Ursolic Acid
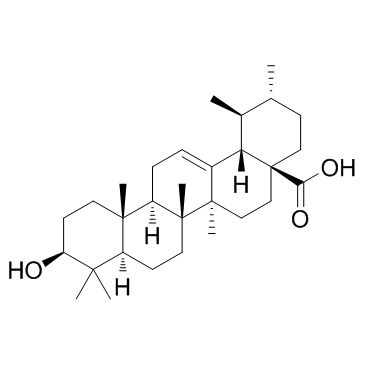
Ursolic Acid structure
|
Common Name | Ursolic Acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 77-52-1 | Molecular Weight | 456.700 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 556.9±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C30H48O3 | Melting Point | 292 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 304.7±26.6 °C | |
Use of Ursolic AcidUrsolic acid(Bungeolic acid) is a natural pentacyclic triterpenoid carboxylic acid, exerts anti-tumor effects and is an effective compound for cancer prevention and therapy. IC50 value:Target:in vitro: UA induced phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase alpha (AMPKα) and suppressed the protein expression of DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) in the dose-dependent manner [1]. The combination of ursolic acid (0.5 μM) and leucine (10 μM) proved to be the most effective in promoting myogenic differentiation. The combination of ursolic acid and leucine significantly increased CK activity than treatment with either agent alone. The level of myosin heavy chain, a myogenic differentiation marker protein, was also enhanced by the combination of ursolic acid and leucine [2]. Ursolic acid efficiently induced apoptosis, possibly via the downregulation of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), the upregulation of Bcl-2-associated X protein and the proteolytic activation of caspase-3. Furthermore, the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase was increased by the administration of ursolic acid. In addition, ursolic acid significantly suppressed the invasive phenotype of the SNU-484 cells and significantly decreased the expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 [3]. ursolic acid (UA) potently induces the apoptosis of gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells. Further mechanistic studies revealed that the ROCK1/PTEN signaling pathway plays a critical role in UA-mediated mitochondrial translocation of cofilin-1 and apoptosis [4].in vivo: UA treatment markedly improved the survival of septic rats, and attenuated CLP-induced lung injury, including reduction of lung wet/dry weight ratio, infiltration of leukocytes and proteins, myeloperoxidase activity, and malondialdehyde content. In addition, UA significantly decreased the serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, and interleukin-1β, inhibited the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in the lung, which are involved in the productions of nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 [5]. |
| Name | ursolic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ursolic acid(Bungeolic acid) is a natural pentacyclic triterpenoid carboxylic acid, exerts anti-tumor effects and is an effective compound for cancer prevention and therapy. IC50 value:Target:in vitro: UA induced phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase alpha (AMPKα) and suppressed the protein expression of DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) in the dose-dependent manner [1]. The combination of ursolic acid (0.5 μM) and leucine (10 μM) proved to be the most effective in promoting myogenic differentiation. The combination of ursolic acid and leucine significantly increased CK activity than treatment with either agent alone. The level of myosin heavy chain, a myogenic differentiation marker protein, was also enhanced by the combination of ursolic acid and leucine [2]. Ursolic acid efficiently induced apoptosis, possibly via the downregulation of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), the upregulation of Bcl-2-associated X protein and the proteolytic activation of caspase-3. Furthermore, the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase was increased by the administration of ursolic acid. In addition, ursolic acid significantly suppressed the invasive phenotype of the SNU-484 cells and significantly decreased the expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 [3]. ursolic acid (UA) potently induces the apoptosis of gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells. Further mechanistic studies revealed that the ROCK1/PTEN signaling pathway plays a critical role in UA-mediated mitochondrial translocation of cofilin-1 and apoptosis [4].in vivo: UA treatment markedly improved the survival of septic rats, and attenuated CLP-induced lung injury, including reduction of lung wet/dry weight ratio, infiltration of leukocytes and proteins, myeloperoxidase activity, and malondialdehyde content. In addition, UA significantly decreased the serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, and interleukin-1β, inhibited the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in the lung, which are involved in the productions of nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 [5]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 556.9±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 292 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C30H48O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 456.700 |
| Flash Point | 304.7±26.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 456.360352 |
| PSA | 57.53000 |
| LogP | 9.01 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.555 |
| Storage condition | 2~8°C |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
|
~75% 
Ursolic Acid CAS#:77-52-1 |
| Literature: Yan, Shiqiang; Ding, Ning; Zhang, Wei; Wang, Peng; Li, Yingxia; Li, Ming Carbohydrate Research, 2012 , vol. 354, p. 6 - 20 |
|
~71% 
Ursolic Acid CAS#:77-52-1 |
| Literature: Sengupta, Pasupati; Sen, Manju; Das, Saktipada Indian Journal of Chemistry, Section B: Organic Chemistry Including Medicinal Chemistry, 1980 , vol. 19, # 8 p. 721 - 722 |
|
~% 
Ursolic Acid CAS#:77-52-1 |
| Literature: Synthetic Communications, , vol. 43, # 1 p. 26 - 33 |
|
~1% 
Ursolic Acid CAS#:77-52-1 |
| Literature: Meksuriyen, Duangdeun; Nanayakkara, N. P. Dhammika; Phoebe, Charles H.; Cordell, Geoffrey A. Phytochemistry (Elsevier), 1986 , vol. 25, # 7 p. 1685 - 1690 |
|
~% 
Ursolic Acid CAS#:77-52-1 |
| Literature: Egyptian Journal of Chemistry, , vol. 54, # 1 p. 99 - 113 |
|
~% 
Ursolic Acid CAS#:77-52-1 |
| Literature: Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications, , # 14 p. 1141 - 1143 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|---|
|
RIPK1 promotes death receptor-independent caspase-8-mediated apoptosis under unresolved ER stress conditions.
