Ursodeoxycholic acid-13C
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 12:31:15
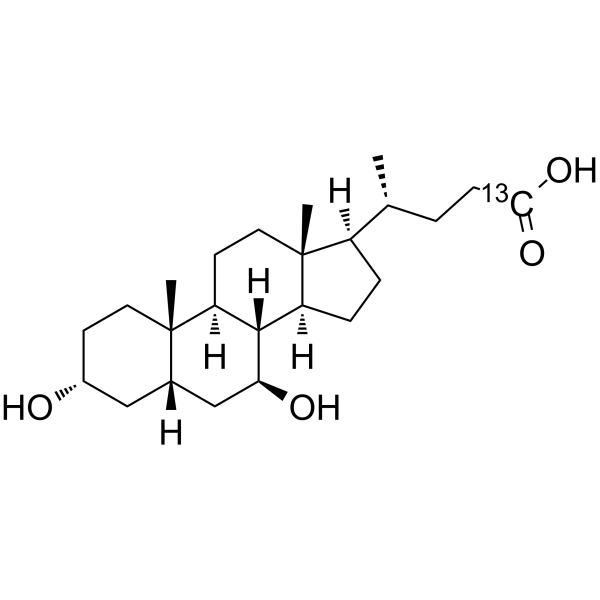
Ursodeoxycholic acid-13C structure
|
Common Name | Ursodeoxycholic acid-13C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 63296-46-8 | Molecular Weight | 393.56 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C2313CH40O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Ursodeoxycholic acid-13CUrsodeoxycholic acid-13C is the 13C labeled Ursodeoxycholic acid. Ursodeoxycholic acid (Ursodeoxycholate) is a secondary bile acid issued from the transformation of (cheno)deoxycholic acid by intestinal bacteria, acting as a key regulator of the intestinal barrier integrity and essential for lipid metabolism. Ursodeoxycholic acid acts as signaling molecule, exerting its effects by interacting with bile acid activated receptors, including G-protein coupled bile acid receptor 5 (TGR5, GPCR19) and the farnesoid X receptor (FXR). Ursodeoxycholic acid can be used for the research of a variety of hepatic and gastrointestinal diseases. Orally active[1][2]. |
| Name | (4R)-4-[(3R,5S,7S,8R,9S,10S,13R,17R)-3,7-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ursodeoxycholic acid-13C is the 13C labeled Ursodeoxycholic acid. Ursodeoxycholic acid (Ursodeoxycholate) is a secondary bile acid issued from the transformation of (cheno)deoxycholic acid by intestinal bacteria, acting as a key regulator of the intestinal barrier integrity and essential for lipid metabolism. Ursodeoxycholic acid acts as signaling molecule, exerting its effects by interacting with bile acid activated receptors, including G-protein coupled bile acid receptor 5 (TGR5, GPCR19) and the farnesoid X receptor (FXR). Ursodeoxycholic acid can be used for the research of a variety of hepatic and gastrointestinal diseases. Orally active[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C2313CH40O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 393.56 |
| Exact Mass | 393.296021 |
| PSA | 77.76000 |
| LogP | 4.47790 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.543 |
| Cholan-24-oic-24-C acid, 3,7-dihydroxy-, (3α,5β,7β)- |
| <24-13C>-Chenodeoxycholsaeure |
| (3α,5β,7β)-3,7-Dihydroxy(24-C)cholan-24-oic acid |