Inosine
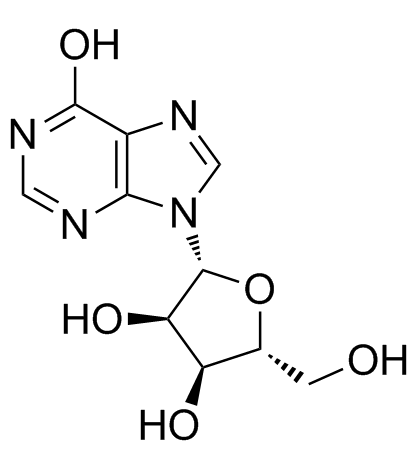
Inosine structure
|
Common Name | Inosine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 58-63-9 | Molecular Weight | 268.226 | |
| Density | 2.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 670.5±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H12N4O5 | Melting Point | 222-226 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 359.3±34.3 °C | |
Use of InosineInosine, an endogenous purine nucleoside, has immunomodulatory, neuroprotective, and analgesic properties. In vitro: Inosine has been shown to stimulate axonal growth in cell culture and promote corticospinal tract axons to sprout collateral branches after stroke, spinal cord injury and TBI in rodent models.[1] Inosine dose-dependently stimulates cAMP production mediated through the A2AR. Inosine dose-dependently induces A2AR-mediated ERK1/2 phosphorylation.[2] In vivo: The reference for Inosine is 1 or 10 mg/kg, i.p. Preventive treatment with inosine inhibits the development and progression of EAE in C57Bl/6 mice. neuroinflammation and demyelinating processes are blocked by inosine treatment. Additionally, inosine consistently inhibits IL-17 levels in peripheral lymphoid tissue, as well as IL-4 levels and A2AR up-regulation in the spinal cord, likely, through an ERK1-independent pathway. [3] inosine acting through adenosine receptors (ARs) exerts a wide range of anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects in vivo. [2] |
| Name | inosine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Inosine, an endogenous purine nucleoside, has immunomodulatory, neuroprotective, and analgesic properties. In vitro: Inosine has been shown to stimulate axonal growth in cell culture and promote corticospinal tract axons to sprout collateral branches after stroke, spinal cord injury and TBI in rodent models.[1] Inosine dose-dependently stimulates cAMP production mediated through the A2AR. Inosine dose-dependently induces A2AR-mediated ERK1/2 phosphorylation.[2] In vivo: The reference for Inosine is 1 or 10 mg/kg, i.p. Preventive treatment with inosine inhibits the development and progression of EAE in C57Bl/6 mice. neuroinflammation and demyelinating processes are blocked by inosine treatment. Additionally, inosine consistently inhibits IL-17 levels in peripheral lymphoid tissue, as well as IL-4 levels and A2AR up-regulation in the spinal cord, likely, through an ERK1-independent pathway. [3] inosine acting through adenosine receptors (ARs) exerts a wide range of anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects in vivo. [2] |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 2.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 670.5±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 222-226 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C10H12N4O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 268.226 |
| Flash Point | 359.3±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 268.080780 |
| PSA | 133.49000 |
| LogP | -1.91 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.879 |
| Water Solubility | 2.1 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2934999090. other heterocyclic compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Characterization, antioxidative and ACE inhibitory properties of hydrolysates obtained from thornback ray (Raja clavata) muscle.
J. Proteomics 128 , 458-68, (2015) Thornback ray muscle hydrolysates (TRMHs) prepared by treatment with proteases from Bacillus subtilis A26 (TRMH-A26), Raja clavata crude alkaline protease extract (TRMH-Crude), Alcalase (TRMH-Alcalase... |
|
|
Solubilization of gliadins for use as a source of nitrogen in the selection of bacteria with gliadinase activity.
