg/rat Administration: 20 mg/mL; s.c. 1.0 mL/h for 72 h Result: Significantly protected the cochlea against impulse noise trauma. |
| References |
| Density | 1.11g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 521.2ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C22H28ClN3O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 401.93000 |
| Flash Point | 269ºC |
| Exact Mass | 401.18700 |
| PSA | 47.36000 |
| LogP | 4.13970 |
|
Possible contribution of pannexin channel to ATP-induced currents in vitro in vasopressin neurons isolated from the rat supraoptic nucleus
Brain Res. 1394 , 71-8, (2011) Release of arginine vasopressin (AVP) from magnocellular neurosecretory cells (MNCs) of the supraoptic nucleus (SON) is controlled by the electrical activity of these neurons. ATP plays a crucial role... |
|
|
[Drug therapy for disturbances of smelling].
Laryngorhinootologie. 83(2) , 124-34, (2004) Disorders of the sense of smell are frequent. This severely can affect the quality of live. Appropriate testing is needed to determine the nature of the patient's complaints. Following the pathogenesi... |
|
|
[Therapy of olfactory loss].
Laryngorhinootologie. 82(8) , 552-4, (2003) Apart from olfactory loss due to sino-nasal disease therapy of olfactory dysfunction is a difficult task.Own investigations were carried out using alpha-lipoic acid (Hummel et al. 2002) and caroverine... |
| Caroverine hydrochloride |
| Spasmium |
| P 201-1 |
| Tinnex |
| Spadon |
| Caroverine HCl |