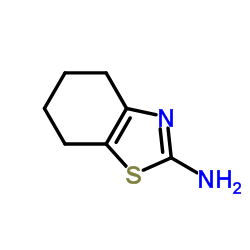
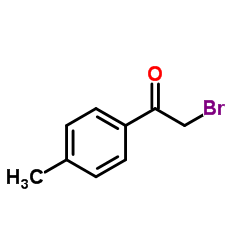
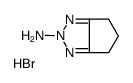
Pifithrin-α hydrobromide
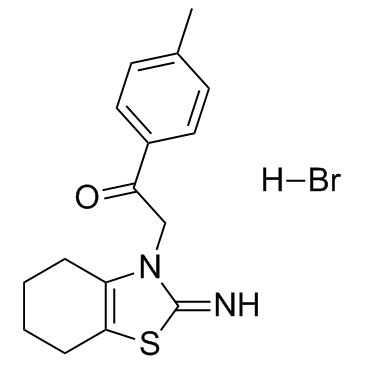
Pifithrin-α hydrobromide structure
|
Common Name | Pifithrin-α hydrobromide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 63208-82-2 | Molecular Weight | 367.304 | |
| Density | 1.28g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 456.8ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H19BrN2OS | Melting Point | 192.1-192.5ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 230.1ºC | |
Use of Pifithrin-α hydrobromidePifithrin-α hydrobromide is a p53 inhibitor which blocks its transcriptional activity and prevents cells from apoptosis. |
| Name | 2-(2-imino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1,3-benzothiazol-3-yl)-1-(4-methylphenyl)ethanone,hydrobromide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Pifithrin-α hydrobromide is a p53 inhibitor which blocks its transcriptional activity and prevents cells from apoptosis. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
p53[1] AhR[2] |
| In Vitro | Pifithrin-α (PFT-α) hydrobromideis a water-soluble compound that could suppress p53 protein transcription. Pifithrin-α can suppress glucose oxidase (GOX)-induced p53 protein increase in whole cell lysates, but cyclosporine A (CsA) fails to show such an inhibition effect. Notably, Pifithrin-α is able to block the GOX-induced Bcl-2 protein reduction. Similarly, it is Pifithrin-α rather than CsA that able to prevent the Bax increasing in whole cell lysates[1]. Pifithrin-α inhibits p53-dependent apoptosis through an undetermined mechanism. Pifithrin-α also acts as an aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) agonist and. Pifithrin-α is a potent AhR agonist as determined by its ability to bind the AhR, induce formation of its DNA binding complex, activate reporter activity, and up-regulate the classic AhR target gene CYP1A1[2]. |
| In Vivo | When the experiment is performed with Pifthirin-α (PFT-α) hydrobromide, a pharmacological p53 inhibitor, the percentage of annexin V-positive Foxe3-/- SMCs decreases to WT levels. Pifithrin-α (2.2 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly reduces the incidence of aortic rupture and intramural hematomas in Foxe3-/- mice that underwent transverse aortic constriction (TAC) (50% to 17%, P<0.05). After Pifthirin-α treatment, the mean diameter of the ascending aorta and the percentage of TUNEL-positive cells in the aortic media are also normalized to WT levels in surviving Foxe3-/- animals (P<0.05)[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | The ligand binding competition assays are performed. Cytosolic cell extracts from Hepa-1 cells are generated by the resuspension of the cell pellets in HEDG buffer [25 mM Hepes, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM dithiothreitol, and 10% (v/v) glycerol, pH 7.5] containing 0.4 mM leupeptin, 4 mg/mL aprotinin, and 0.3 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, homogenization, and centrifugation at 100,000 g for 45 min. Aliquots of the supernatant (120 μg) are incubated at room temperature for 2 h with the indicated concentrations of Pifithrin-α in the presence of 3 nM [3H]TCDD in HEDG buffer. After incubation on ice with hydroxyapatite for 30 min, HEDG buffer with 0.5% Tween 80 is added. The samples are centrifuged, washed twice, resuspended in 0.2 mL of scintillation fluid, and subjected to scintillation counting. Nonspecific binding is determined using a 150-fold molar excess of TCDF and subtracted from the total binding to obtain the specific binding. The specific binding is reported relative to [3H]TCDD alone[2]. |
