4-O-Methyl honokiol
Modify Date: 2024-01-03 13:26:03
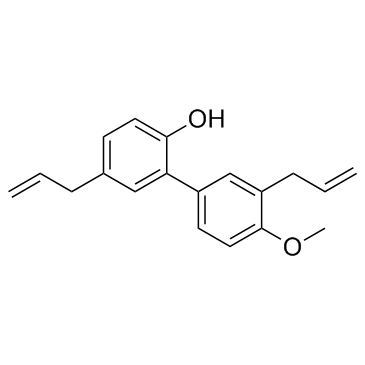
4-O-Methyl honokiol structure
|
Common Name | 4-O-Methyl honokiol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 68592-15-4 | Molecular Weight | 280.36100 | |
| Density | 1.054g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 396.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H20O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 176.2ºC | |
Use of 4-O-Methyl honokiol4-O-Methyl honokiol is a natural neolignan isolated from Magnolia officinalis, acts as a PPARγ agonist, and inhibtis NF-κB activity, used for cancer and inflammation research. |
| Name | 2-(4-methoxy-3-prop-2-enylphenyl)-4-prop-2-enylphenol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 4-O-Methyl honokiol is a natural neolignan isolated from Magnolia officinalis, acts as a PPARγ agonist, and inhibtis NF-κB activity, used for cancer and inflammation research. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
PPARγ NF-κB |
| In Vitro | 4-O-Methyl honokiol is a natural neolignan isolated from Magnolia officinalis, acts as a PPARγ agonist, and inhibtis NF-κB activity. 4-O-Methyl honokiol (20 μM) increases the expression, transcription and DNA binding activities, and nuclear translocation of PPARγ in both in prostate PC-3 and LNCap cells. 4-O-Methyl honokiol (0-30 μM) inhibits LNCaP and PC-3 cancer cells growth, causes G0/G1 phase arrest and induces apoptotic cell death, and such effects can be reversed by PPARγ antagonist. 4-O-Methyl honokiol inhibits NF-κB activity and cancer cell growth, but such effects as well as its activation of PPARγ can be abolished by knock-down of p21[1]. 4-O-methylhonokiol (0.5, 1 and 2 μM) reduces LPS-induced release of NO, PGE2, ROS, TNF-α and IL-1β in cultured astrocytes, and amyloidogenesis in cultured astrocytes and microglial BV-2 cells[2]. |
| In Vivo | 4-O-Methyl honokiol (40 or 80 mg/kg, i.p. everyday for 4 weeks) inhibits the growth of SW620 and PC3 tumours in SW620 and PC3 xenograft model. 4-O-Methyl honokiol significantly increases the expression of p21 and PPARγ in the tumour tissues[1]. 4-O-Methyl honokiol (0.5 or 1 mg/kg/day daily for 3 weeks) significantly ameliorates LPS-induced memory impairment, and inhibits LPS-induced iNOS and COX-2 expression in mice. 4-O-Methyl honokiol also shows inhibitory activities against the Aβ1-42 accumulation, and activates astrocytes and microglia in LPS-injected mice brain[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Cells (5 × 104 cells per well) are plated onto 24-well plates. The cell growth inhibitory effect of 4-O-Methyl honokiol is evaluated in cells treated with 4-O-Methyl honokiol (0-30 μM) for 0-72 h, using an excluded trypan blue assay[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Six-week-old male BALB/c athymic nude mice are used in the assay. SW620 and PC3 cells are injected s.c. (1 × 107 cells in 0.1 mL PBS per animal) into the lower right flanks of mice. After 20 days, when the tumours have reached an average volume of 300-400 mm3 or about 50 mm3, the tumour-bearing nude mice are i.p. injected with 4-O-Methyl honokiol (40 and 80 mg/kg dissolved in 0.1% DMSO) twice per week for 3 weeks. Cisplatin (10 mg/kg) is also i.p. injected once a week as a positive control. The group treated with 0.1% DMSO is designated as the control. The tumour volumes are measured with vernier calipers and calculated by the following formula: (A × B2)/2, where A is the larger and B is the smaller of the two dimensions[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.054g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 396.5ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C19H20O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 280.36100 |
| Flash Point | 176.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 280.14600 |
| PSA | 29.46000 |
| LogP | 4.52480 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.569 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 4 | |
| 3,5'-diallyl-2'-hydroxy-4-methoxy-1,1'-biphenyl |
| 4'-O-Methylhonokiol |
| 3,5'-diallyl-2'-hydroxy-4-methoxybiphenyl |
| METHYLHONOKIOL |
| methoxyhonokiol |
| 4-methoxyhonokiol |
| 4-O-Methyl honokiol |
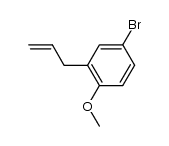 CAS#:114303-65-0
CAS#:114303-65-0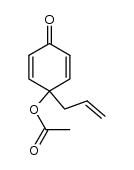 CAS#:108886-90-4
CAS#:108886-90-4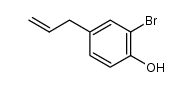 CAS#:17269-79-3
CAS#:17269-79-3 CAS#:1378871-34-1
CAS#:1378871-34-1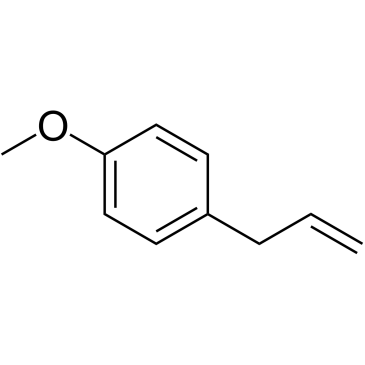 CAS#:140-67-0
CAS#:140-67-0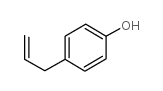 CAS#:501-92-8
CAS#:501-92-8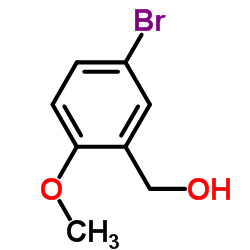 CAS#:80866-82-6
CAS#:80866-82-6 CAS#:184970-28-3
CAS#:184970-28-3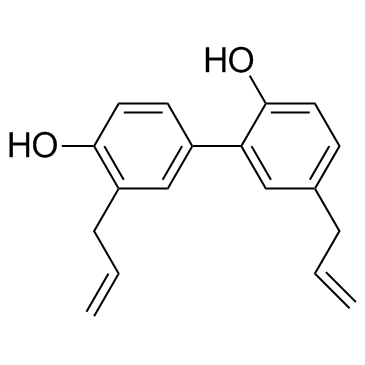 CAS#:35354-74-6
CAS#:35354-74-6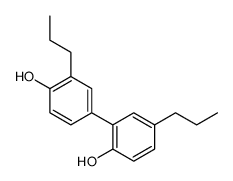 CAS#:35406-31-6
CAS#:35406-31-6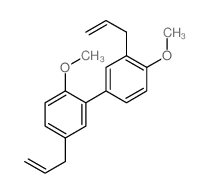 CAS#:68592-18-7
CAS#:68592-18-7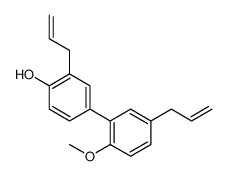 CAS#:68592-19-8
CAS#:68592-19-8