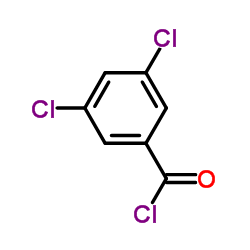
Tafamidis

Tafamidis structure
|
Common Name | Tafamidis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 594839-88-0 | Molecular Weight | 308.116 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 486.7±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H7Cl2NO3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 248.1±27.3 °C | |
Use of TafamidisTafamidis(Fx1006A) is a potent and selective transthyretin kinetic stabilizer that inhibits the amyloid cascade.Target: OthersTafamidis is a drug for the amelioration of transthyretin-related hereditary amyloidosis.Tafamidis functions by kinetic stabilization of the correctly folded tetrameric form of the transthyretin (TTR) protein. Tafamidis binds selectively and with negative cooperativity (K(d)s ~2 nM and ~200 nM) to the two normally unoccupied thyroxine-binding sites of the tetramer, and kinetically stabilizes TTR. Patient-derived amyloidogenic variants of TTR, including kinetically and thermodynamically less stable mutants, are also stabilized by tafamidis binding. The crystal structure of tafamidis-bound TTR suggests that binding stabilizes the weaker dimer-dimer interface against dissociation, the rate-limiting step of amyloidogenesis [1]. |
| Name | tafamidis |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Tafamidis(Fx1006A) is a potent and selective transthyretin kinetic stabilizer that inhibits the amyloid cascade.Target: OthersTafamidis is a drug for the amelioration of transthyretin-related hereditary amyloidosis.Tafamidis functions by kinetic stabilization of the correctly folded tetrameric form of the transthyretin (TTR) protein. Tafamidis binds selectively and with negative cooperativity (K(d)s ~2 nM and ~200 nM) to the two normally unoccupied thyroxine-binding sites of the tetramer, and kinetically stabilizes TTR. Patient-derived amyloidogenic variants of TTR, including kinetically and thermodynamically less stable mutants, are also stabilized by tafamidis binding. The crystal structure of tafamidis-bound TTR suggests that binding stabilizes the weaker dimer-dimer interface against dissociation, the rate-limiting step of amyloidogenesis [1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 486.7±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C14H7Cl2NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 308.116 |
| Flash Point | 248.1±27.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 306.980286 |
| PSA | 63.33000 |
| LogP | 5.29 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.677 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
|
~% 
Tafamidis CAS#:594839-88-0 |
| Literature: Chemistry - A European Journal, , vol. 17, # 36 p. 10113 - 10122 |
|
~% 
Tafamidis CAS#:594839-88-0 |
| Literature: Chemistry - A European Journal, , vol. 17, # 36 p. 10113 - 10122 |
|
~% 
Tafamidis CAS#:594839-88-0 |
| Literature: Chemistry - A European Journal, , vol. 17, # 36 p. 10113 - 10122 |
|
~% 
Tafamidis CAS#:594839-88-0 |
| Literature: WO2013/168014 A1, ; |
| 6-Benzoxazolecarboxylic acid, 2-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)- |
| Tafamidis |
| 8FG9H9D31J |
| 2-(3,5-Dichlorophenyl)-1,3-benzoxazole-6-carboxylic acid |
| UNII-8FG9H9D31J |
| FX-1006 |
| 3MI |
![Benzo[d]oxazole-6-carboxylic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/449/154235-77-5.png)