Food Chem. 168 , 439-44, (2014) For patients with celiac disease, gliadin detoxification via the use of gliadinases may provide an alternative to a gluten-free diet. A culture medium, in which gliadins were the sole source of nitrog... |
|
|
A novel surface-confined glucaminium-based ionic liquid stationary phase for hydrophilic interaction/anion-exchange mixed-mode chromatography.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1360 , 240-7, (2014) Glucaminium-based ionic liquids are a new class of recently developed ionic liquids and prepared by functionalizing the amine group of N-methyl-d-glucamine, which renders them good hydrophilicity due ... |
| 6-Oxopurine riboside |
| HXR |
| RIBOXINE |
| nosine |
| Ino |
| EINECS 200-390-4 |
| 9-β-δ-Ribofuranosylhypoxanthine |
| Hypoxanthine, 9-β-D-ribofuranosyl- |
| 1,9-dihydro-9-b-D-ribofuranosyl-6H-Purin-6-one |
| 9-β-D-ribofuranosyl-Hypoxanthine |
| 9-β-D-Ribofuranosylhypoxanthine |
| Inosie |
| 9-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-Dihydroxy-5-(hydroxyméthyl)tétrahydro-2-furanyl]-1,9-dihydro-6H-purin-6-one |
| INO 495 |
| hypoxanthine |
| Oxiamin |
| 9-b-D-Ribofuranosylhypoxanthine |
| Atorel |
| MFCD00066770 |
| 6H-Purin-6-one, 1,9-dihydro-9-β-D-ribofuranosyl- |
| 9β-D-Ribofuranosylhypoxanthine |
| 6-oxy-purine riboside |
| 9H-Purin-6-ol, 9-β-D-ribofuranosyl- |
| 9-β-D-ribofuranosyl-1,9-dihydro-6H-purin-6-one |
| 9-b-D-ribofuranosyl-Hypoxanthine |
| Inosine |
| 9-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-Dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2-furanyl]-1,9-dihydro-6H-purin-6-one |
| T56 BN DN FN HNJ IQ D- BT5OTJ CQ DQ E1Q &&β-D-Ribo Form |
| Inosine (8CI,9CI) |
| Selfer |
 CAS#:58-61-7
CAS#:58-61-7 CAS#:5746-29-2
CAS#:5746-29-2 CAS#:2004-06-0
CAS#:2004-06-0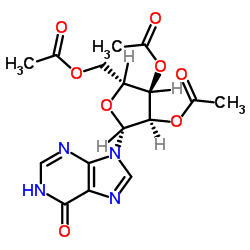 CAS#:3181-38-2
CAS#:3181-38-2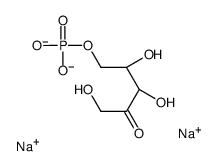 CAS#:108321-99-9
CAS#:108321-99-9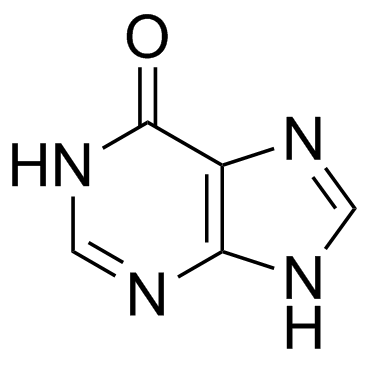 CAS#:68-94-0
CAS#:68-94-0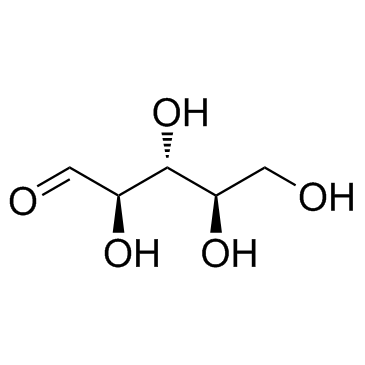 CAS#:50-69-1
CAS#:50-69-1 CAS#:6974-32-9
CAS#:6974-32-9 CAS#:2140-11-6
CAS#:2140-11-6 CAS#:5746-27-0
CAS#:5746-27-0 CAS#:104940-65-0
CAS#:104940-65-0 CAS#:36791-04-5
CAS#:36791-04-5 CAS#:42867-68-5
CAS#:42867-68-5 CAS#:4294-16-0
CAS#:4294-16-0 CAS#:5987-73-5
CAS#:5987-73-5 CAS#:20125-39-7
CAS#:20125-39-7![9-[3,4-dihydroxy-5-(iodomethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-3H-purin-6-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/095/18945-36-3.png) CAS#:18945-36-3
CAS#:18945-36-3
