miglustat
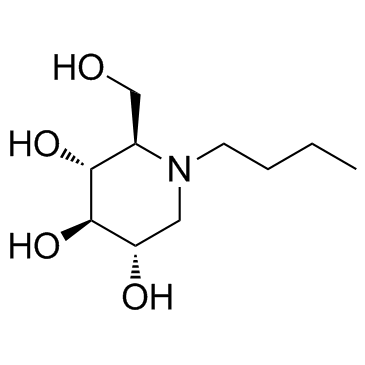
miglustat structure
|
Common Name | miglustat | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 72599-27-0 | Molecular Weight | 219.278 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 394.7±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H21NO4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 215.4±26.5 °C | |
Use of miglustatMiglustat(OGT918) is an inhibitor of glucosylceramide synthase, primarily to treat Type I Gaucher disease (GD1).Target: OthersMiglustat is an inhibitor of the ceramide-specific glycosyltransferase, which catalyzes the first step of glycosphingolipid biosynthesis and is currently approved for the oral treatment of type 1 GD [1]. Consumption of a standard high-fat breakfast within 30 minutes before administration of miglustat significantly reduced peak exposure but did not significantly affect the extent of systemic exposure to miglustat. The peak plasma concentration (C(max)) decreased by 36% on average following administration with food. Area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC(0-infinity)) showed a modest (14%) decrease with food, but the 90% confidence interval was within the acceptance limit of 80% to 125%. The median (min-max) time to C(max) (t(max)) was prolonged from 2.5 (1.0-4.0) hours in the fasted state to 4.5 (1.5-8.0) hours in the fed state, whereas the apparent terminal half-life was approximately 8 hours and not affected by food [2]. |
| Name | miglustat |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Miglustat(OGT918) is an inhibitor of glucosylceramide synthase, primarily to treat Type I Gaucher disease (GD1).Target: OthersMiglustat is an inhibitor of the ceramide-specific glycosyltransferase, which catalyzes the first step of glycosphingolipid biosynthesis and is currently approved for the oral treatment of type 1 GD [1]. Consumption of a standard high-fat breakfast within 30 minutes before administration of miglustat significantly reduced peak exposure but did not significantly affect the extent of systemic exposure to miglustat. The peak plasma concentration (C(max)) decreased by 36% on average following administration with food. Area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC(0-infinity)) showed a modest (14%) decrease with food, but the 90% confidence interval was within the acceptance limit of 80% to 125%. The median (min-max) time to C(max) (t(max)) was prolonged from 2.5 (1.0-4.0) hours in the fasted state to 4.5 (1.5-8.0) hours in the fed state, whereas the apparent terminal half-life was approximately 8 hours and not affected by food [2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 394.7±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C10H21NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 219.278 |
| Flash Point | 215.4±26.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 219.147064 |
| PSA | 84.16000 |
| LogP | 0.46 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.546 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| HS Code | 2933399090 |
| HS Code | 2933399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933399090. other compounds containing an unfused pyridine ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Development of a cell-based hepatitis C virus infection fluorescent resonance energy transfer assay for high-throughput antiviral compound screening.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53(10) , 4311-9, (2009) A major obstacle in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection has been the lack of effective, well-tolerated therapeutics. Notably, the recent development of the HCV cell culture infe... |
|
|
Inhibitors of the tick-borne, hemorrhagic fever-associated flaviviruses.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58(6) , 3206-16, (2014) No antiviral therapies are available for the tick-borne flaviviruses associated with hemorrhagic fevers: Kyasanur Forest disease virus (KFDV), both classical and the Alkhurma hemorrhagic fever virus (... |
|
|
Modulation of hepatitis C virus genome replication by glycosphingolipids and four-phosphate adaptor protein 2.
J. Virol. 88(21) , 12276-95, (2014) Hepatitis C virus (HCV) assembles its replication complex on cytosolic membrane vesicles often clustered in a membranous web (MW). During infection, HCV NS5A protein activates PI4KIIIα enzyme, causing... |
| nojirimycin, N-butyldeoxy- |
| Butyldeoxynojirimycin |
| N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin |
| N-Butyl-deoxynojirimycin |
| 1,5-(BUTYLIMINO)-1,5-DIDEOXY-D-GLUCITOL |
| N-Butylmoranoline |
| (2R,3R,4R,5S)-1-Butyl-2-(hydroxymethyl)-3,4,5-piperidinetriol |
| (2R,3R,4R,5S)-1-Butyl-2-(hydroxymethyl)piperidine-3,4,5-triol |
| MFCD00272581 |
| N-(n-Butyl)deoxynojirimycin |
| BuDNJ |
| NB-DNJ |
| 3,4,5-Piperidinetriol, 1-butyl-2-(hydroxymethyl)-, (2R,3R,4R,5S)- |
| miglustat |
| N-butyl-1-deoxynojirimycin |
| n-Butyl deoxynojirimycin |
| Zavesca |
| n-Butyl dnj |
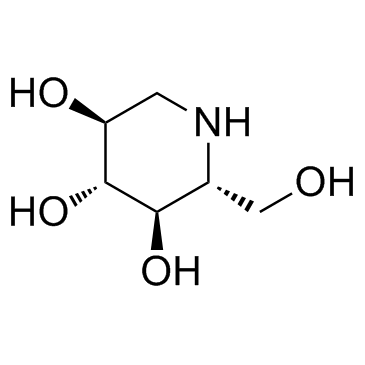 CAS#:19130-96-2
CAS#:19130-96-2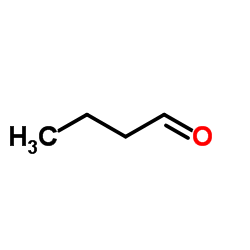 CAS#:123-72-8
CAS#:123-72-8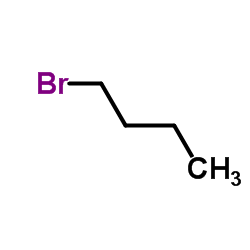 CAS#:109-65-9
CAS#:109-65-9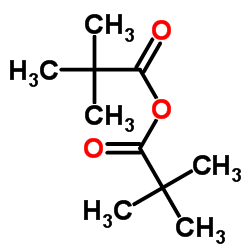 CAS#:1538-75-6
CAS#:1538-75-6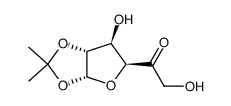 CAS#:19684-32-3
CAS#:19684-32-3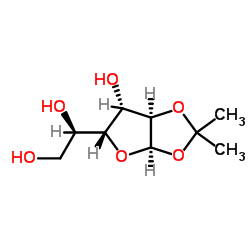 CAS#:18549-40-1
CAS#:18549-40-1 CAS#:6564-72-3
CAS#:6564-72-3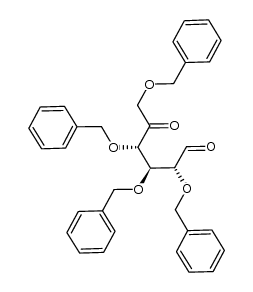 CAS#:214041-43-7
CAS#:214041-43-7