Hypoxanthine
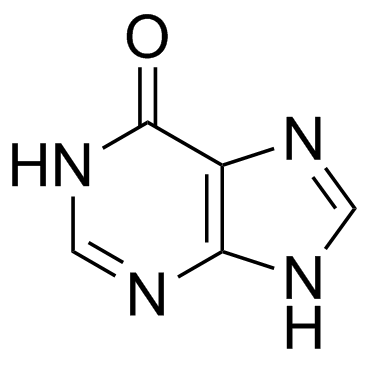
Hypoxanthine structure
|
Common Name | Hypoxanthine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 68-94-0 | Molecular Weight | 136.111 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 551.0±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H4N4O | Melting Point | >300 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 287.0±24.6 °C | |
Use of HypoxanthineHypoxanthine, a purine derivative, is a potential free radical generator and could be used as an indicator of hypoxia. |
| Name | Hypoxanthine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Hypoxanthine, a purine derivative, is a potential free radical generator and could be used as an indicator of hypoxia. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Hypoxanthine is a potential free radical generator. Hypoxanthine seems to play a role in posthypoxic reoxygenation cell injury through oxygen radical production and is therefore involved in the pathogenesis of a number of diseases. Hypoxanthine also modulates a number of other processes because it reacts with benzodiazepine receptors and inhibits phosphodiesterase in the brain. Hypoxanthine inhibits the effect of several cytotoxic drugs and may therefore influence treatment with such drugs[1]. |
| In Vivo | In pigs, a linear increase of plasma hypoxanthine with duration of hypoxemia is found, and there is no difference between arterial and venous plasma. There are good correlations between hypoxanthine and lactate, base deficit and pH. There is also a direct relationship between survival time and increase in plasma hypoxanthine. Survival time correlates negatively with the rate of hypoxanthine increase (r=-0.62).All animals die when hypoxanthine exceeds 125 pM/liter. The increase of hypoxanthine therefore reflected the prognosis of acute hypoxia in contrast to base deficit[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 551.0±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | >300 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C5H4N4O |
| Molecular Weight | 136.111 |
| Flash Point | 287.0±24.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 136.038513 |
| PSA | 74.43000 |
| LogP | -0.91 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.816 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | practically insoluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25-S37/39-S26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | UP0791000 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Hypoxanthine uptake by skeletal muscle microvascular endothelial cells from equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 (ENT1)-null mice: effect of oxidative stress.
Microvasc. Res. 98 , 16-22, (2015) Adenosine is an endogenous regulator of vascular tone. This activity of adenosine is terminated by its uptake and metabolism by microvascular endothelial cells (MVEC). The predominant transporter invo... |
|
|
In Vitro Protective Effect and Antioxidant Mechanism of Resveratrol Induced by Dapsone Hydroxylamine in Human Cells.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0134768, (2015) Dapsone (DDS) hydroxylamine metabolites cause oxidative stress- linked adverse effects in patients, such as methemoglobin formation and DNA damage. This study evaluated the ameliorating effect of the ... |
|
|
Oxidative stress modulates nucleobase transport in microvascular endothelial cells
Microvasc. Res. 95 , 68-75, (2014) Purine nucleosides and nucleobases play key roles in the physiological response to vascular ischemia/reperfusion events. The intra- and extracellular concentrations of these compounds are controlled, ... |
| 3,9-Dihydro-6H-purin-6-on |
| 1,7-Dihydro-6H-purin-6-on |
| 6-Oxopurine |
| 1,7-Dihydro-6H-purin-6-one |
| 7H-Purin-6-ol |
| PURIN-6-OL |
| Hypexanthine |
| SARKIN |
| SARCINE |
| Hypoxathine |
| 3,9-Dihydro-6H-purin-6-one |
| MFCD00005725 |
| Hypoxanthine |
| Purine-6-ol |
| 6-oxypurine |
| Sarkine |
| Hypoxanthin |
| 6-Hydroxypurine |
| EINECS 200-697-3 |
| 1H,7H-Hypoxanthine |
| 1,7-dihydro-purin-6-one |
| 1,7-Dihydro-6H-purine-6-one |
 CAS#:7440-02-0
CAS#:7440-02-0 CAS#:69-89-6
CAS#:69-89-6 CAS#:890-38-0
CAS#:890-38-0 CAS#:73-24-5
CAS#:73-24-5 CAS#:52502-66-6
CAS#:52502-66-6 CAS#:77287-34-4
CAS#:77287-34-4 CAS#:7501-32-8
CAS#:7501-32-8 CAS#:631-61-8
CAS#:631-61-8 CAS#:122-51-0
CAS#:122-51-0 CAS#:360-97-4
CAS#:360-97-4 CAS#:50-44-2
CAS#:50-44-2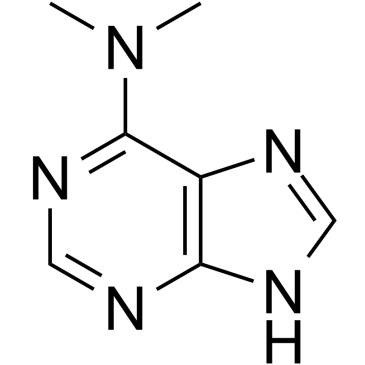 CAS#:938-55-6
CAS#:938-55-6 CAS#:207220-30-2
CAS#:207220-30-2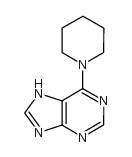 CAS#:1928-81-0
CAS#:1928-81-0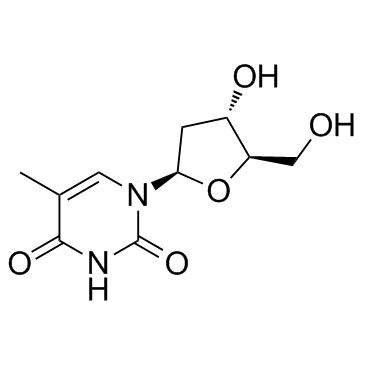 CAS#:50-89-5
CAS#:50-89-5 CAS#:66-22-8
CAS#:66-22-8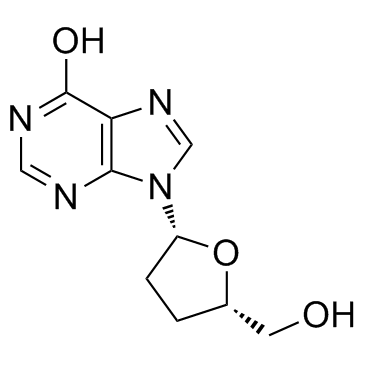 CAS#:69655-05-6
CAS#:69655-05-6 CAS#:2846-96-0
CAS#:2846-96-0
