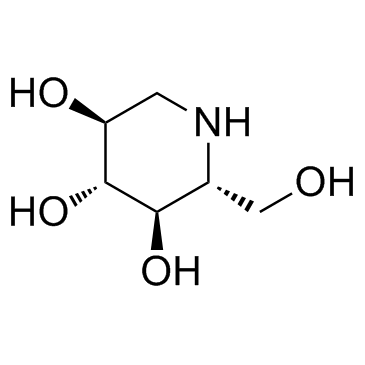
N-Methylmoranoline

N-Methylmoranoline structure
|
Common Name | N-Methylmoranoline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 69567-10-8 | Molecular Weight | 177.19800 | |
| Density | 1.394g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 367.2ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H15NO4 | Melting Point | 126-128ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 220.3ºC | |
Use of N-MethylmoranolineN-Methylmoranoline (MOR 14) is an α-glucosidase inhibitor. |
| Name | n-methyl-1-deoxynojirimycin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | N-Methylmoranoline (MOR 14) is an α-glucosidase inhibitor. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | N-Methylmoranoline dose-dependently decreases the α-1,6-glucosidase activity in rabbit heart extract. The myocardial uptake of a considerable amount of N-Methylmoranoline is sufficient to fully inhibit alpha-1,6-glucosidase. Preischemic treatment with 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg of N-Methylmoranoline dose-dependently reduces the infarct size without altering the blood pressure or heart rate[1]. MOR-14 significantly increases levels of PKC-ε in the particulate fraction at 20 and 30 min of ischaemia and in the cytosolic fraction at 30 min of ischaemia[2]. |
| In Vivo | N-Methylmoranoline decreases the alpha-1,6-glucosidase activity to approximately 20%, reduces the glycogen breakdown, and attenuates the lactate accumulation at both 10 and 30 minutes of ischemia[1]. MOR-14 is protective against postischemic left ventricular dysfunction through the inhibition of glycogenolysis in the isolated rat heart[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | The inhibitory action of N-Methylmoranoline against myocardial α-1,6-glucosidase is first examined in rabbit heart extracts. The substrate mixture contained 44 mM glycylglycine (pH 6.5), 12.5% rabbit liver glycogen, 2.5 mM [14C]glucose (20 μCi/μM), 2.1 mM EDTA, 4.1 mM mercaptoethanol, 0.02% gelatin, and N-Methylmoranoline (0, 0.01, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, or 1.0 μM). This solution (16 μL) is warmed at 30°C for 2 minutes, and the reaction is then initiated by the addition of 4 μL of the rabbit heart homogenate. The reaction is stopped 60 minutes later by the addition of 20 μL of 0.2N HCl. An aliquot (30 μL) is spotted onto a Whatman GF/A glass fiber disk. The disk is immediately washed in 66% ethanol for 20 minutes three times each and dipped in 15 mL of acetone for 10 minutes. Then the disk is dried, and the [14C] activity incorporated into glycogen is measured with a liquid scintillation counter[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Rabbits: To investigate the infarct size-reducing effect of N-Methylmoranoline, 54 rabbits are assigned randomly into drug treatment or saline control groups. There are four drug treatment groups, ie, three preischemic treatment groups given 100 mg/kg, 50 mg/kg, or 25 mg/kg of N-Methylmoranoline 10 minutes before ischemia, and one prereperfusion treatment group given 100 mg/kg of the drug 5 minutes before reperfusion. In all treatments, the injected volume is <1 mL/kg body wt. After the treatment, the coronary artery is occluded for 30 minutes and reperfused. The blood pressure and heart rate are monitored throughout the experiment until 20 minutes after reperfusion and are recorded at baseline, at 0, 1, 3, 5, 10, 20, and 30 minutes of ischemia, and at 5, 10, and 20 minutes of reperfusion[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.394g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 367.2ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 126-128ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C7H15NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 177.19800 |
| Flash Point | 220.3ºC |
| Exact Mass | 177.10000 |
| PSA | 84.16000 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.58 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
~91% 
N-Methylmoranoline CAS#:69567-10-8 |
| Literature: Kajimoto, Tetsuya; Liu, Kevin K.-C.; Pederson, Richard L.; Zhong, Ziyang; Ichikawa, Yoshitaka; Porco Jr., John A.; Wong, Chi-Huey Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1991 , vol. 113, # 16 p. 6187 - 6196 |
|
~% 
N-Methylmoranoline CAS#:69567-10-8 |
| Literature: US5221746 A1, ; |
|
~% 
N-Methylmoranoline CAS#:69567-10-8 |
| Literature: US4806650 A1, ; |
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain canc... |
|
|
Rapid degradation of the heavy chain of class I major histocompatibility complex antigens in the endoplasmic reticulum of human cytomegalovirus-infected cells.
J. Virol. 68 , 7933, (1994) Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection results in a marked reduction in the surface expression of class I major histocompatibility complex antigens on the host cells, which is thought to be one of the... |
|
|
Glucosidase and mannosidase inhibitors mediate increased secretion of mutant alpha1 antitrypsin Z.
J. Biol. Chem. 275(3) , 1987-92, (2000) It is now well known that the addition and trimming of oligosaccharide side chains during post-translational modification play an important role in determining the fate of secretory, membrane, and lys... |
| DEOXYNOJIRIMYCIN,N-METHYL |
| N-MDJN |
| N-METHYL-1,5-DIDEOXY-1,5-IMINO-D-GLUCITOL |
| Mednj |
| MOR-14 |
| N-Methylmoranolin |
| N-methyl deoxynojirimycin |
| EINECS 203-703-2 |
| 1,5-(methylimino)-1,5-dideoxy-D-glucitol |
| N-methylmoranoline |
| MFCD00133609 |
| (2R,3R,4R,5S)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1-methylpiperidine-3,4,5-triol |