CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
-
RTECS NUMBER :
-
AU7175000
-
CHEMICAL NAME :
-
Adenosine
-
CAS REGISTRY NUMBER :
-
58-61-7
-
LAST UPDATED :
-
199701
-
DATA ITEMS CITED :
-
16
-
MOLECULAR FORMULA :
-
C10-H13-N5-O4
-
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :
-
267.28
-
WISWESSER LINE NOTATION :
-
T56 BN DN FN HNJ IZ D- BT5OTJ CQ DQ E1Q
HEALTH HAZARD DATA
ACUTE TOXICITY DATA
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intravenous
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - woman
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
240 ug/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Cardiac - arrhythmias (including changes in conduction)
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intravenous
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - man
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
143 ug/kg/I
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Sense Organs and Special Senses (Eye) - effect, not otherwise specified Behavioral - headache
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intravenous
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - man
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
50 ug/kg/1M-I
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Lungs, Thorax, or Respiration - bronchiolar constriction
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intravenous
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - woman
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
360 ug/kg/1H-I
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Cardiac - pulse rate increase, without fall in BP Cardiac - change in rate
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intravenous
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - man
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
257 ug/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Cardiac - pulse rate increase, without fall in BP Lungs, Thorax, or Respiration - cyanosis
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intravenous
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - man
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
171 ug/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Behavioral - convulsions or effect on seizure threshold Behavioral - coma Cardiac - pulse rate
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intravenous
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - man
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
257 ug/kg/1D-I
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Cardiac - arrhythmias (including changes in conduction) Cardiac - change in rate Vascular - BP lowering not characterized in autonomic section
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
>20 gm/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intraperitoneal
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
500 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
Cytogenetic analysis
MUTATION DATA
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
DNA damage
-
TEST SYSTEM :
-
Mammal - species unspecified Lymphocyte
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
60 mmol/L
-
REFERENCE :
-
PNASA6 Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. (National Academy of Sciences, Printing & Pub. Office, 2101 Constitution Ave., Washington, DC 20418) V.1- 1915- Volume(issue)/page/year: 48,686,1962 *** REVIEWS *** TOXICOLOGY REVIEW ARZNAD Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. (Editio Cantor Verlag, Postfach 1255, W-7960 Aulendorf, Fed. Rep. Ger.) V.1- 1951- Volume(issue)/page/year: 7,24,1957 *** NIOSH STANDARDS DEVELOPMENT AND SURVEILLANCE DATA *** NIOSH OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE SURVEY DATA : NOES - National Occupational Exposure Survey (1983) NOES Hazard Code - X3937 No. of Facilities: 77 (estimated) No. of Industries: 2 No. of Occupations: 2 No. of Employees: 556 (estimated) No. of Female Employees: 387 (estimated)
|
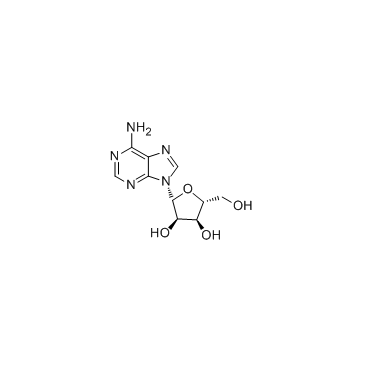
 CAS#:2946-39-6
CAS#:2946-39-6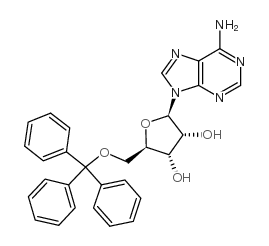 CAS#:18048-85-6
CAS#:18048-85-6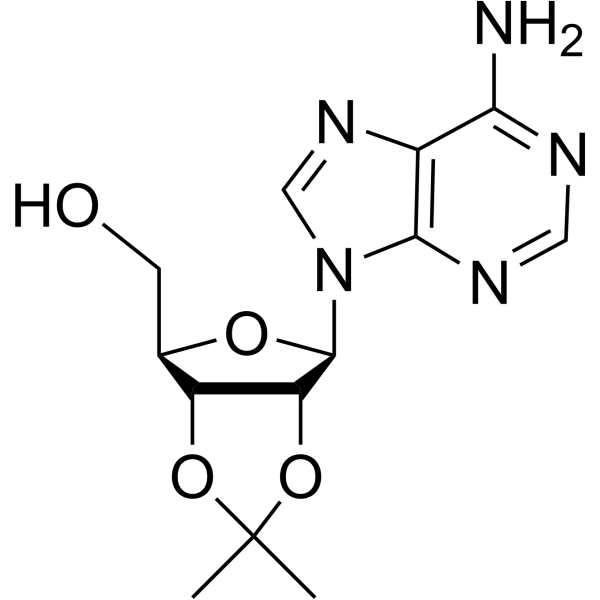 CAS#:362-75-4
CAS#:362-75-4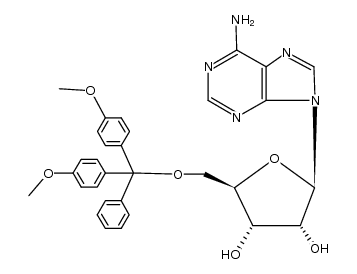 CAS#:57018-82-3
CAS#:57018-82-3 CAS#:66224-66-6
CAS#:66224-66-6 CAS#:58-96-8
CAS#:58-96-8 CAS#:35638-82-5
CAS#:35638-82-5 CAS#:3080-30-6
CAS#:3080-30-6 CAS#:7387-57-7
CAS#:7387-57-7![[(2S,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-4-azidooxolan-2-yl]methanol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/130/110142-99-9.png) CAS#:110142-99-9
CAS#:110142-99-9 CAS#:4097-22-7
CAS#:4097-22-7 CAS#:628-13-7
CAS#:628-13-7 CAS#:104579-36-4
CAS#:104579-36-4 CAS#:527-85-5
CAS#:527-85-5 CAS#:342-69-8
CAS#:342-69-8 CAS#:4546-55-8
CAS#:4546-55-8 CAS#:42822-84-4
CAS#:42822-84-4 CAS#:5142-22-3
CAS#:5142-22-3 CAS#:5142-23-4
CAS#:5142-23-4
