liothyronine

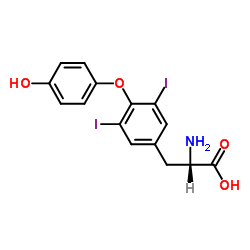
liothyronine structure
|
Common Name | liothyronine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6893-02-3 | Molecular Weight | 650.974 | |
| Density | 2.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 563.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H12I3NO4 | Melting Point | 234-238 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 294.6±30.1 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of liothyronine3,3',5-Triiodo-L-thyronine is a potent agonist of thyroid hormone receptors TRα and TRβ with Kis of 2.3 nM. |
| Name | 3,3',5-triiodo-L-thyronine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 3,3',5-Triiodo-L-thyronine is a potent agonist of thyroid hormone receptors TRα and TRβ with Kis of 2.3 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | 3,3',5-Triiodo-L-thyronine (T3, 100 nM) stimulates the proliferation of hepatocarcinema cells in which TRβ1 is overexpressed[1]. 3,3',5-Triiodo-L-thyronine binds to human β1 thyroid hormone receptor (hTRβ1), and change its conformation. 3,3',5-Triiodo-L-thyronine promotes growth, induces differentiation and regualtes metabolic effects[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Thyroid hormone depleted (Td) serum is prepared. The growth of hepatocarcinoma cells in methylcellulose is performed. To determine the effect of 3,3',5-Triiodo-L-thyronine (T3) on the growth of cells, cells are plated at a density of 3 × l04 cells/60 mm dish on day 0, and incubated in medium containing 5% regular serum, 5% Td or 5% Td and 100 nM T3. The colony formation in methylcellulose is scored 3 weeks after initial plating[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 2.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 563.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 234-238 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C15H12I3NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 650.974 |
| Flash Point | 294.6±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 650.790039 |
| PSA | 92.78000 |
| LogP | 5.08 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.763 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H301 + H311 + H331-H370 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P260-P280-P301 + P310 + P330-P302 + P352 + P312-P370 + P378 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S36-S26 |
| RIDADR | UN1230 - class 3 - PG 2 - Methanol, solution |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | AY6750000 |
| HS Code | 2922509090 |
|
~% 
liothyronine CAS#:6893-02-3 |
| Literature: Biochemical Journal, , vol. 53, p. 645,647 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
| HS Code | 2922509090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2922509090. other amino-alcohol-phenols, amino-acid-phenols and other amino-compounds with oxygen function. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI typ... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals ... |
| 3,3',5 TRIIODOTHYRONINE (T3), IRMM STANDARD |
| 3,5,3′-tri-iodo-l-thyronine |
| Liothyronine (T3) |
| T3, O-(4-HYDROXY-3-IODOPHENYL)-3,5-DIIODO-L-TYROSINE |
| O-(4-Hydroxy-3-iodophenyl)-3,5-diiodotyrosine |
| L-TYROSINE,O-(4-HYDROXY-3-IODOPHENYL)-3,5-DIIODO- |
| Alanine, 3-[4- (4-hydroxy-3-iodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl]-, L- |
| L T3 |
| Tyrosine, O-(4-hydroxy-3-iodophenyl)-3,5-diiodo- |
| O-(4-Hydroxy-3-iodophenyl)-3,5-diiodo-L-tyrosine |
| 3,3',5-Triiodothyronine |
| Triiodothyronine |
| L-3-[4-(4-Hydroxy-3-iodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl]alanine |
| 3,5,3′-Triiodo-L-thyronine |
| 3,3',5'-TRIIODO-DL-THYRONINE |
| L-3,3',5-triiodo-Thyronine |
| T 3 |
| (S)-2-Amino-3-(4-(4-hydroxy-3-iodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl)propanoic acid |
| EINECS 229-999-3 |
| MFCD00036864 |
| O-(4-hydroxy-3-iodo-phenyl)-3,5-diiodo-L-tyrosine |
| 3,5,3'-TRIIODO-L-THYRONINE |
| L-triiodothyronine |
| L-3-[4-(4-hydroxy-3-iodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl]-Alanine |
| 3,3',5'-TRIIODO-L-THYRONINE |
| 3,3',5-TRIIODO-L-THYRONINE, FREE ACID |
| 3,3',5-Triiodo-L-thyronine |
| L-3,3',5-TRIIODOTHYRONINE, FREE ACID |
| LIOTHYRONINE-D3 |
| (2S)-2-Amino-3-[4-(4-hydroxy-3-iodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl]propanoic acid |
| LIOTHYRONINE |
![Naphtho[1,8-cd]-1,2-thiaselenole structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/005/64869-35-8.png) CAS#:64869-35-8
CAS#:64869-35-8 CAS#:70-40-6
CAS#:70-40-6