Cell Death Dis. 5 , e1555, (2014) Accumulation of unfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) causes ER stress and results in the activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR), which aims at restoring ER homeostasis. Howev... |
|
|
Chemical profile and in vivo hypoglycemic effects of Syzygium jambos, Costus speciosus and Tapeinochilos ananassae plant extracts used as diabetes adjuvants in Puerto Rico.
BMC Complement Altern. Med. 15 , 244, (2015) The increasing numbers of people who use plant-based remedies as alternative or complementary medicine call for the validation of less known herbal formulations used to treat their ailments. Since Pue... |
|
|
Analysis of triterpenoids and phytosterols in vegetables by thin-layer chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1381 , 229-38, (2015) Three TLC methods were used for an initial screening of some common plant triterpenoids and phytosterols in cuticular wax extracts of different vegetables (zucchini, eggplant, tomato, red pepper, mang... |
| Masterin |
| URSON |
| Merotaine |
| Neoage UR |
| EINECS 201-034-0 |
| PRUNOL |
| MICROMEROL |
| Ursolicacid |
| Ursolic acid |
| MALOL |
| MFCD00009621 |
| Ursolic |

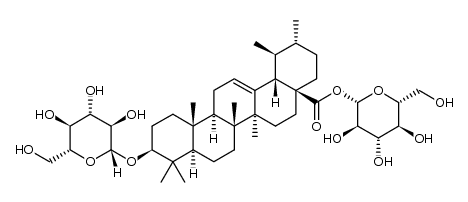

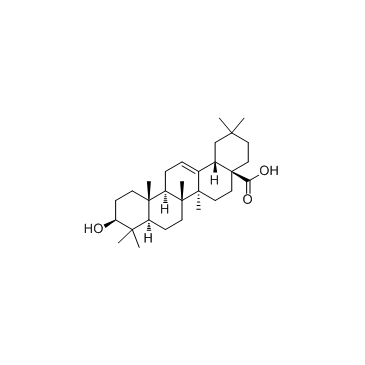
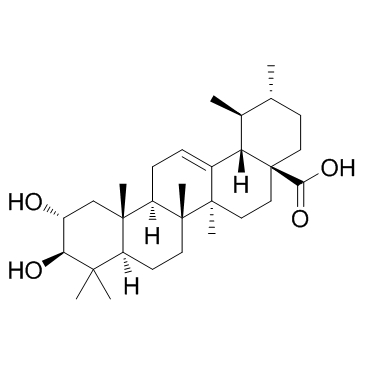 CAS#:4547-24-4
CAS#:4547-24-4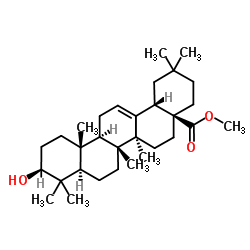 CAS#:1724-17-0
CAS#:1724-17-0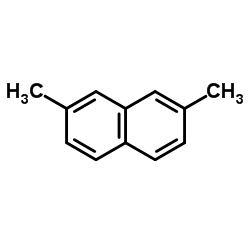 CAS#:582-16-1
CAS#:582-16-1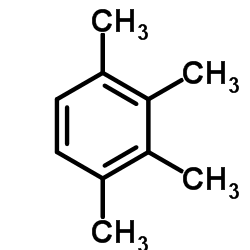 CAS#:488-23-3
CAS#:488-23-3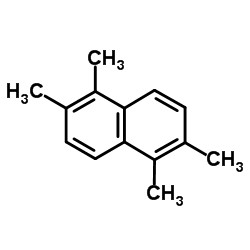 CAS#:2131-43-3
CAS#:2131-43-3 CAS#:486-34-0
CAS#:486-34-0 CAS#:192211-41-9
CAS#:192211-41-9 CAS#:545-48-2
CAS#:545-48-2
