(RS)-AMPA monohydrate
Modify Date: 2024-01-08 17:33:07
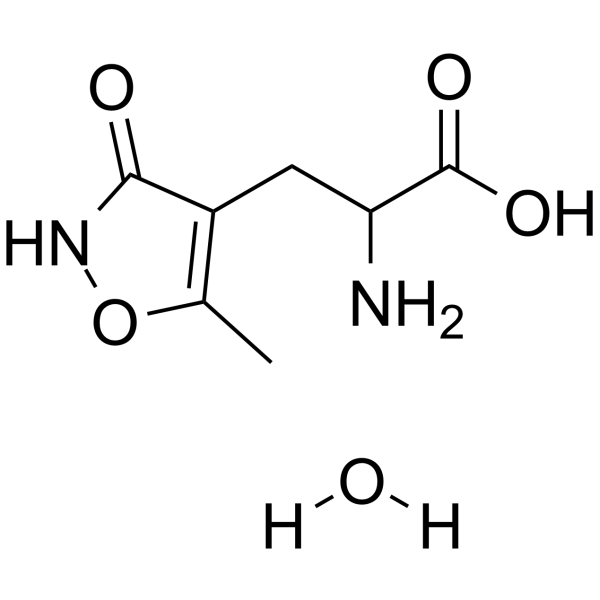
(RS)-AMPA monohydrate structure
|
Common Name | (RS)-AMPA monohydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 76463-67-7 | Molecular Weight | 204.18 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H12N2O5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of (RS)-AMPA monohydrate(RS)-AMPA ((±)-AMPA) monohydrate is a glutamate analogue and a potent and selective excitatory neurotransmitter L-glutamic acid agonist. (RS)-AMPA monohydrate does not interfere with binding sites for kainic acid or NMDA receptors[1][2]. |
| Name | (RS)-AMPA monohydrate |
|---|
| Description | (RS)-AMPA ((±)-AMPA) monohydrate is a glutamate analogue and a potent and selective excitatory neurotransmitter L-glutamic acid agonist. (RS)-AMPA monohydrate does not interfere with binding sites for kainic acid or NMDA receptors[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | (RS)-AMPA monohydrate (10-3-10-4 M) causes depolarizations of cultured rat spinal and brainstem neurones. The depolarization by (RS)-AMPA monohydrate is clearly dose-dependent, although there is a great variability of effects between individual neurones. Application of (RS)-AMPA monohydrate at 10-5 M produces only small depolarizations (3-7 mV), whereas at 10-4 M, the amplitudes of the depolarizations ranged from 4 to 33 mV. (RS)-AMPA monohydrate also causes an increase of the discharge rate of spontaneously firing neurones or sometimes evoked a short burst of action potentials in silent cells. (RS)-AMPA monohydrate exerts its depolarizing effects by activating glutamate/quisqualate receptors without affecting NMDA receptors[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C7H12N2O5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 204.18 |