N-acetyl-L-methionine

N-acetyl-L-methionine structure
|
Common Name | N-acetyl-L-methionine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 65-82-7 | Molecular Weight | 191.248 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 371.3±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H13NO3S | Melting Point | 104-107ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese | Flash Point | 178.3±30.7 °C | |
Use of N-acetyl-L-methionineN-Acetyl-L-methionine, a human metabolite, is nutritionally and metabolically equivalent to L-methionine. L-methionine is an indispensable amino acid required for normal growth and development[1]. |
| Name | N-acetyl-L-methionine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | N-Acetyl-L-methionine, a human metabolite, is nutritionally and metabolically equivalent to L-methionine. L-methionine is an indispensable amino acid required for normal growth and development[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 371.3±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 104-107ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C7H13NO3S |
| Molecular Weight | 191.248 |
| Flash Point | 178.3±30.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 191.061615 |
| PSA | 91.70000 |
| LogP | 0.95 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.532 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 3 | |
| HS Code | 29309070 |
|---|
|
Importance of product inhibition in the kinetics of the acylase hydrolysis reaction by differential stopped flow microcalorimetry.
Anal. Biochem. 308 , 285-293, (2002) The hydrolysis of N-acetyl-L-methionine, N-acetylglycine, N-acetyl-L-phenylalanine, and N-acetyl-L-alanine at 298.35K by porcine kidney acylase I (EC 3.5.1.14) was monitored by the heat released upon ... |
|
|
Model sclerotization studies. 4. Generation of N-acetylmethionyl catechol adducts during tyrosinase-catalyzed oxidation of catechols in the presence of N-acetylmethionine.
Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 38(1) , 44-52, (1998) Incubation of catechol with mushroom tyrosinase in the presence of N-acetylmethionine resulted in the generation of an adduct. This product was identified to be N-acetylmethionyl catechol, on the basi... |
|
|
Identification of N-acetylmethionine as the product released during the NH2-terminal processing of a pseudo-class I actin.
J. Biol. Chem. 264(19) , 11491-6, (1989) Genes for the various isoactins define two classes of actin. Class I actin genes code for Met-Asp(Glu)-actin, and class II actin genes code for Met-X-Asp(Glu)-actin where X is usually cysteine. Amino ... |
| EINECS 200-617-7 |
| MFCD00064441 |
| N-Acetyl-L-methionine |
| N-acetyl-methionine |
| Thiomedon |
| L-Methionine, N-acetyl- |
| (2S)-2-acetamido-4-methylsulfanylbutanoic acid |
| Acetylmethionine |
| Methionine, N-acetyl-, L- |
| Methionamine |
| L-N-Acetyl-Methionine |
| L-(N-Acetyl)methionine |
| Ac-Met-OH |
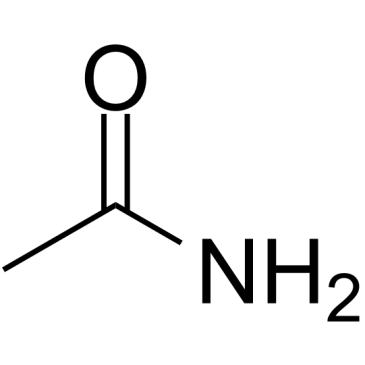 CAS#:60-35-5
CAS#:60-35-5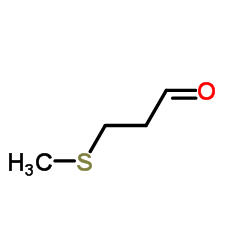 CAS#:3268-49-3
CAS#:3268-49-3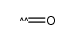 CAS#:201230-82-2
CAS#:201230-82-2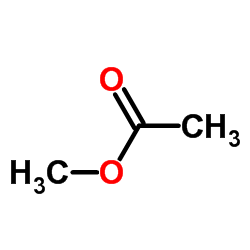 CAS#:79-20-9
CAS#:79-20-9 CAS#:59-51-8
CAS#:59-51-8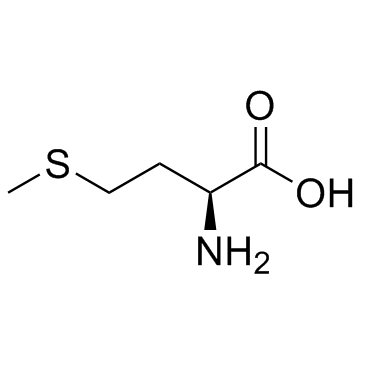 CAS#:63-68-3
CAS#:63-68-3 CAS#:108-24-7
CAS#:108-24-7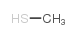 CAS#:74-93-1
CAS#:74-93-1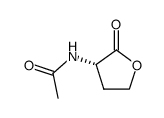 CAS#:51524-71-1
CAS#:51524-71-1 CAS#:17351-39-2
CAS#:17351-39-2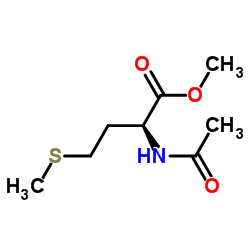 CAS#:35671-83-1
CAS#:35671-83-1 CAS#:1115-47-5
CAS#:1115-47-5
