Metalaxyl-M
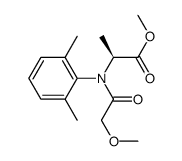
Metalaxyl-M structure
|
Common Name | Metalaxyl-M | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 70630-17-0 | Molecular Weight | 279.33200 | |
| Density | 1.117 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 394.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H21NO4 | Melting Point | 38.7ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 192.3ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Metalaxyl-MMetalaxyl-M ((R)-Metalaxyl) is the active (R)-enantiomer of Metalaxyl. Metalaxyl-M is a broad-spectrum fungicide that inhibits protein and ribosomal RNA synthesis in fungi. Metalaxyl is used for research of plant diseases caused by pathogens of the Oomycota division[1]. |
| Name | metalaxyl-M |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Metalaxyl-M ((R)-Metalaxyl) is the active (R)-enantiomer of Metalaxyl. Metalaxyl-M is a broad-spectrum fungicide that inhibits protein and ribosomal RNA synthesis in fungi. Metalaxyl is used for research of plant diseases caused by pathogens of the Oomycota division[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: fungi[1] |
| References |
| Density | 1.117 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 394.3ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 38.7ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C15H21NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 279.33200 |
| Flash Point | 192.3ºC |
| Exact Mass | 279.14700 |
| PSA | 55.84000 |
| LogP | 1.84430 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.527 |
| Storage condition | 0-6°C |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H318 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-39-46 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
The cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of metalaxy-M on earthworms (Eisenia fetida).
Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 33(10) , 2344-50, (2014) As the main optical isomer of metalaxyl, metalaxyl-M has been widely used worldwide in recent years because of its notable effect on the prevention and control of crop diseases. Together with the toxi... |
|
|
Degradation of metalaxyl and mefenoxam and effects on the microbiological properties of tropical and temperate soils.
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2 , 272-85, (2006) The degradation of various formulations of the racemic mixture and the enantiomers (including mefenoxam) of metalaxyl in typical soils from Germany and Cameroon in controlled incubation experiments wa... |
|
|
Comparative genomics reveals insight into virulence strategies of plant pathogenic oomycetes.
PLoS ONE 8 , e75072, (2013) The kingdom Stramenopile includes diatoms, brown algae, and oomycetes. Plant pathogenic oomycetes, including Phytophthora, Pythium and downy mildew species, cause devastating diseases on a wide range ... |
| methyl (2R)-2-(N-(2-methoxyacetyl)-2,6-dimethylanilino)propanoate |
| Metalaxyl-M |
| Metalaxil |
| methyl N-(methoxyacetyl)-N-2,6-xylyl-D-alaninate |
| methyl N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N-(methoxyacetyl)-D-alaninate |
| Methenoxam |
| (-)-Metalaxyl |
| R-metalaxyl |
| (-)-(R)-metalaxyl |
| MFCD03701742 |
| Methyl N-(methoxyacetyl)-N-(2,6-xylyl)-D-alaninate |
| [(R)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N-(methoxyacetylamino)propionic acid methyl ester] |
| Subdue Maxx |
| mefenoxam |
| Ridomil Gold |
| (R)-2-[(2,6-dimethylphenyl)methoxyacetylamino]propionic acid methyl ester |
| Metalaxyl-M [ISO:BSI] |