| Cell Assay | The human hepatoma cell lines HepG2 (p53++) are cultured in RMPI 1640 medium with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), and 1% penicillin/streptomycin at 37°C in an atmosphere containing 5% CO2. Cells are exposed to GOX (0-5 0U) for 0-8 hours with or without Pifithrin-α (20 μM/L), Pifithrin-μ (5 μM/L), CsA (10 μM/L), Sanglifehrin A (20 μM/L) and NAC (5 mM/L) for 1 hour, respectively. After treatment, cells are collected and processed for further experiments[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] The Foxe3-null (Foxe3-/-) mice are used. To investigate the role of p53 in Foxe3-related apoptosis, Pifithrin-α is administered by i.p. injection at a dosage of 2.2 mg/kg, then dissolved in PBS 1 hour before TAC and then every 48 hours. Animals are euthanized 2 weeks after the surgery, and the ascending aortic tissues are harvested for either RNA, total protein, histomorphometric analysis, or TUNEL assay. |
| References |
| Density | 1.28g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 456.8ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 192.1-192.5ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C16H19BrN2OS |
| Molecular Weight | 367.304 |
| Flash Point | 230.1ºC |
| Exact Mass | 366.040131 |
| PSA | 74.09000 |
| LogP | 4.15700 |
| Appearance of Characters | powder |
| Index of Refraction | 1.666 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: 20 mg/mL |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
~67% 
Pifithrin-α hyd... CAS#:63208-82-2 |
| Literature: Zhu, Xiaoxiang; Yu, Qian-sheng; Cutler, Roy G.; Culmsee, Carsten W.; Holloway, Harold W.; Lahiri, Debomoy K.; Mattson, Mark P.; Greig, Nigel H. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2002 , vol. 45, # 23 p. 5090 - 5097 |
|
~57% 
Pifithrin-α hyd... CAS#:63208-82-2 |
| Literature: Murru, Siva; Singh; Kavala, Veerababurao; Patel, Bhisma K. Tetrahedron, 2008 , vol. 64, # 8 p. 1931 - 1942 |
|
~% 
Pifithrin-α hyd... CAS#:63208-82-2 |
| Literature: Pietrancosta, Nicolas; Maina, Flavio; Dono, Rosanna; Moumen, Anice; Garino, Cedrik; Laras, Younes; Burlet, Stephane; Quelever, Gilles; Kraus, Jean-Louis Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2005 , vol. 15, # 6 p. 1561 - 1564 |
|
A chemical inhibitor of p53 that protects mice from the side effects of cancer therapy.
Science 285 , 1733-1737, (1999) Chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer often have severe side effects that limit their efficacy. Because these effects are in part determined by p53-mediated apoptosis, temporary suppression of... |
|
|
Suppression of p53: a new approach to overcome side effects of antitumor therapy.
Biochemistry 65 , 41-48, (2000) The p53 protein is traditionally believed to be a tumor suppressor. Activation of p53-dependent apoptosis in response to damage to cell DNA provides for the elimination of possible tumor cell precurso... |
|
|
p53 protein-mediated up-regulation of MAP kinase phosphatase 3 (MKP-3) contributes to the establishment of the cellular senescent phenotype through dephosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2).
J. Biol. Chem. 290(2) , 1129-40, (2015) Growth arrest is one of the essential features of cellular senescence. At present, the precise mechanisms responsible for the establishment of the senescence-associated arrested phenotype are still in... |
| Pifithrin-α hydrobromide |
| Pifithrin-a |
| 1-(4-methylphenyl)-2-(4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-2-imino-3(2H)- benzothiazolyl)ethanone hydrobromide |
| 2-imino-3-phenacyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzothiazole hydrobromide |
| PFT-α |
| Pifithrin-α |
| PFTalpha |
| Pifithrin-|A |
| Ethanone, 1-(4-methylphenyl)-2-(4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-2-imino-3(2H)-benzothiazolyl)-, hydrobromide (1:1) |
| 2-(2-Imino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1,3-benzothiazol-3(2H)-yl)-1-(4-methylphenyl)ethanone hydrobromide (1:1) |
| Pifithrin-Alpha |
| MFCD00417851 |
| Pifithrin-Alpha (hydrobromide) |
| Pifithrin-α (hydrobromide) |
| Pifithrin |